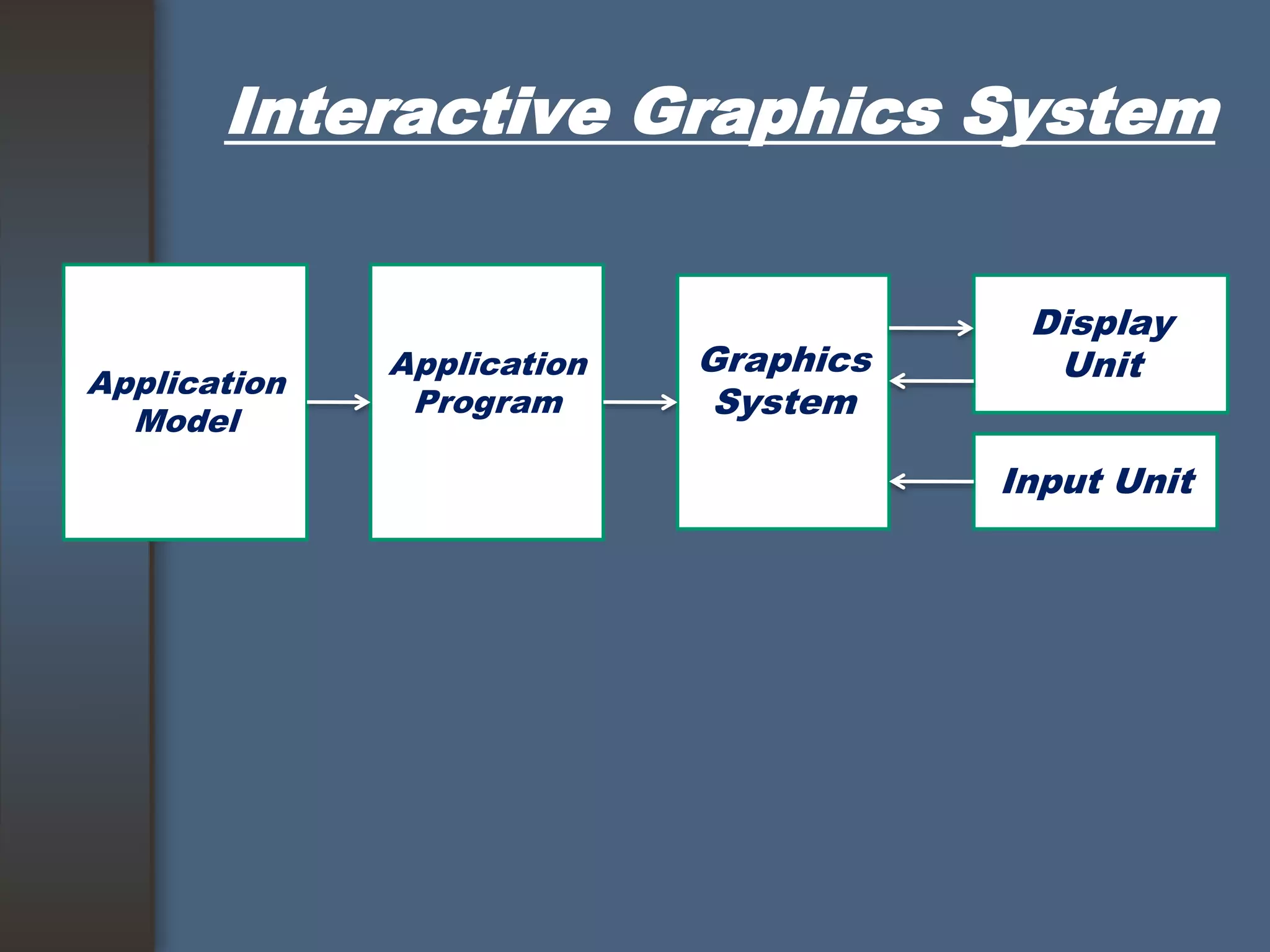
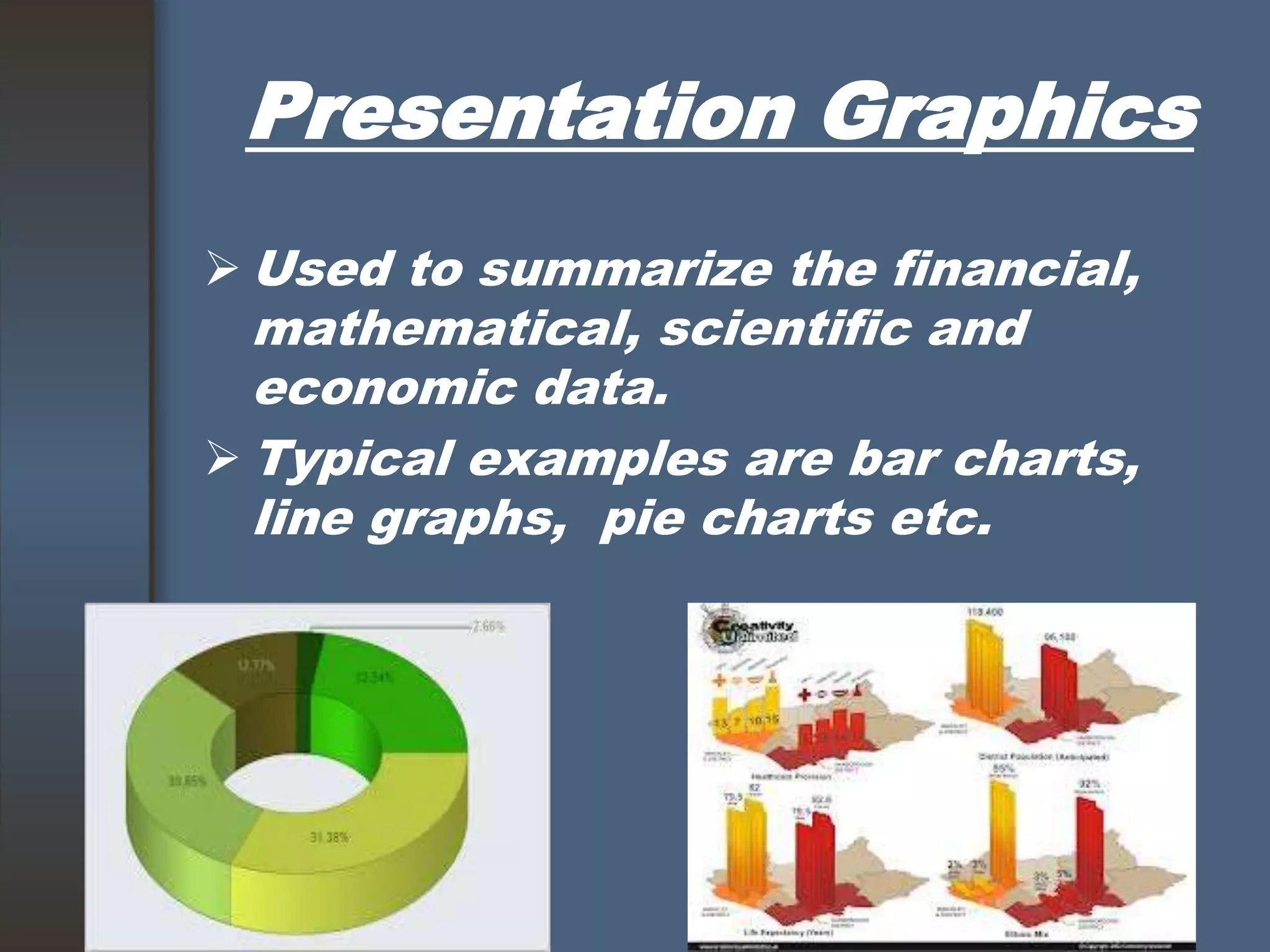
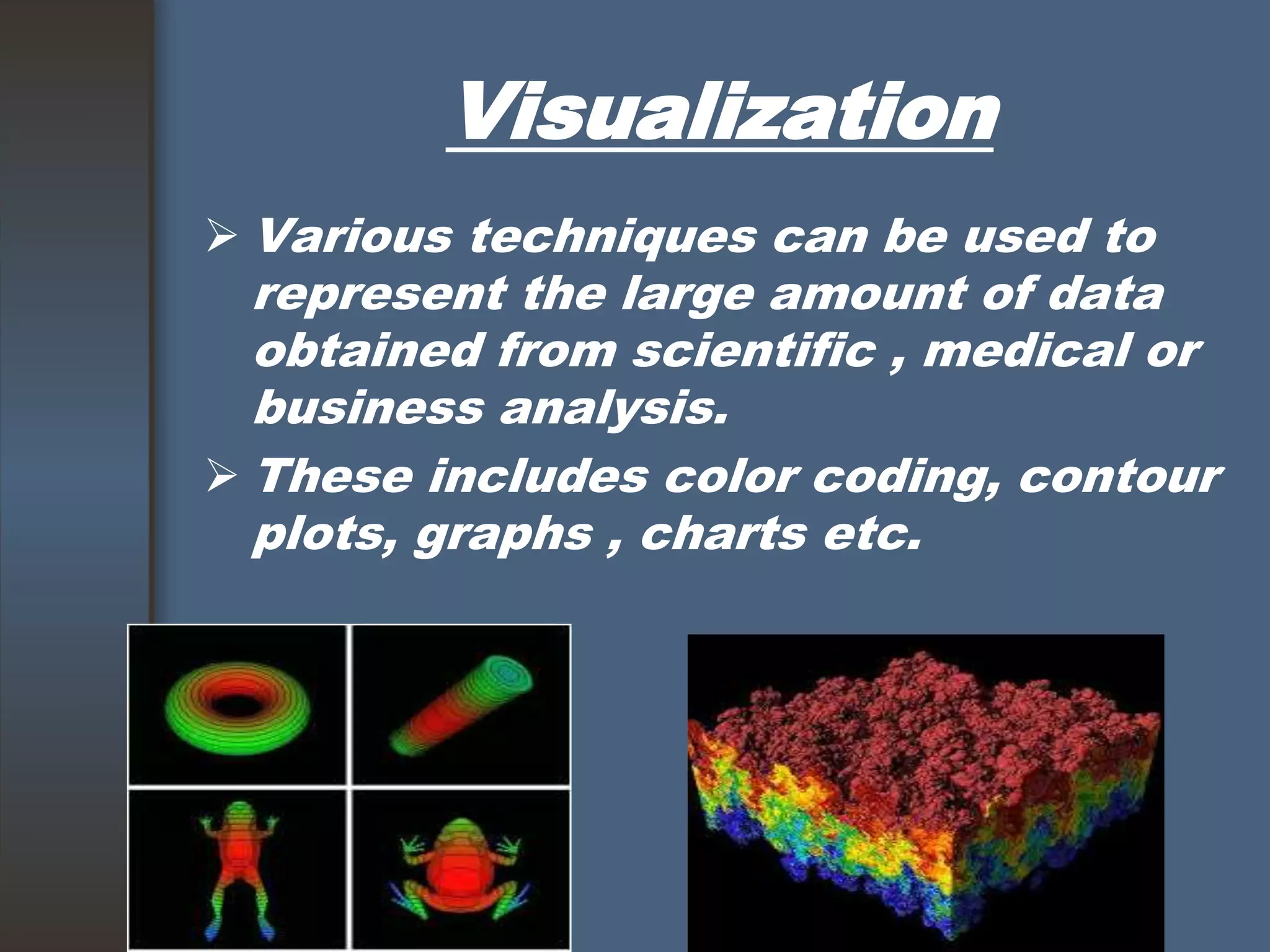
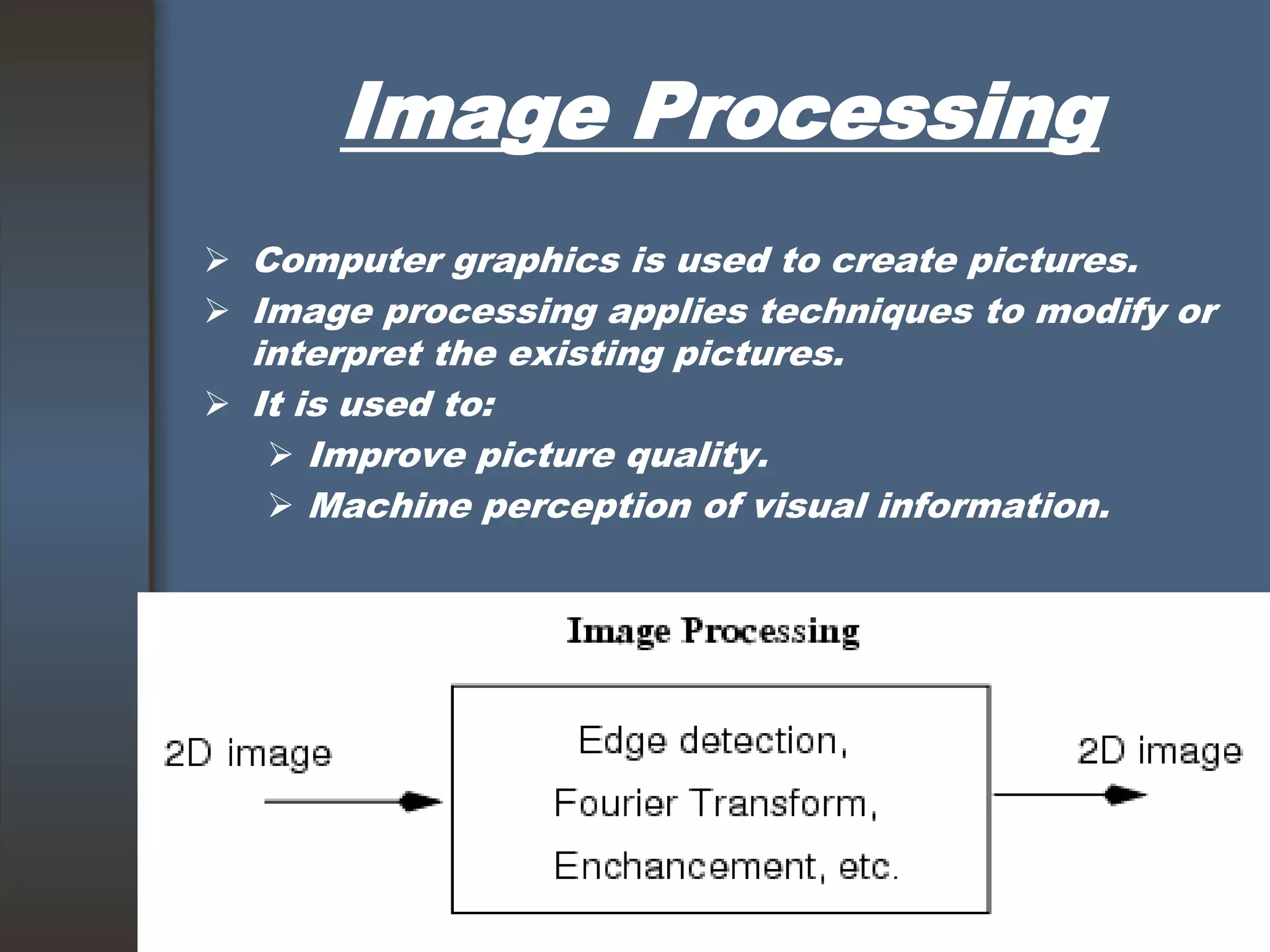
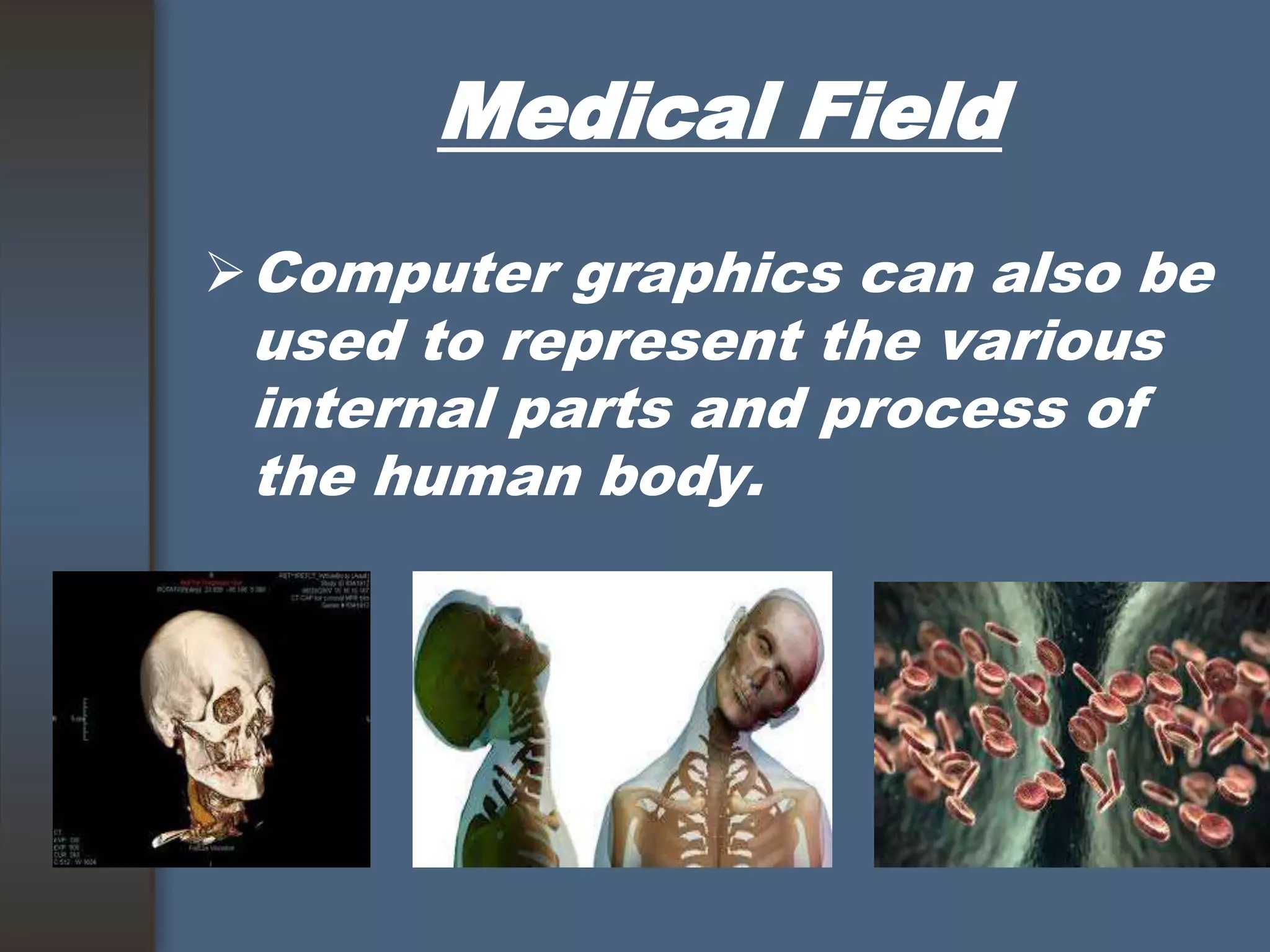
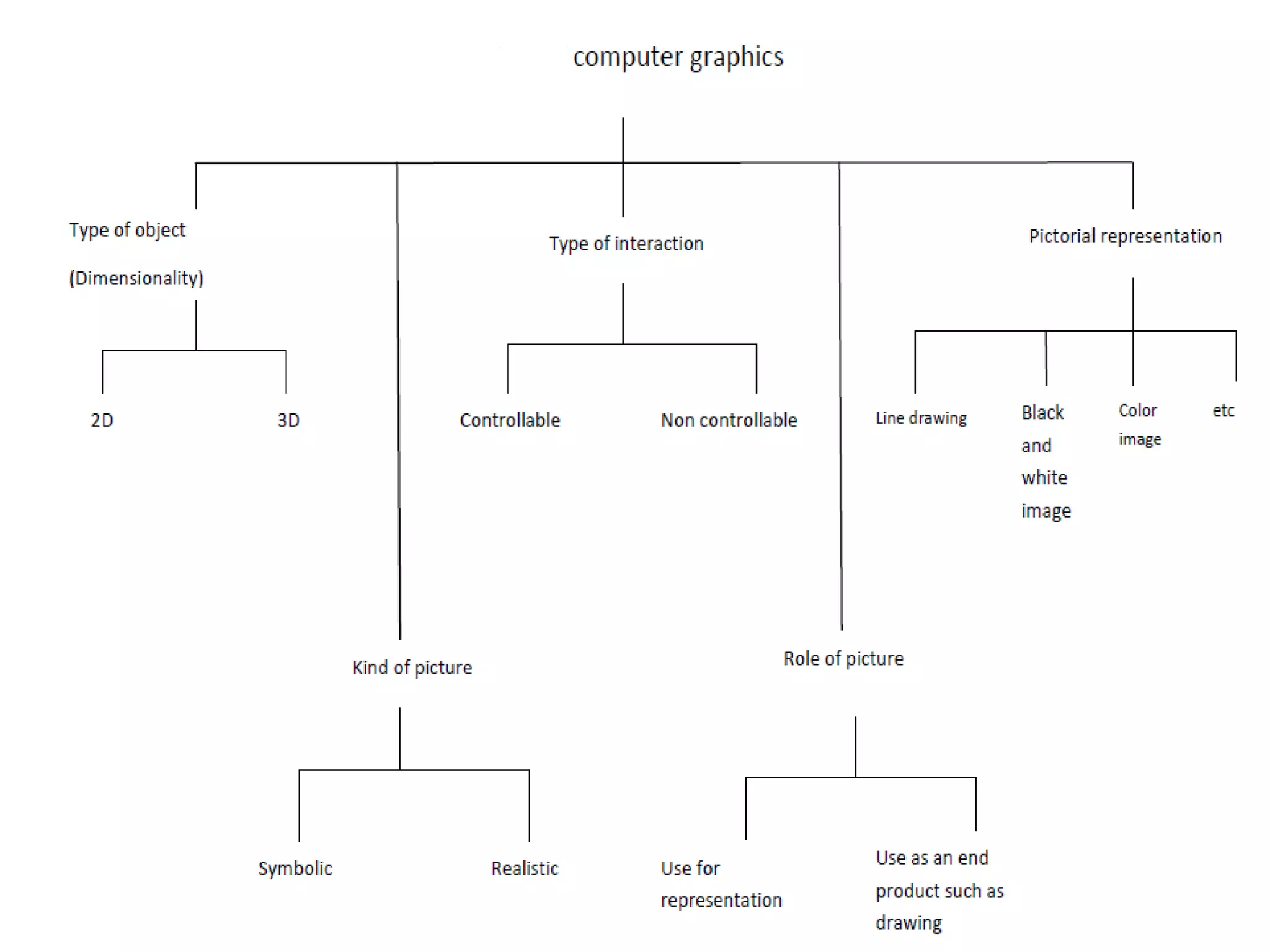
This document discusses computer graphics and its applications. It begins by defining computer graphics as the display and manipulation of data for visualization using a computer. It then discusses modeling, rendering, and animation as the main tasks of computer graphics. The document outlines typical computer graphics systems and their components. It notes several advantages of computer graphics like high quality displays and the ability to produce animations. Finally, it discusses many areas of application for computer graphics, including CAD, presentation graphics, education/training, visualization, image processing, entertainment, medical imaging, and graphical user interfaces.