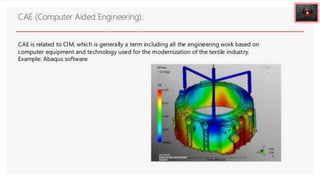
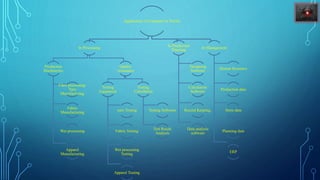
The document discusses the application of computer technology in textile industries, covering areas such as research and development, production planning, and quality control. It emphasizes the importance of learning programming languages, CAD, CAM, and CIM, as well as various software tools for different processes in textile technology. Additionally, it highlights the integration of these technologies to enhance productivity and efficiency in textile manufacturing.