The document discusses several topics related to language:
1) It examines the juxtaposition of globalization of culture through languages like English while preserving local languages.
2) It describes policies of forced assimilation in countries that suppressed indigenous languages in the 20th century.
3) It discusses Benjamin Whorf’s hypothesis of linguistic relativity and how the structure of language can influence thought.
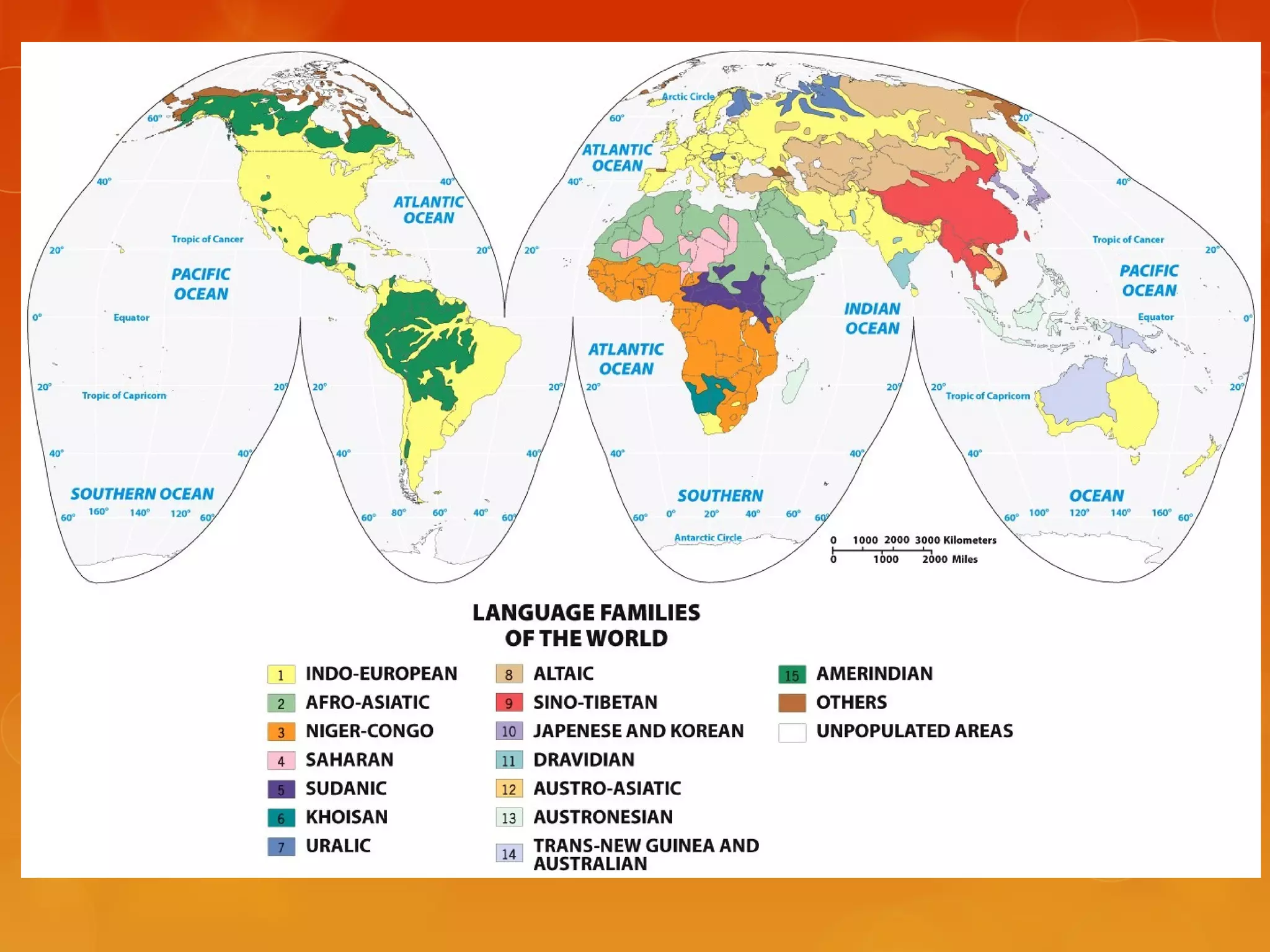
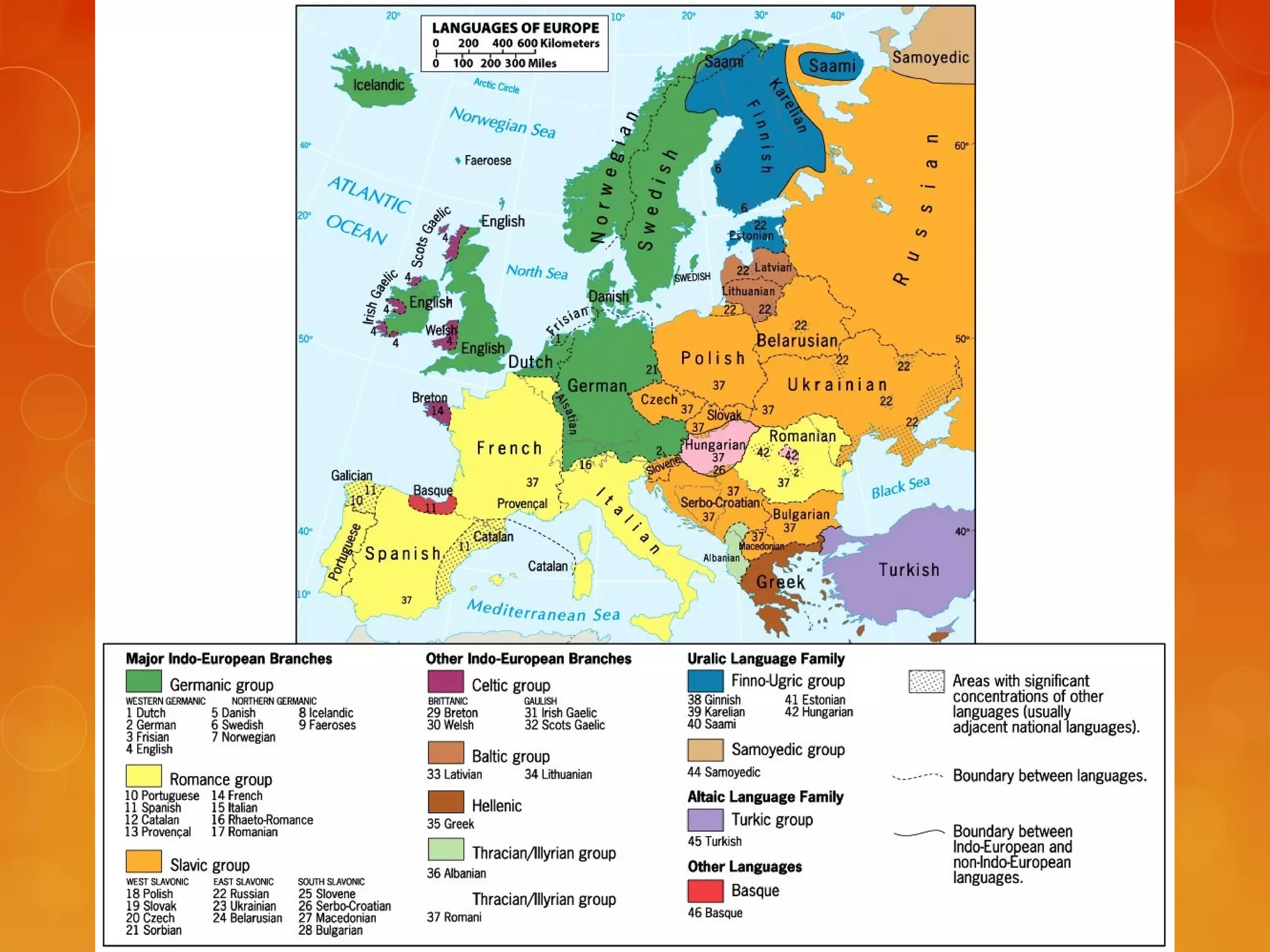
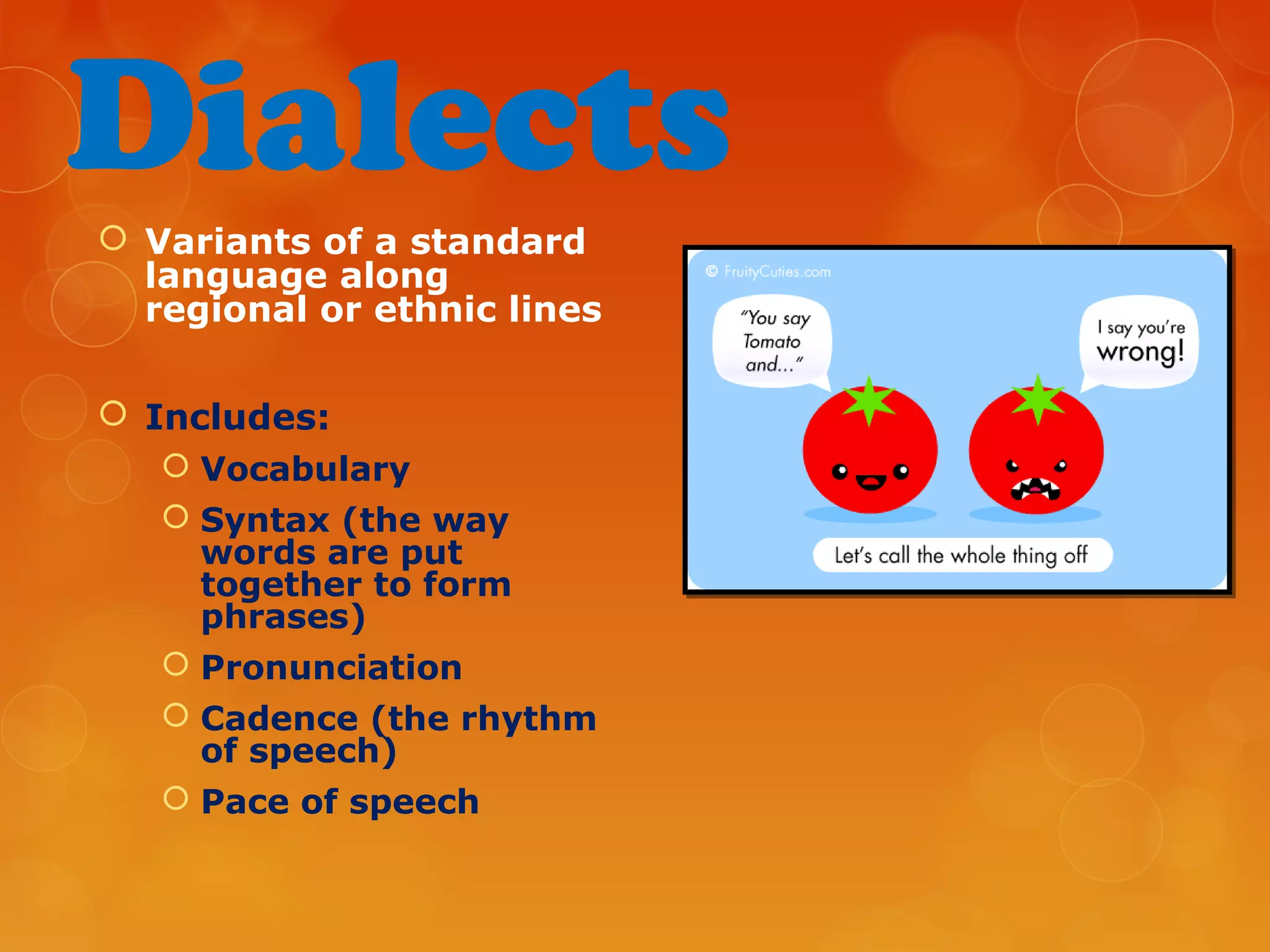
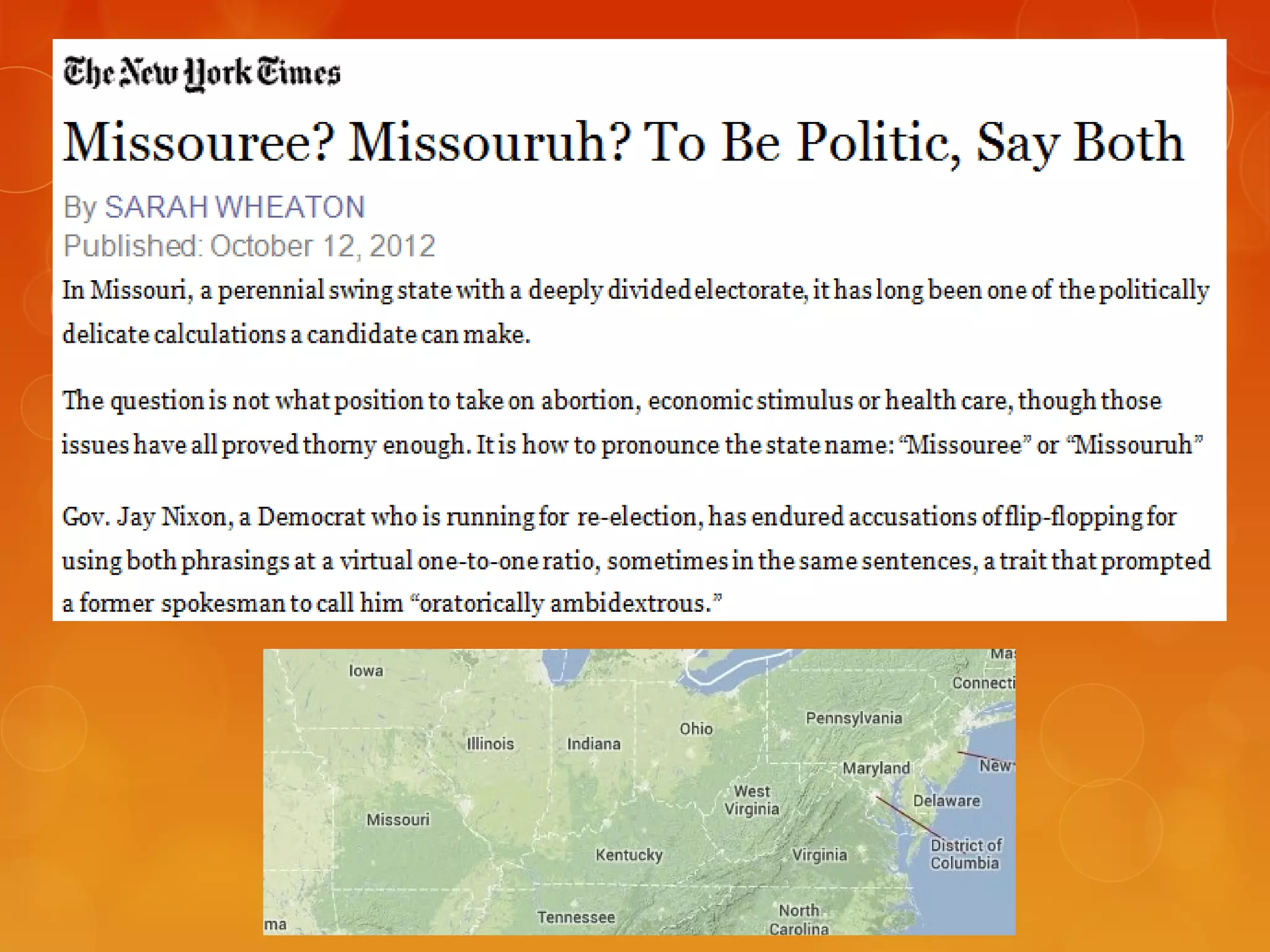
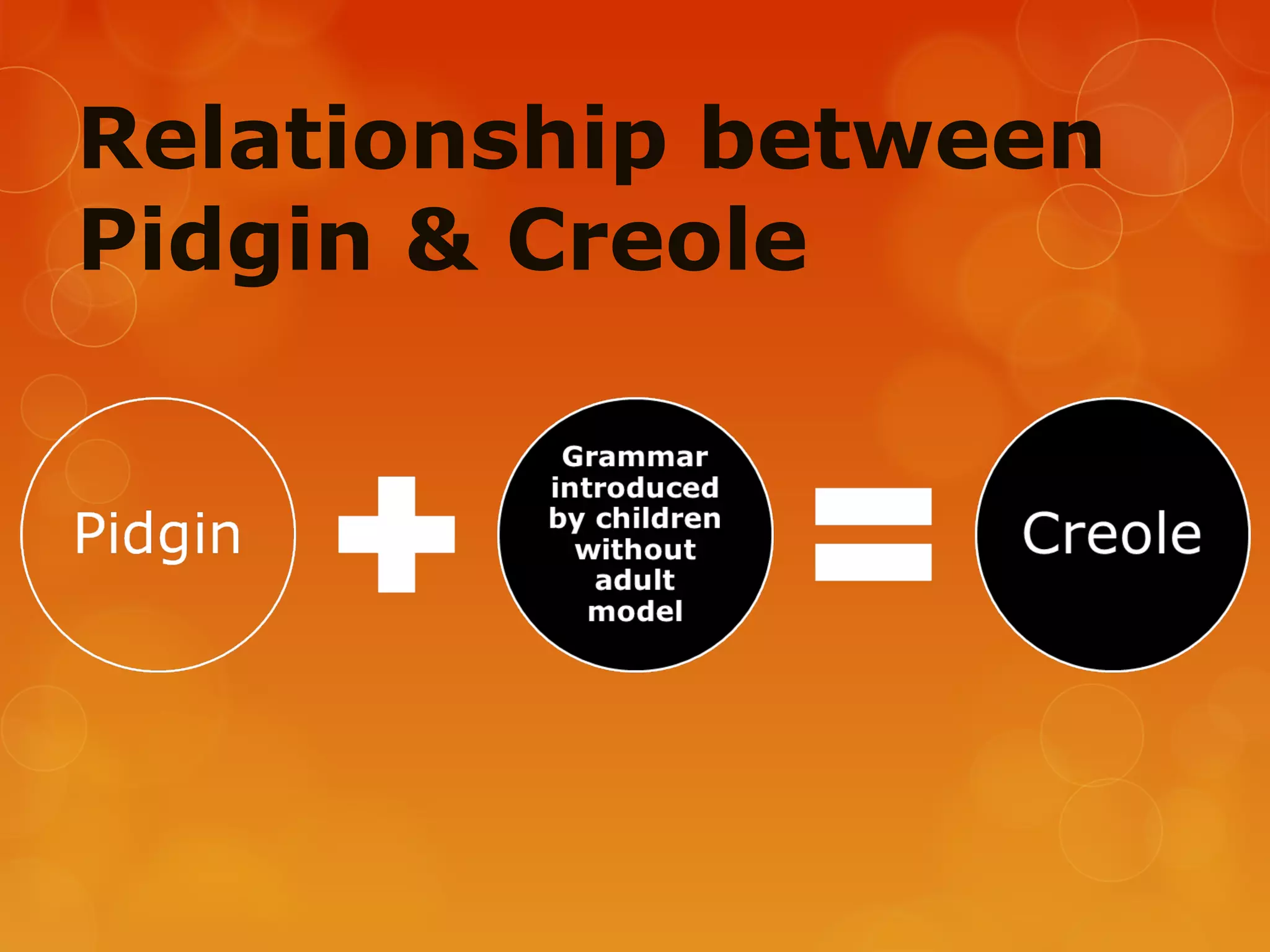
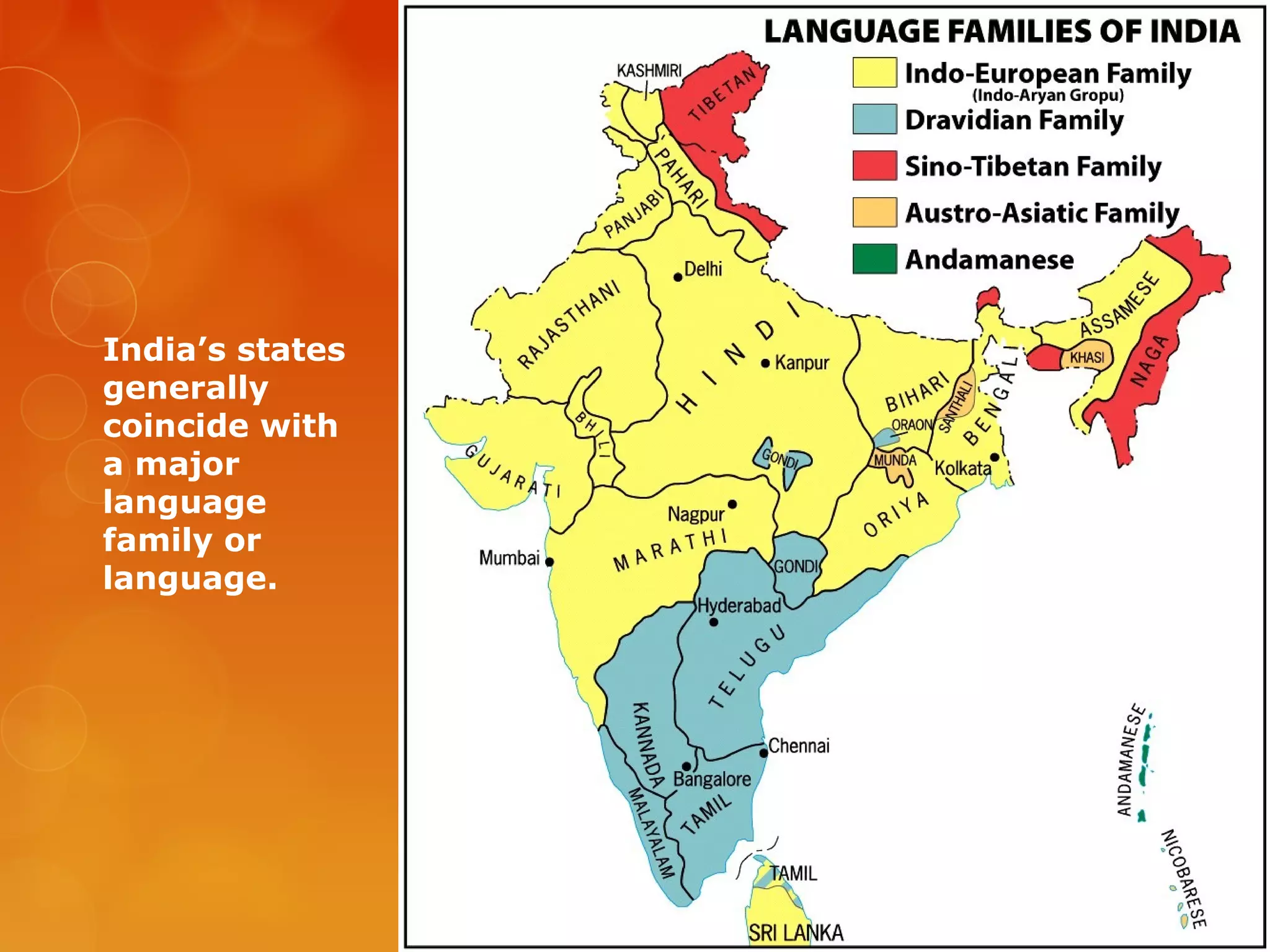
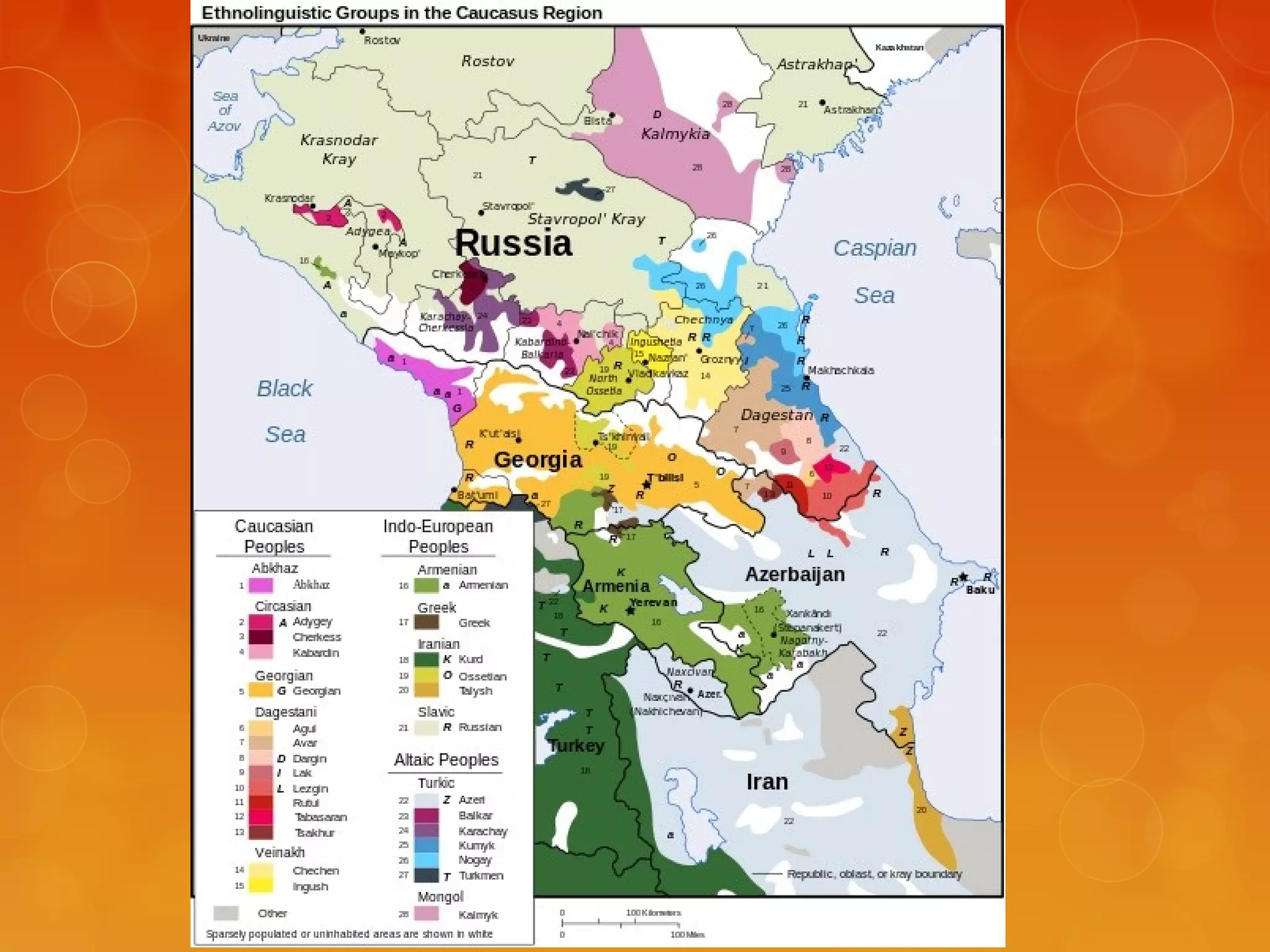
4) Various linguistic concepts are defined, including language, dialects, pidgins, creoles, lingua francas, and more.