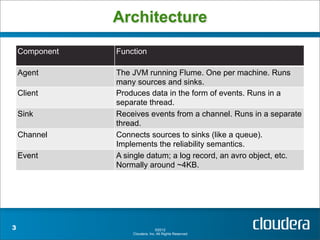
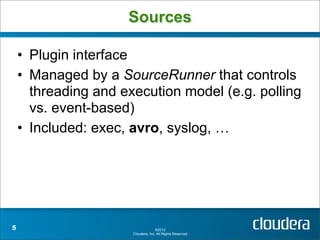
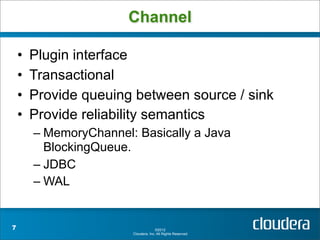
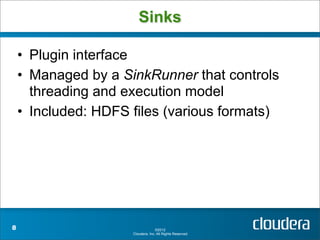
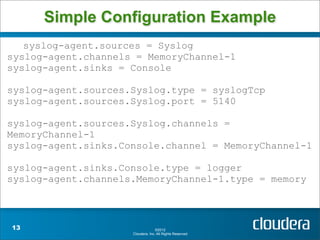
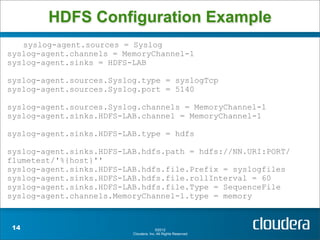
Apache Flume is a system for collecting streaming data from various sources and transporting it to destinations such as HDFS or HBase. It has a configurable architecture that allows data to flow from clients to sinks via channels. Sources produce events that are sent to channels, which then deliver the events to sinks. Flume agents run sources and sinks in a configurable topology to provide reliable data transport.