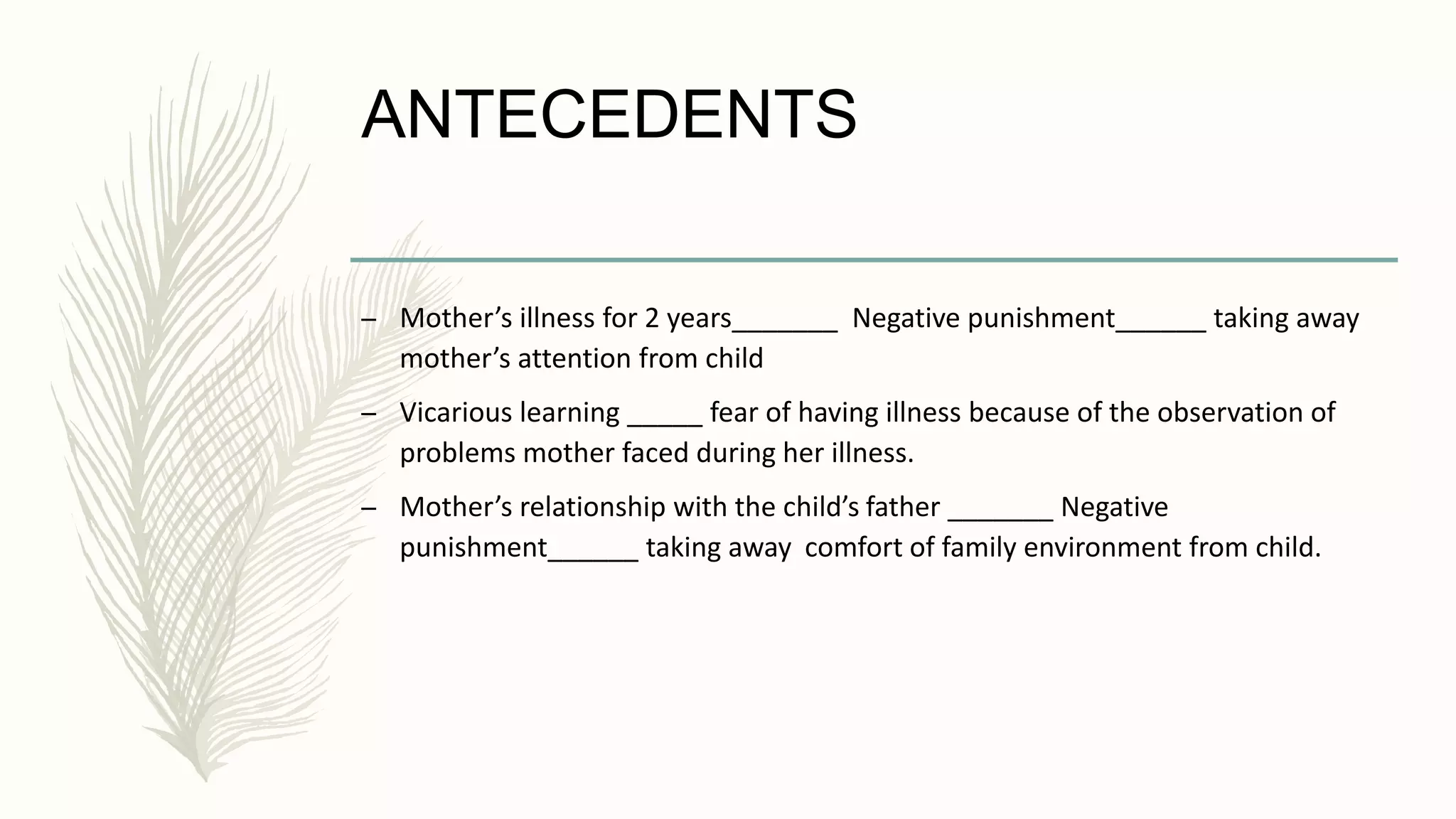
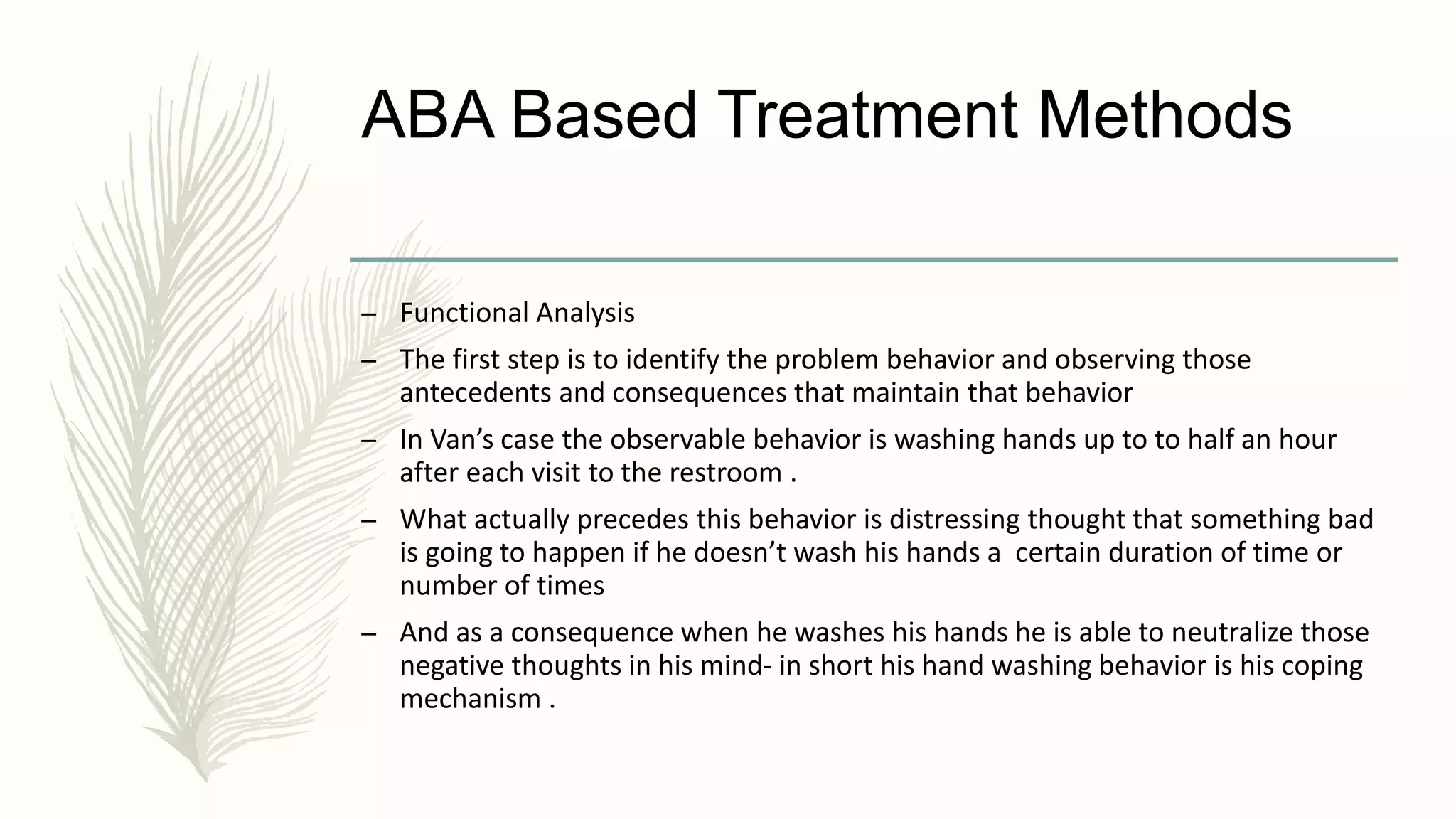
Van, a 7-year-old boy, developed severe germ phobia and compulsive behaviors like spending 20-30 minutes cleaning himself after using the bathroom. His parents were under stress due to his mother's chronic illness and their poor relationship. ABA treatment for Van's OCD included identifying antecedents like his mother's illness and consequences like relief from obsessive thoughts. Treatment methods included escape extinction to reduce hand washing, contingent reinforcement for avoiding the behavior, and behavior shaping to gradually reduce cleaning time. Research shows ABA interventions using functional analysis and differential reinforcement can effectively reduce compulsive behaviors. While effective, ABA may not fully address unconscious causes of OCD.