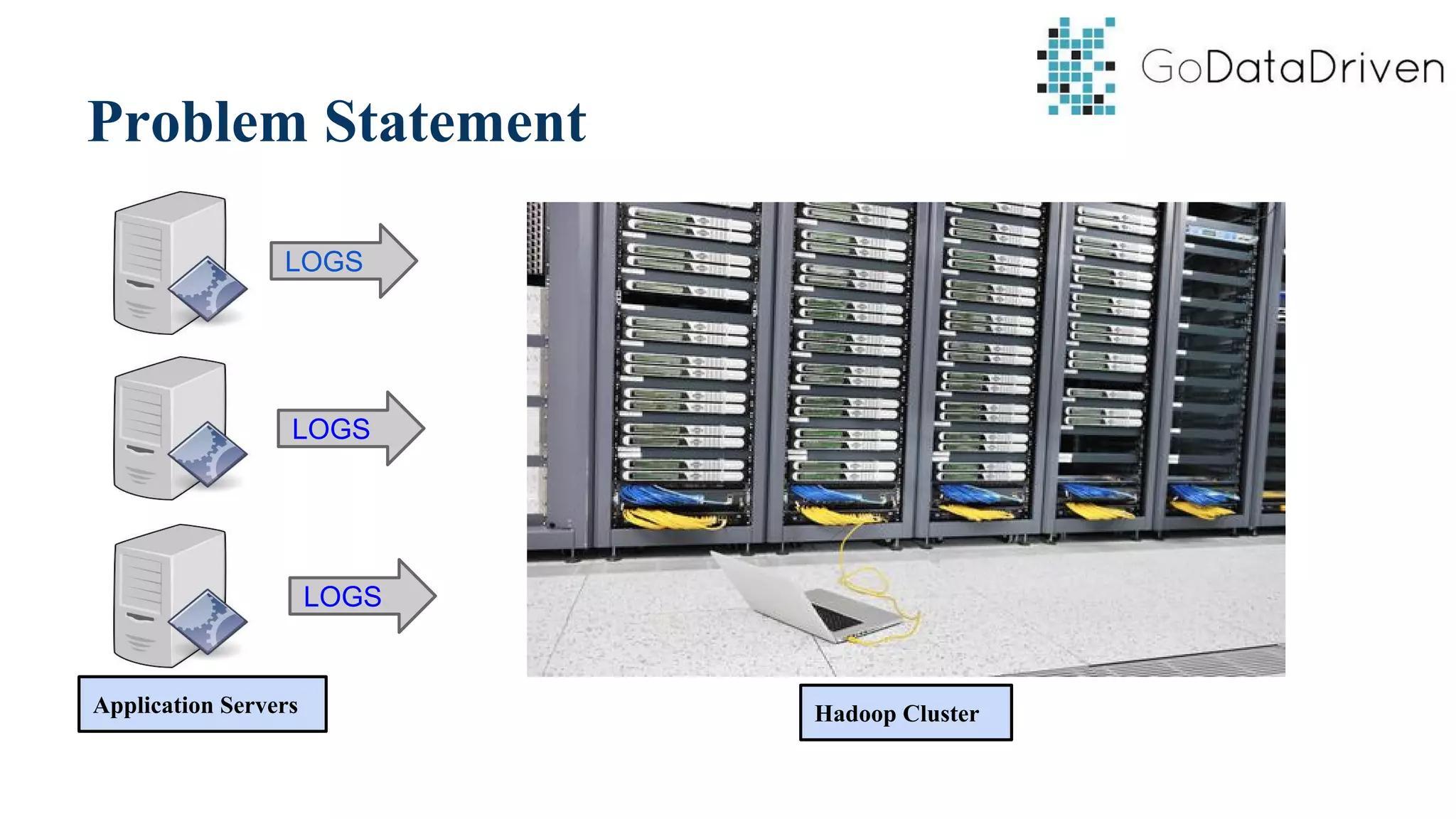
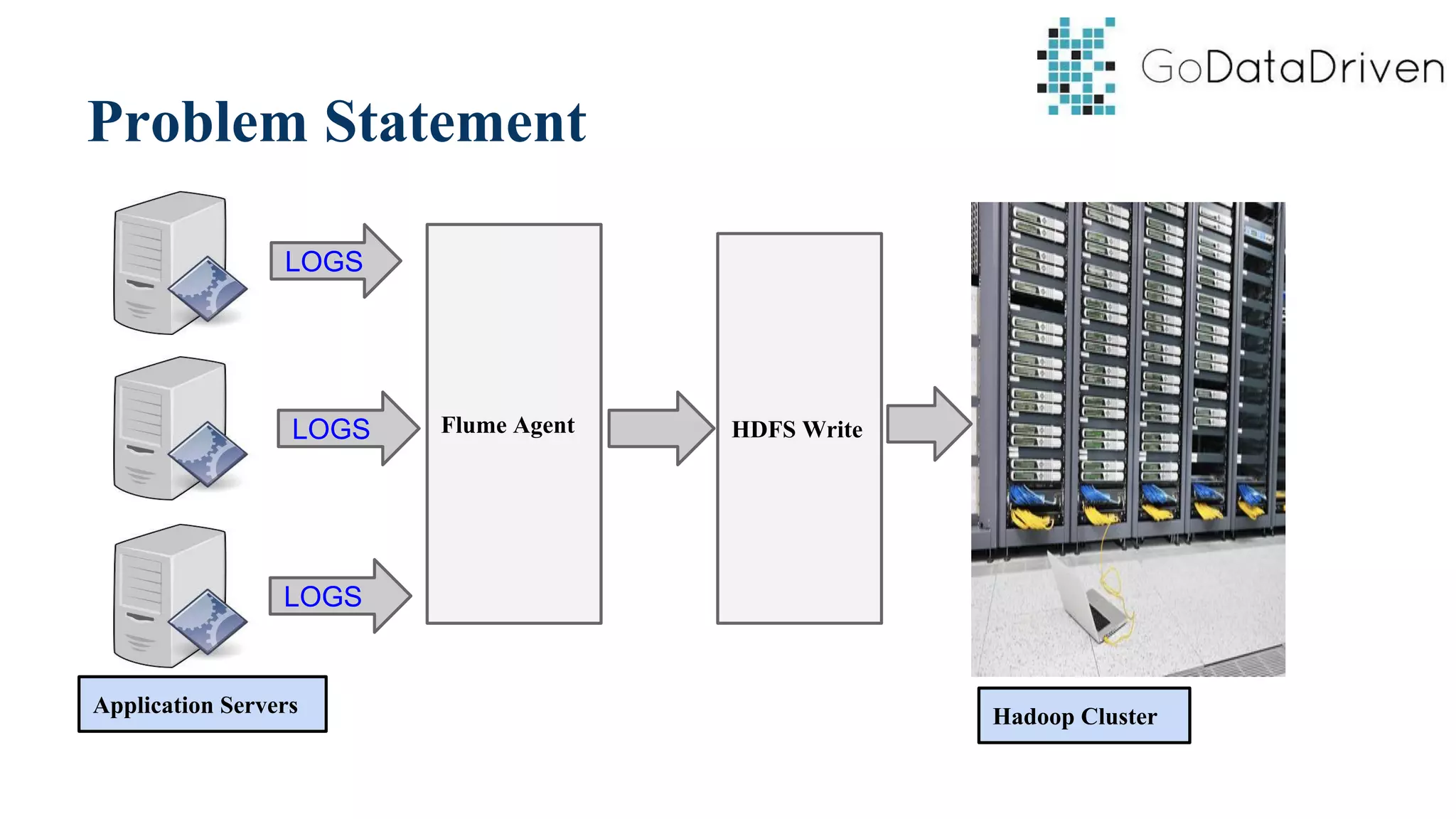
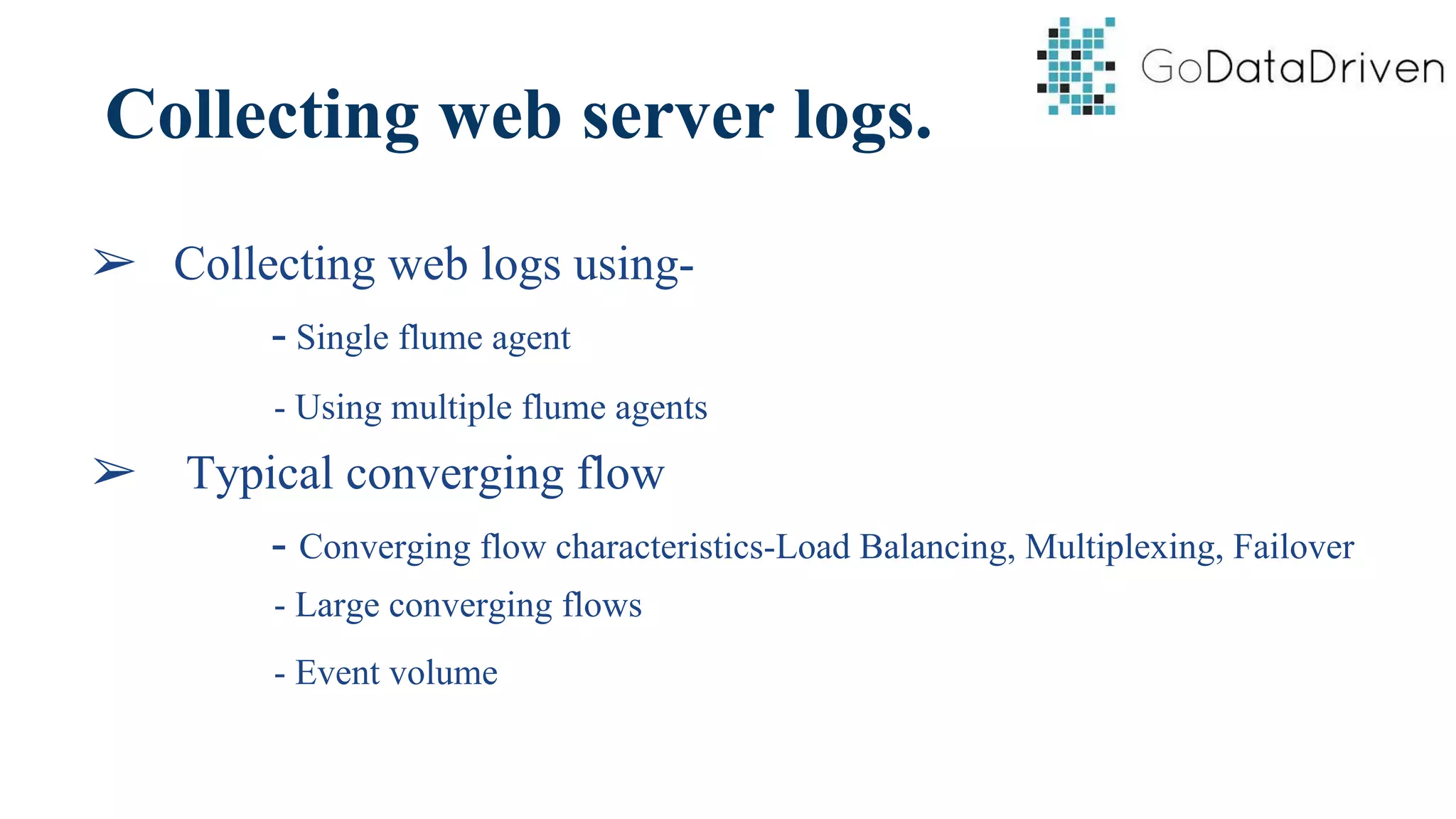
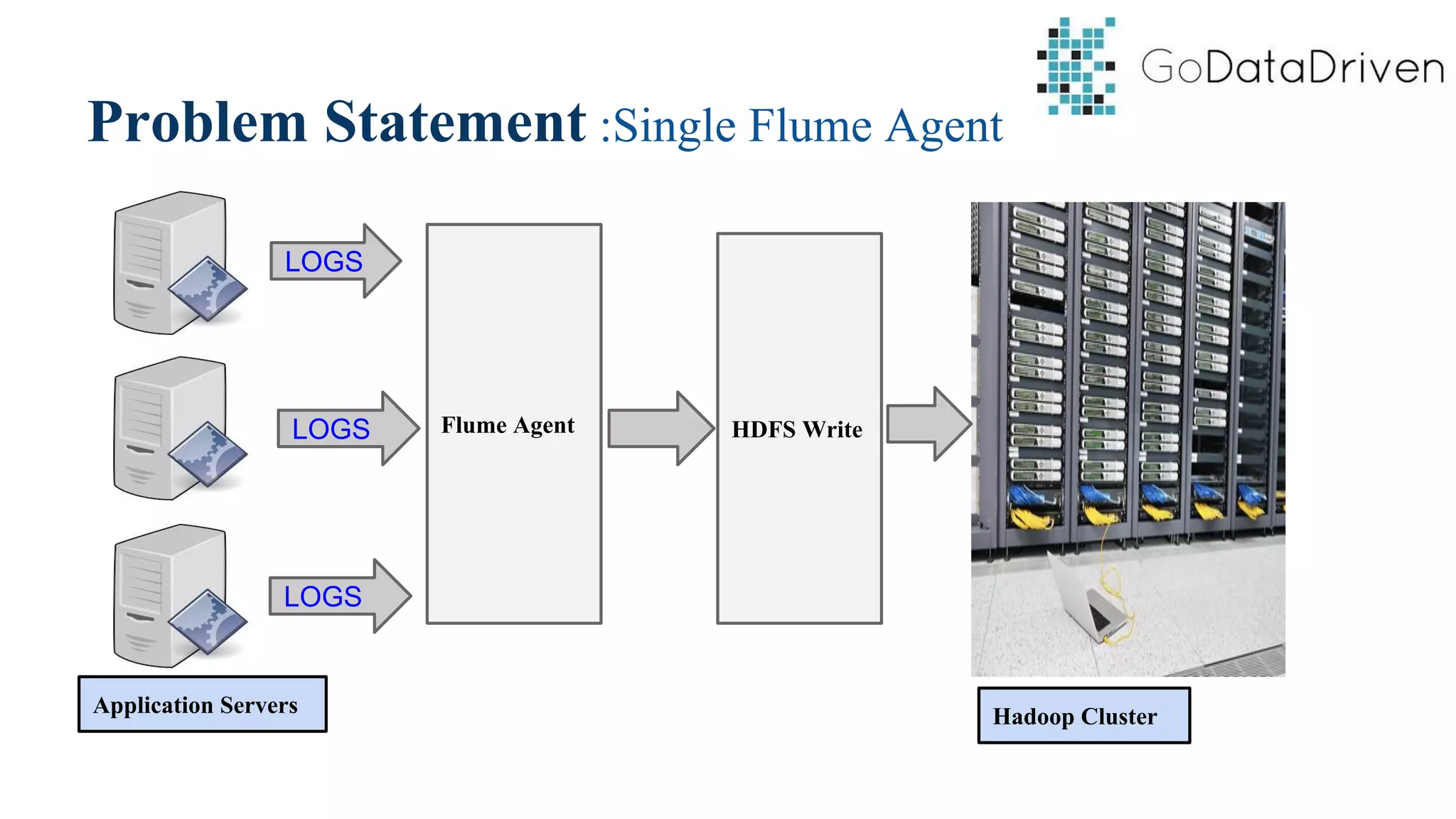
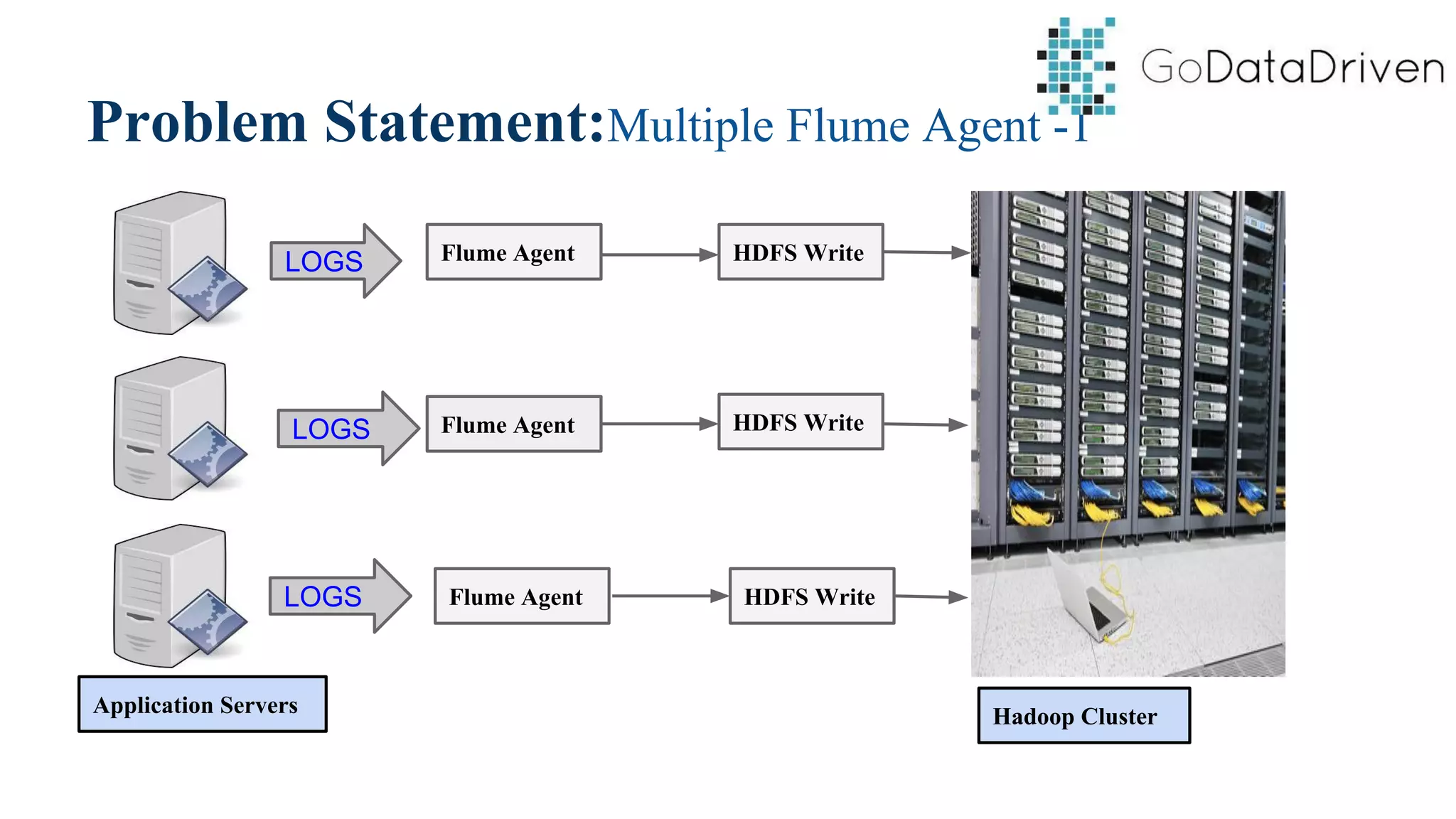
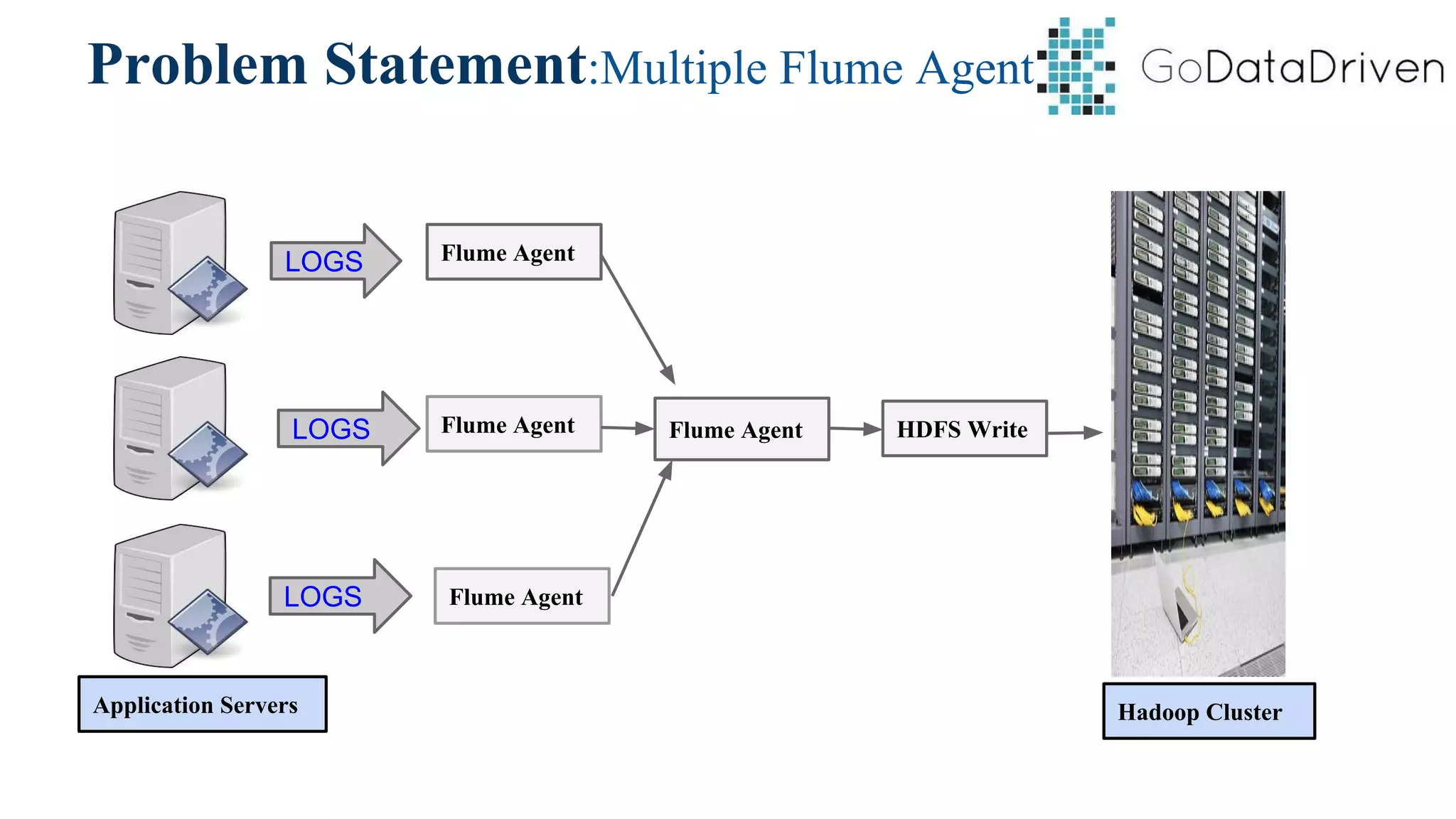
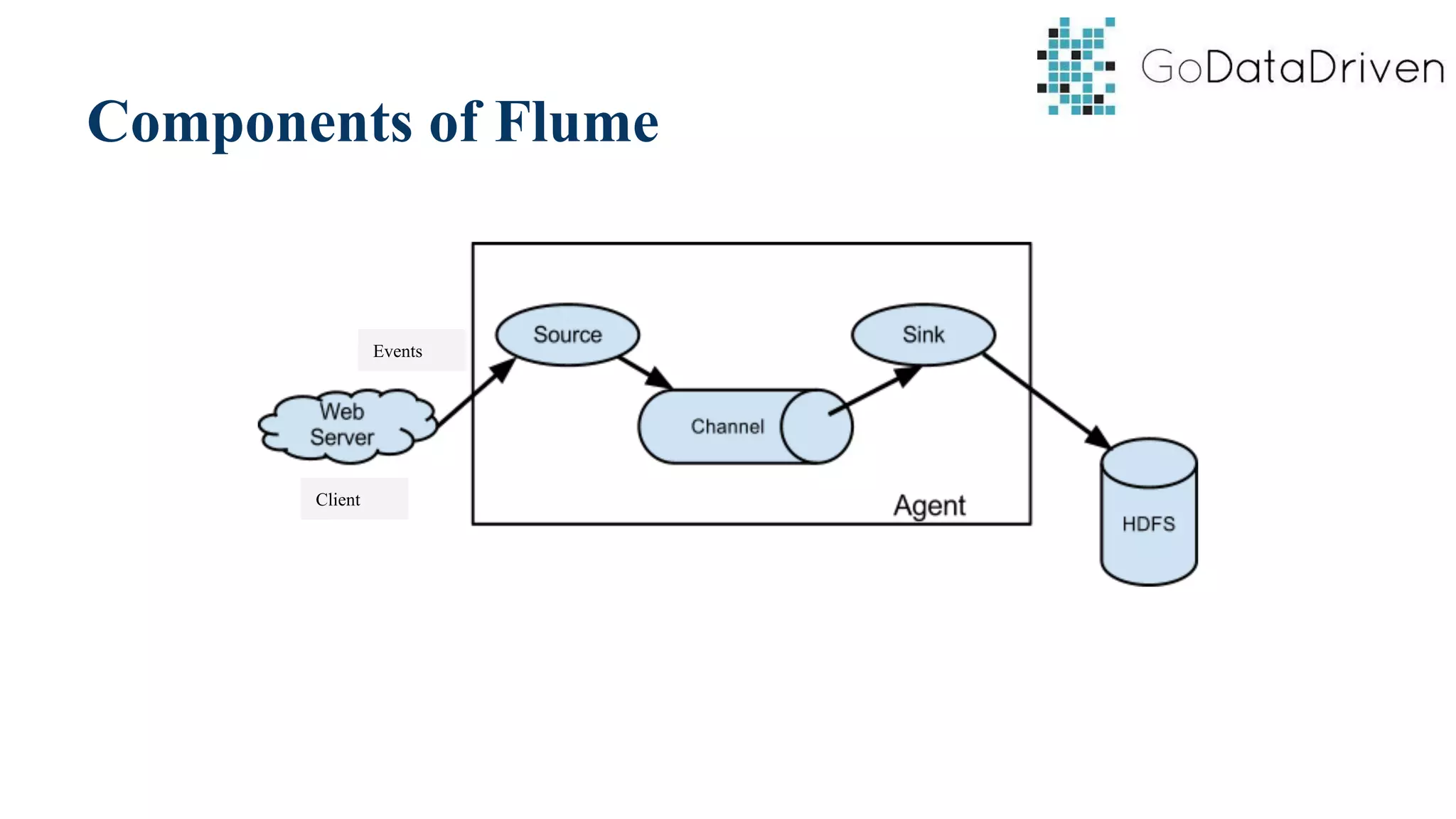
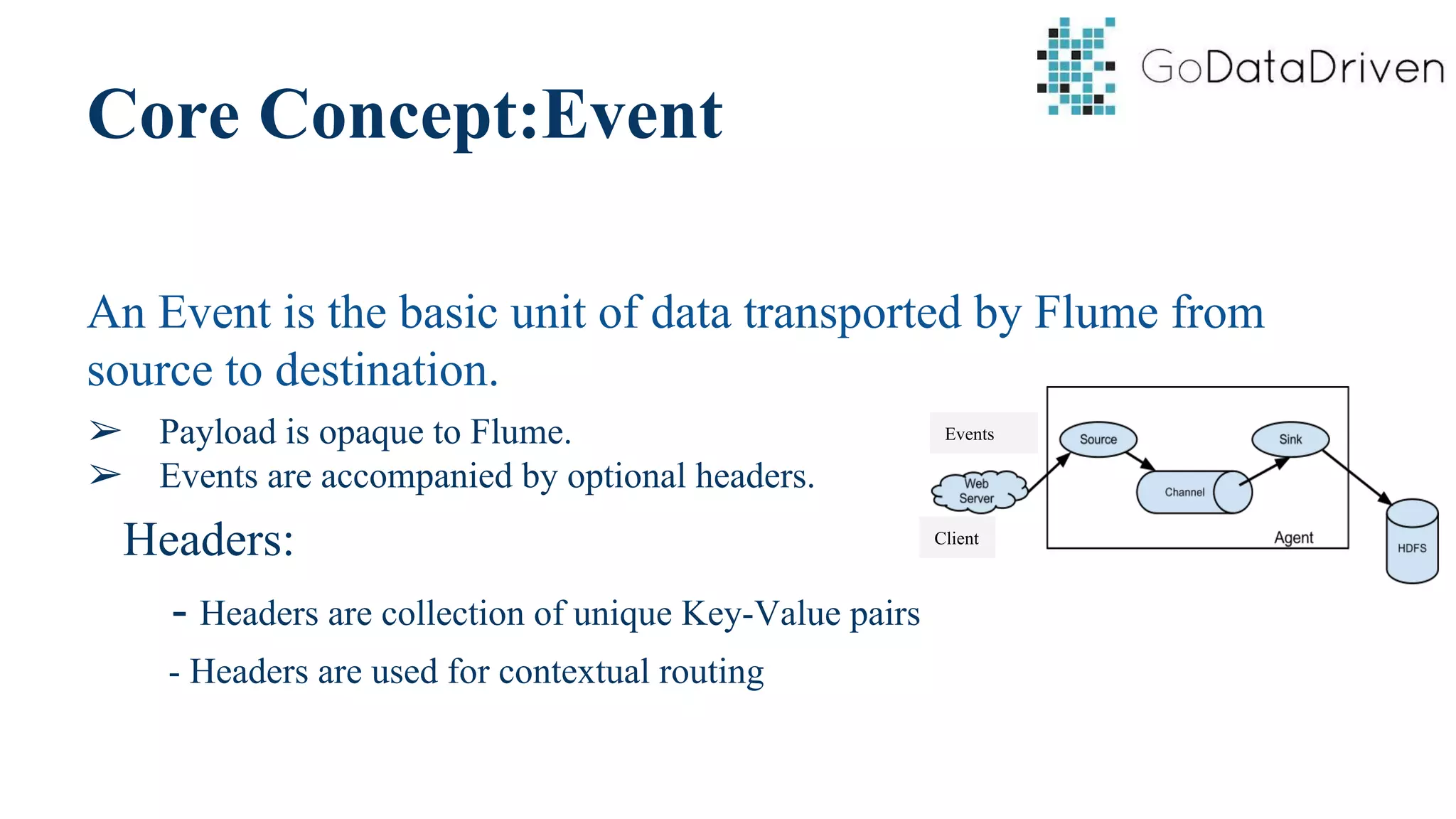
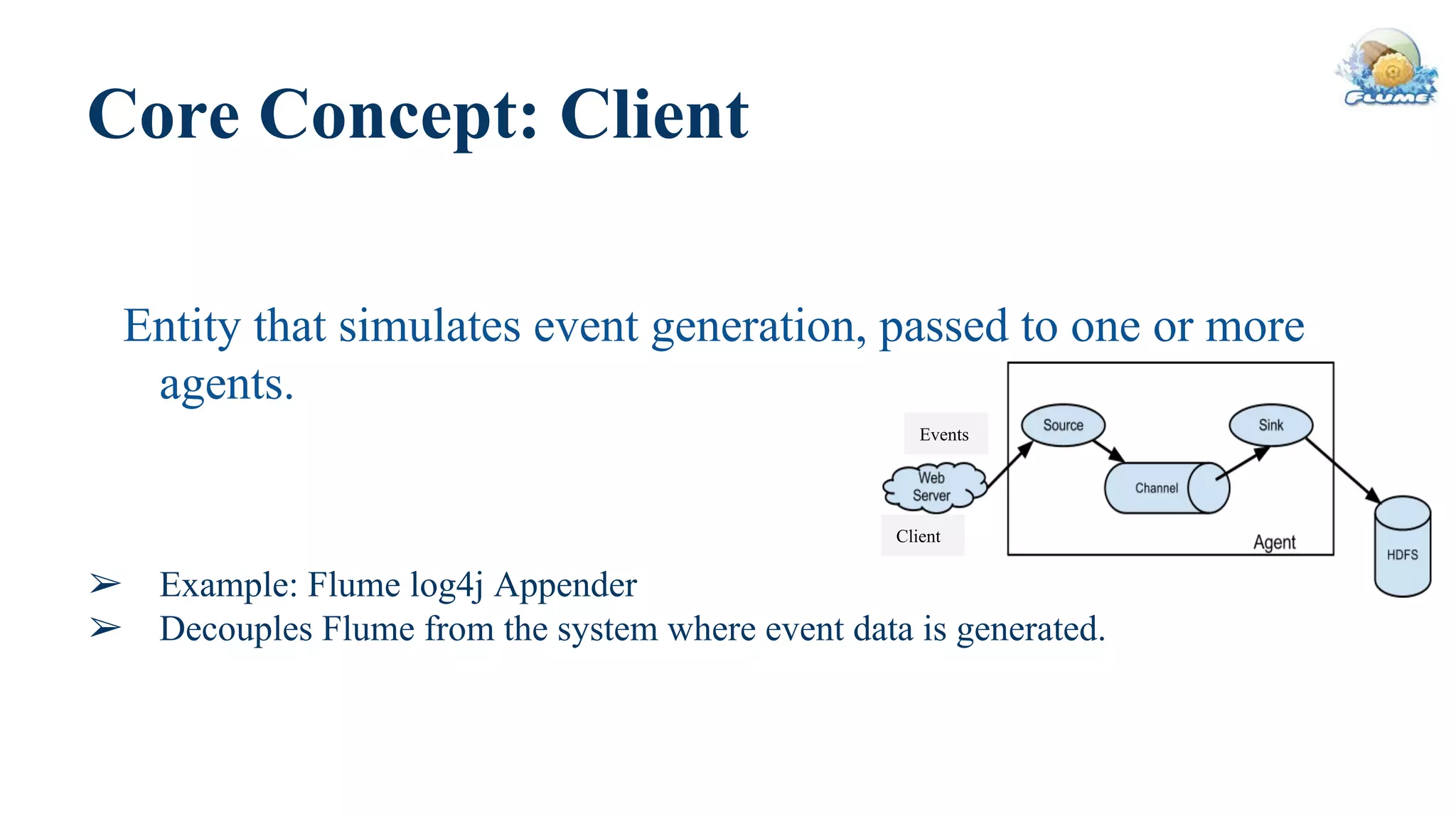
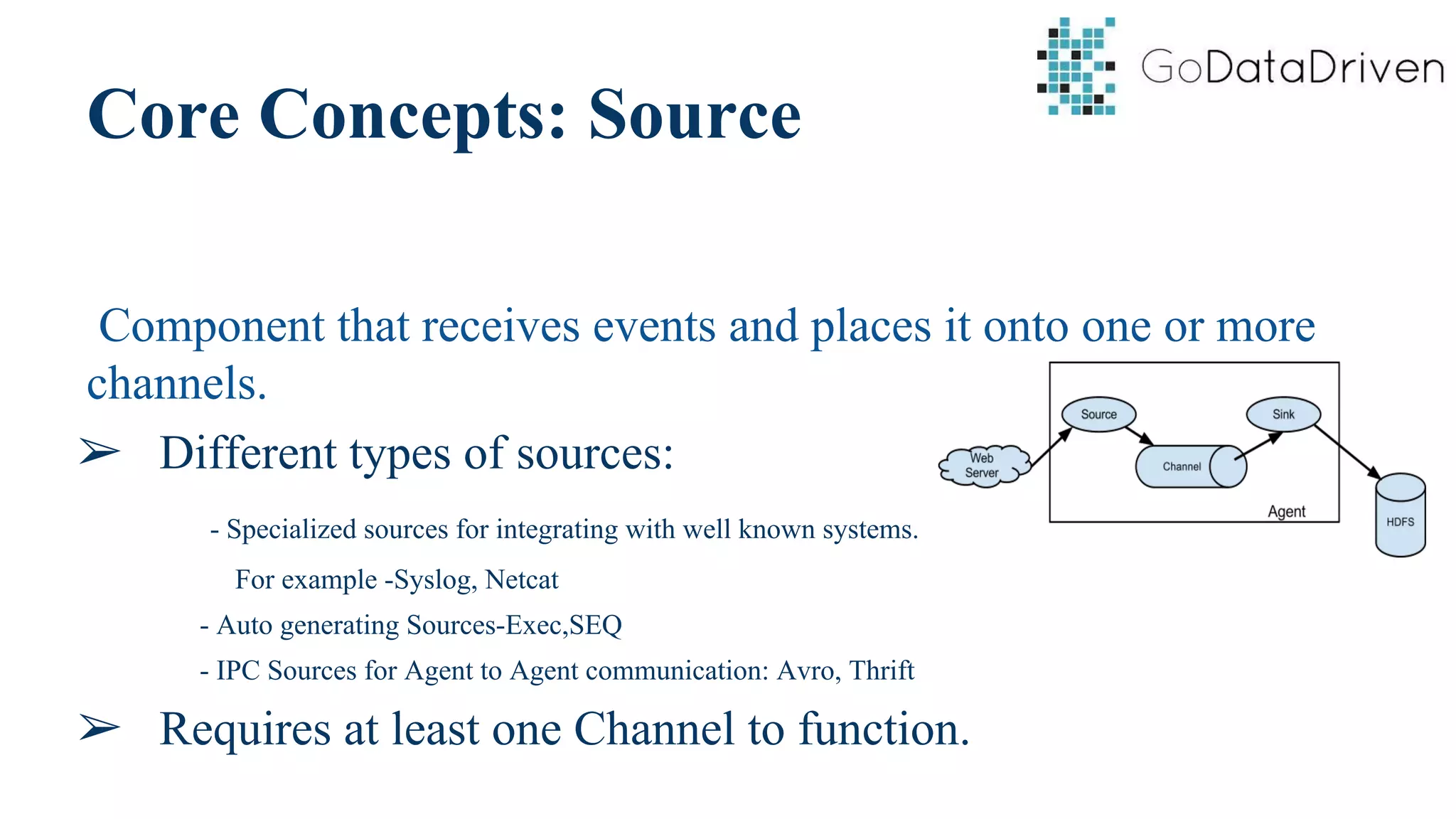
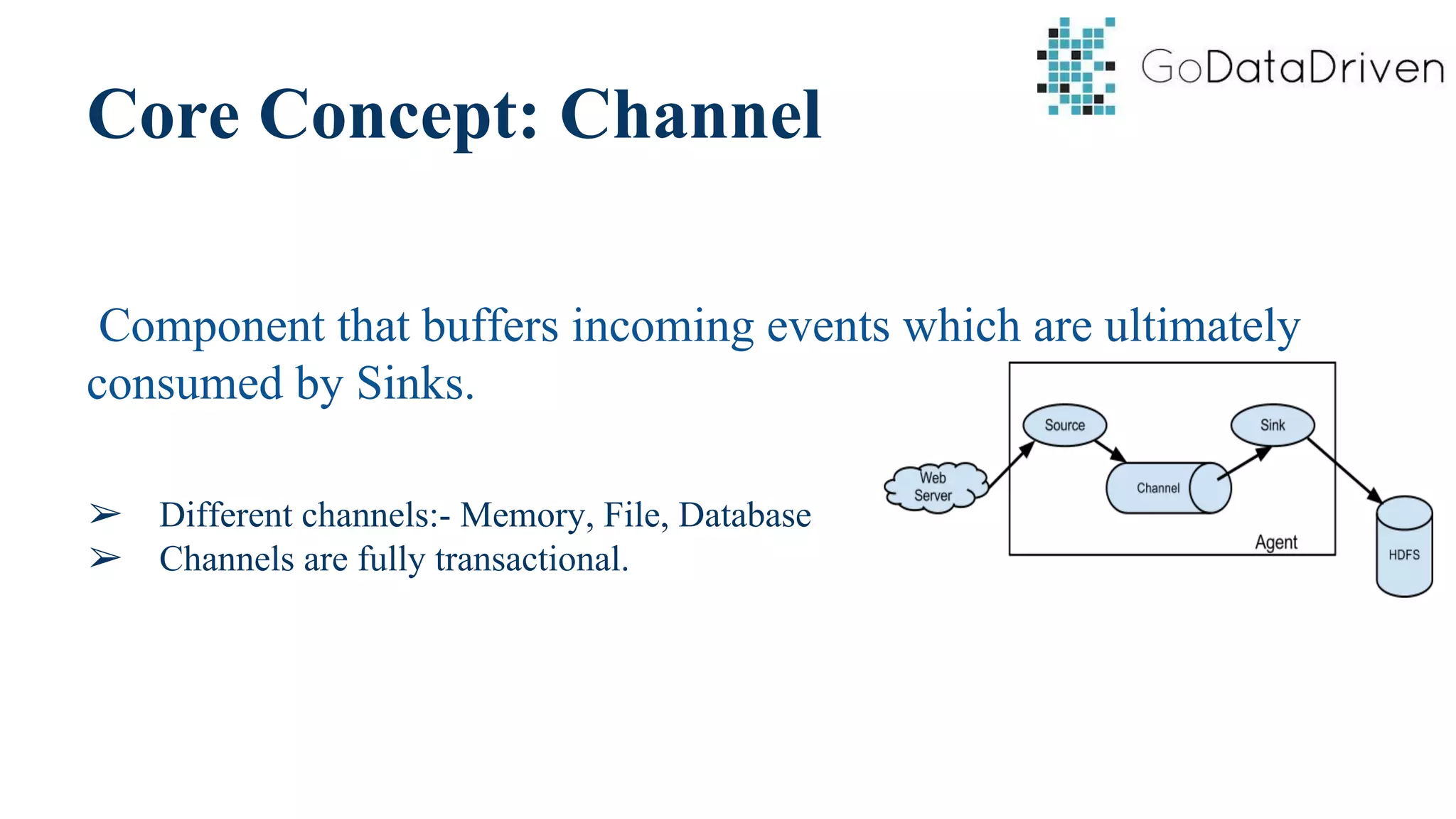
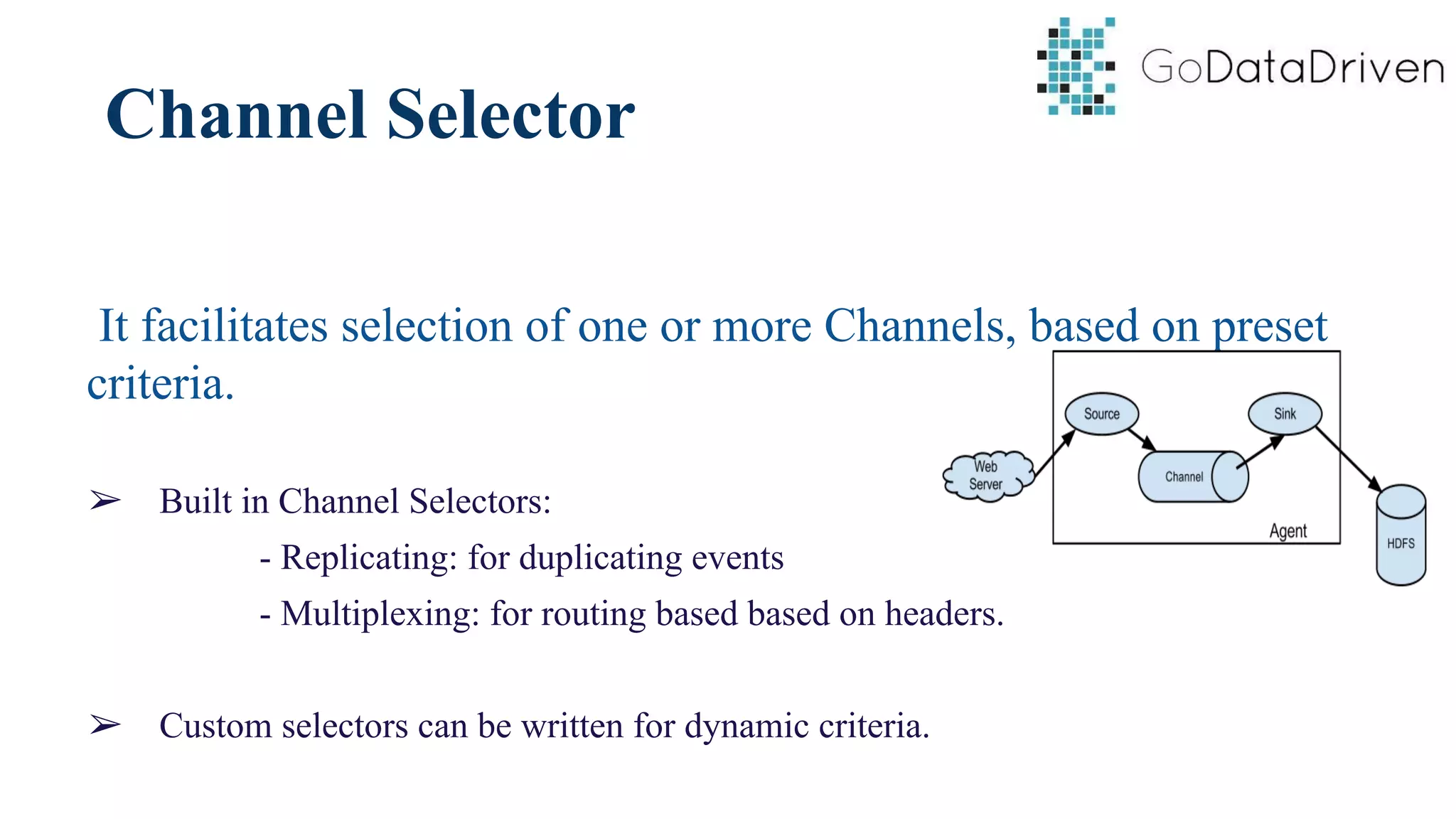
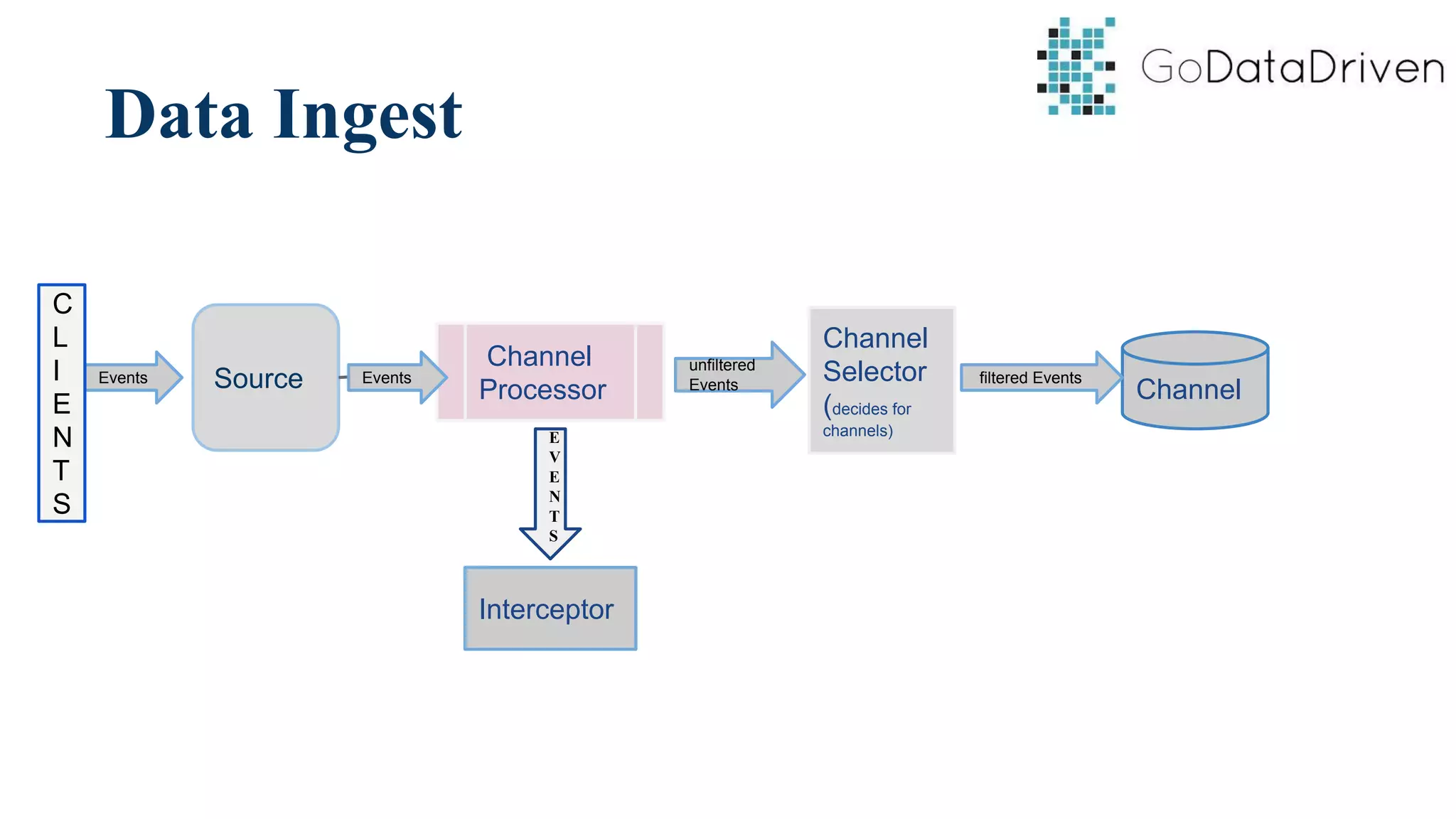
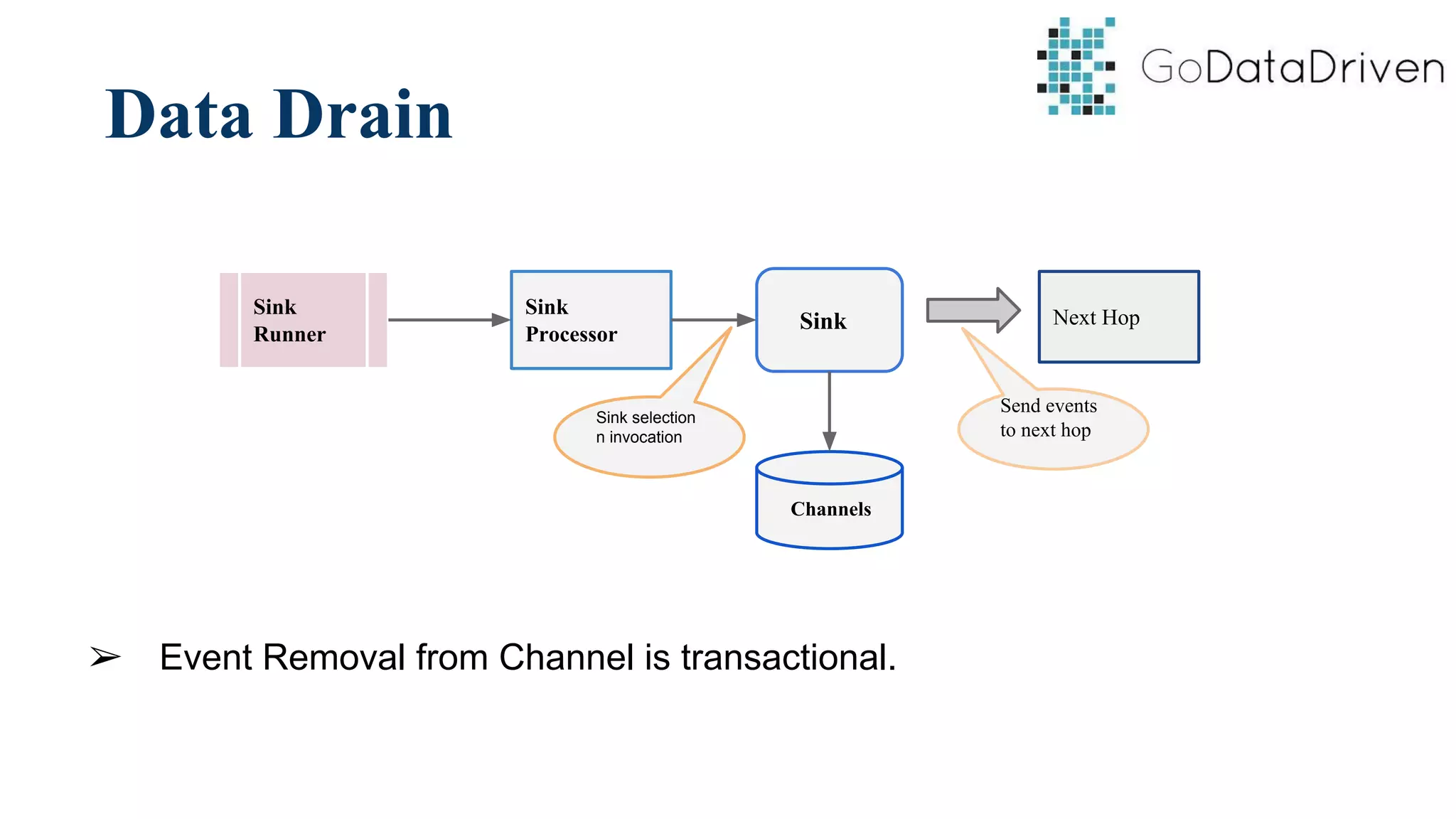
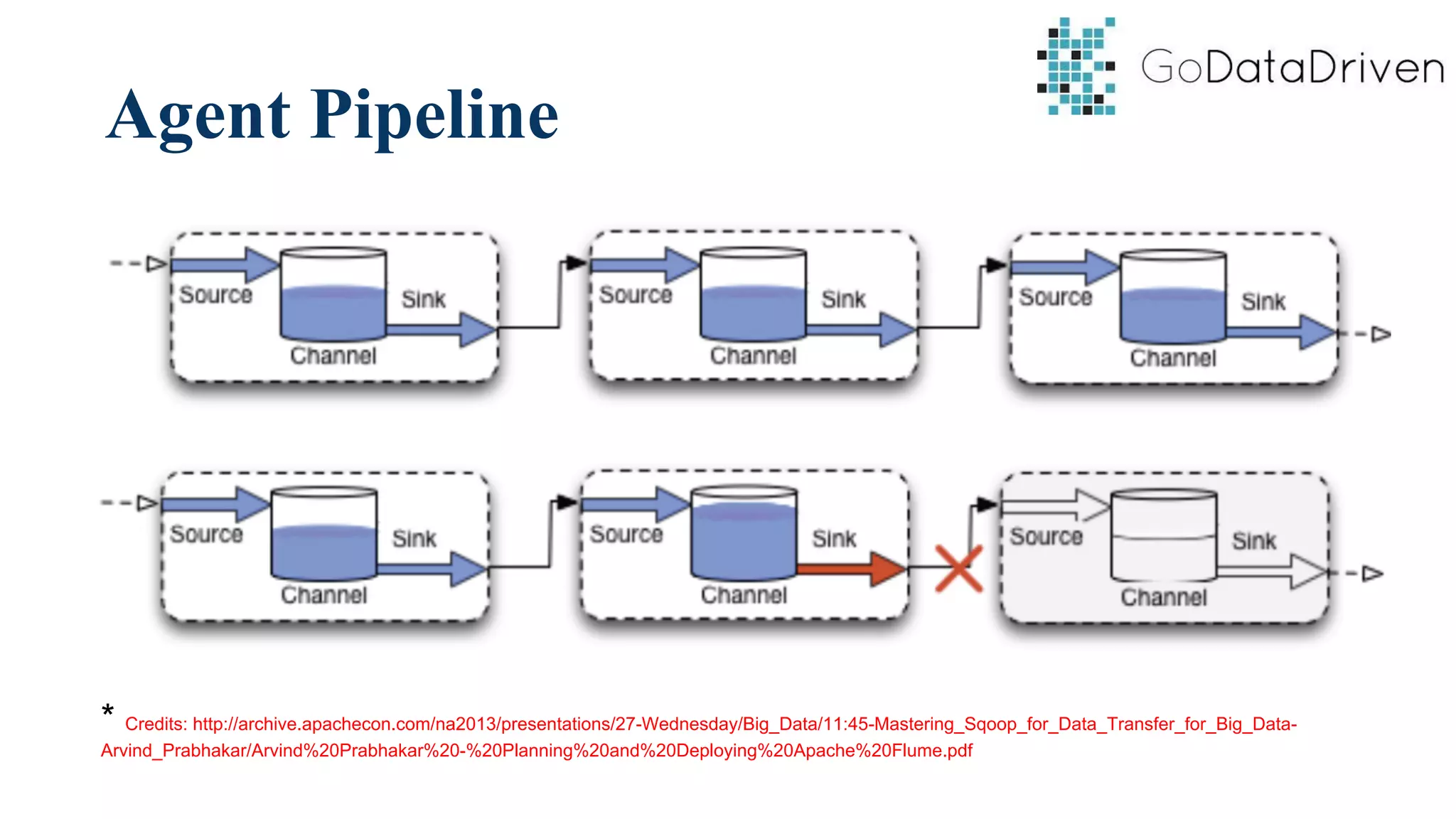
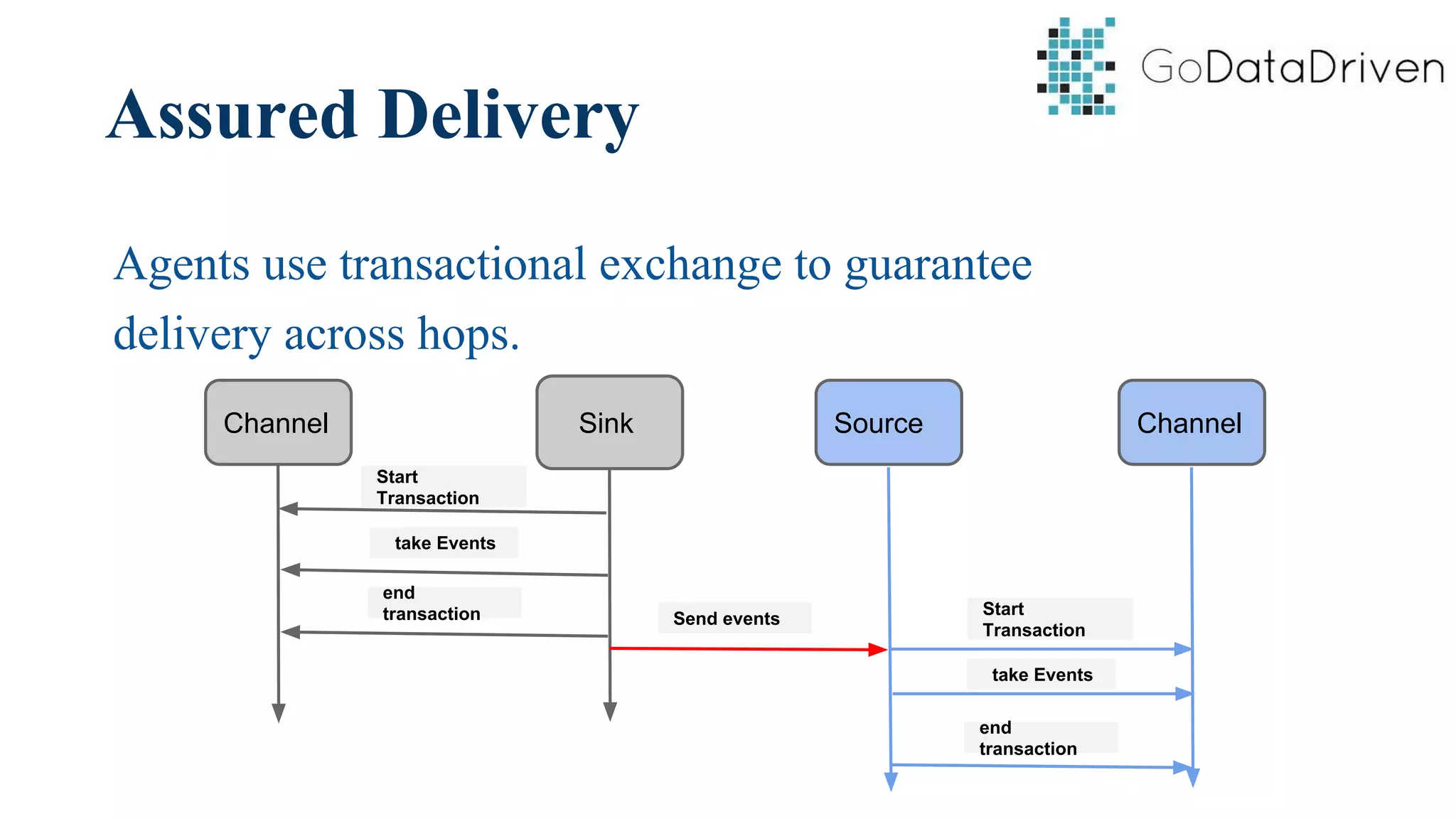
This document provides an overview of Apache Flume and how it can be used to load streaming data into a Hadoop cluster. It describes Flume's core components like sources, channels, sinks and how they work together in an agent. It also gives examples of using a single Flume agent and multiple agents to collect web server logs. Advanced features like interceptors, fan-in/fan-out are also briefly covered along with a simple configuration example to ingest data into HDFS.