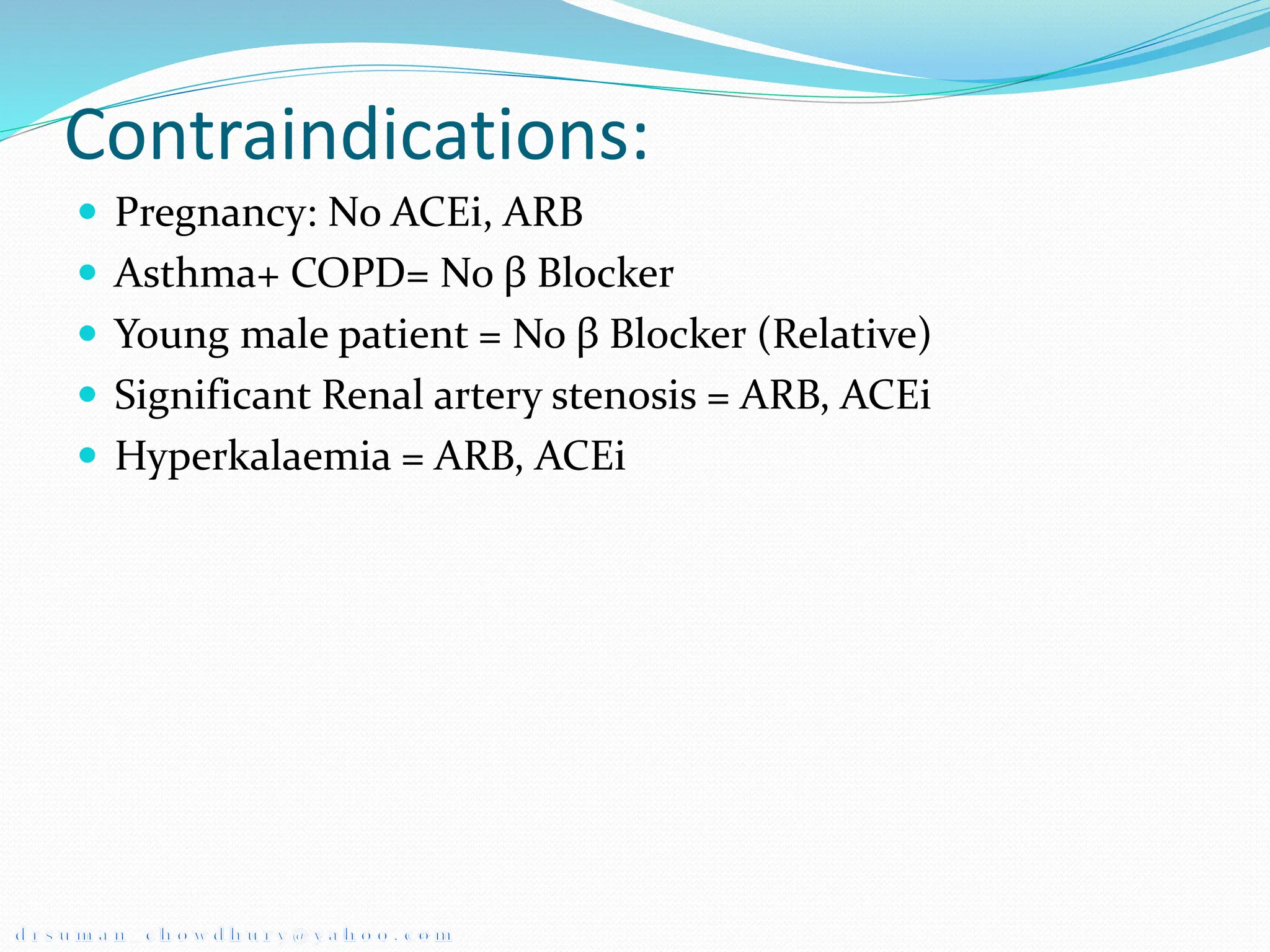
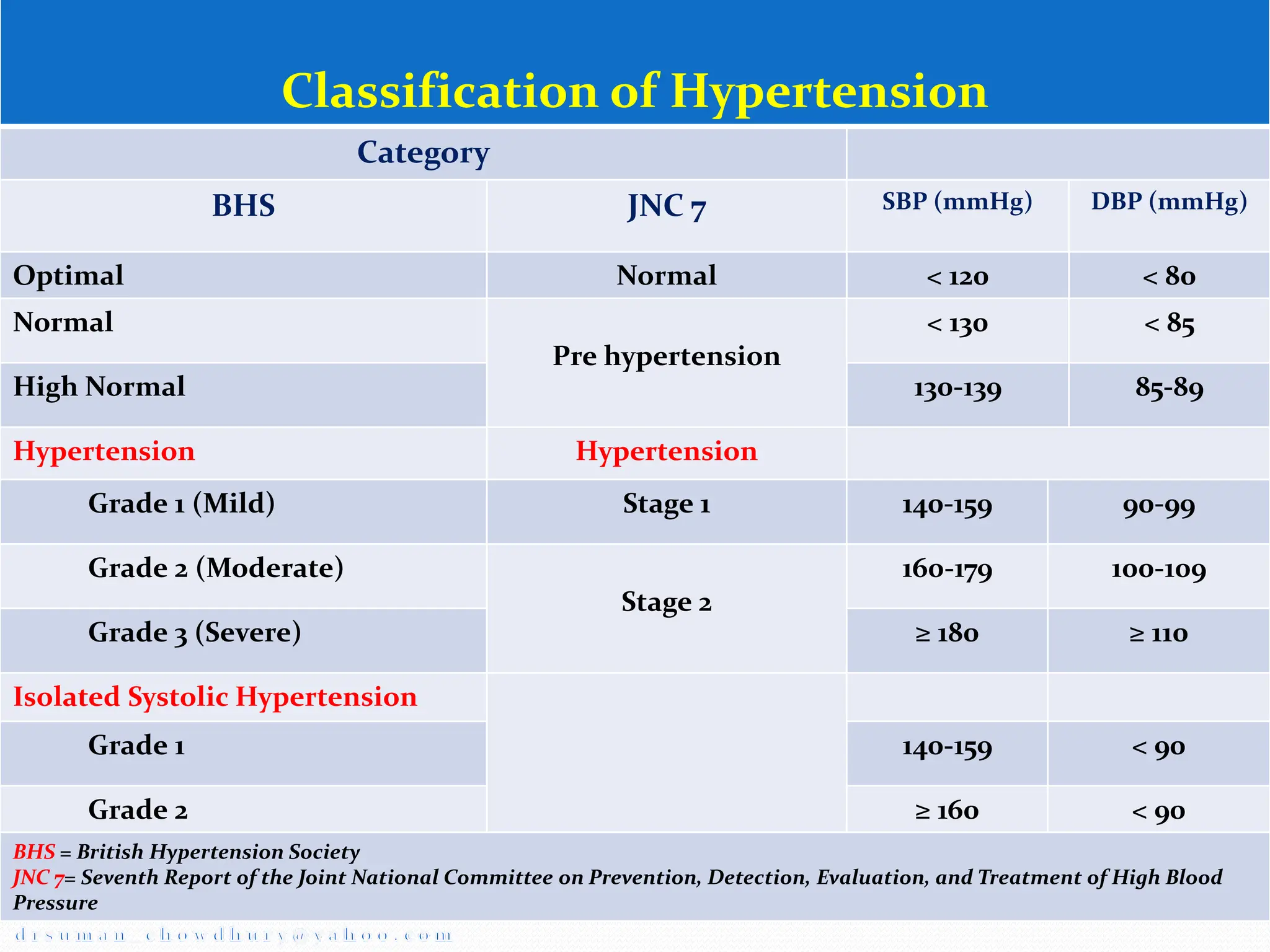
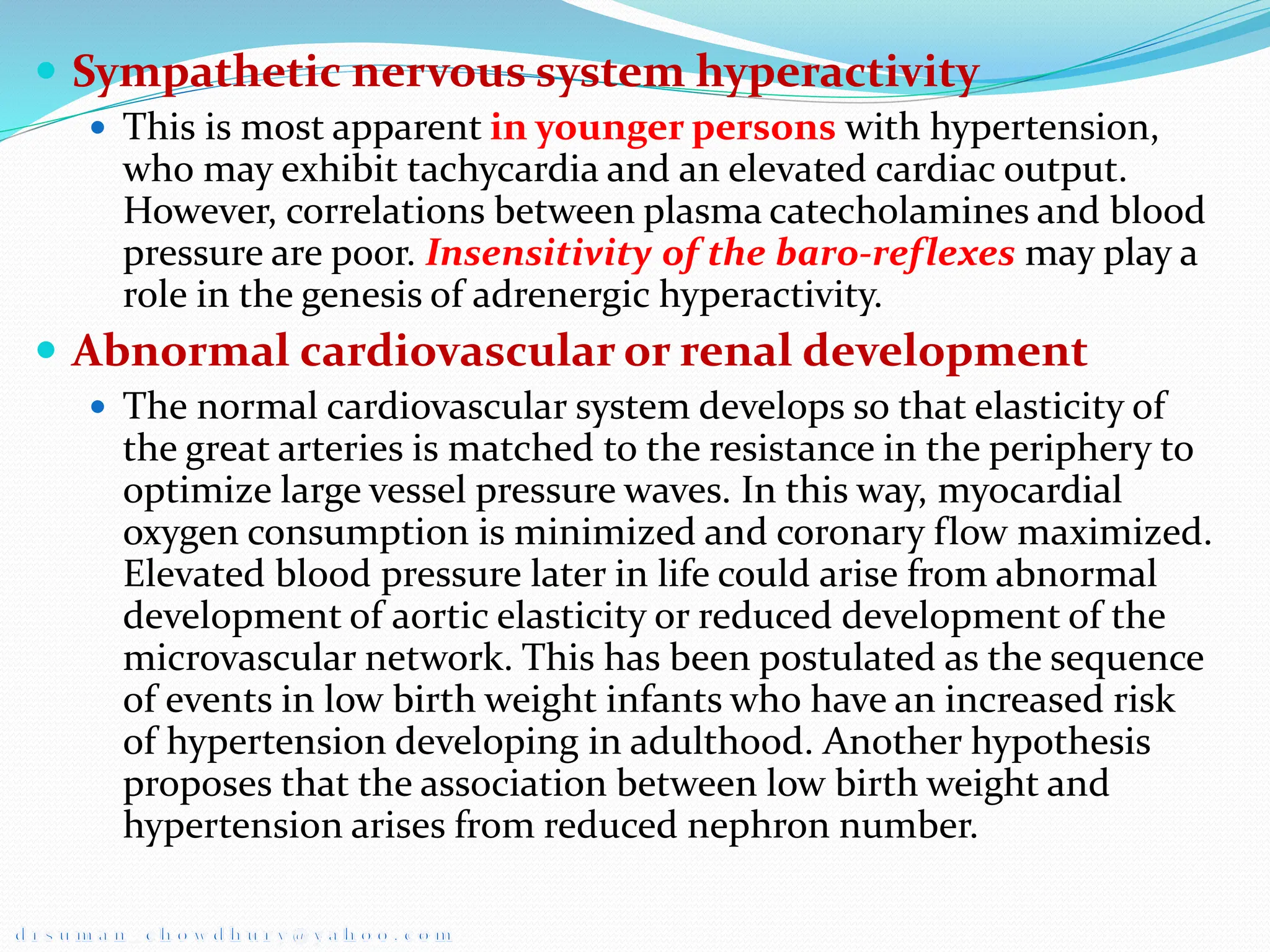
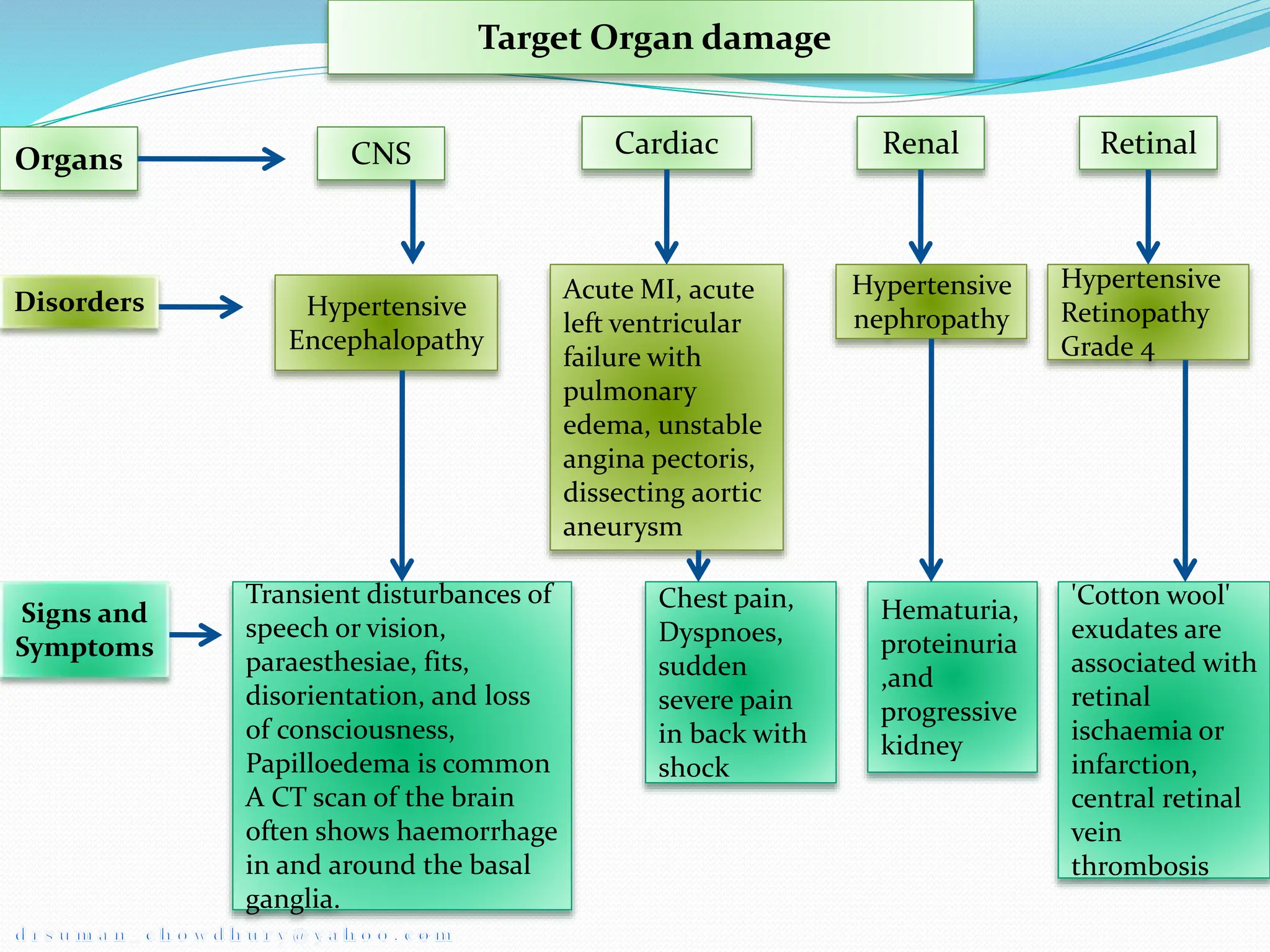
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is defined as a systolic blood pressure above 140 mmHg or a diastolic blood pressure above 90 mmHg. It can be classified based on severity from stage 1 to stage 2. Primary causes include sympathetic nervous system hyperactivity, renin-angiotensin system activity, and defects in natriuresis. Target organ damage may occur in the eyes, heart, brain, kidneys, and vasculature. Hypertensive emergencies require rapid blood pressure reduction to prevent end organ damage and include hypertensive encephalopathy and eclampsia. Intravenous drugs like sodium nitroprusside, labetalol, and hydralazine are used to slowly

































![Lifestyle modifications to manage hypertension
Modification Recommendation Approximate
Systolic BP
Reduction,
Range
Weight reduction Maintain Norma l Body weight (BMI 18.5-24.9) 5-20mmHg, 10
kg weight loss
Adopt DASH
eating plan
Consume a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and low-
fat dairy products with a reduced content of
saturated fat and total fat
8–14 mm Hg
Dietary Sodium
restriction
Reduce dietary sodium intake to no more than 100
mEq/d (2.4 g sodium or 6 g sodium chloride)
2–8 mm Hg
Physical activity Engage in regular aerobic physical activity such as
brisk walking (at least 30 minutes per day, most
days of the week)
4–9 mm Hg
Moderation of
alcohol
consumption
Limit consumption to no more than two drinks
per day (1 oz or 30 mL ethanol [eg, 24 oz beer, 10 oz
wine, or 3 oz 80-proof whiskey]) in most men and
no more than one drink per day in women and
2–4 mm Hg](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/approach-to-htn-and-its-management-240217152049-46404b17/75/Approach-to-HTN-and-Its-managements-pptx-37-2048.jpg)