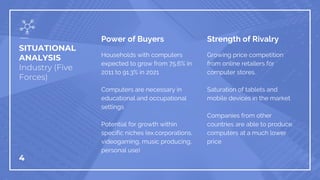
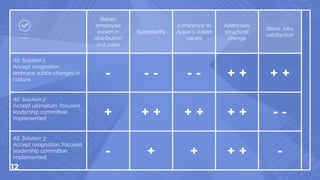
In 1985, Donna Dubinsky, a middle manager at Apple, issued an ultimatum for greater authority over distribution decisions, highlighting miscommunication and leadership issues within the company. A PESTLE analysis outlines competing factors, while a recommended solution suggests forming a task force under Dubinsky to address distribution challenges and foster a more balanced decision-making structure. The outcome aims to align Apple's operations more closely with its core values by decreasing political bias and enhancing collaboration between management and staff.