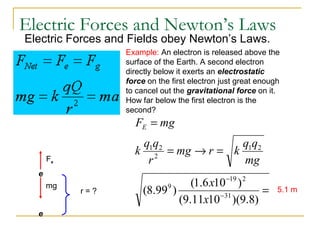
Electric fields are produced by electric charges and describe the interaction between charges. There are two types of charges - positive and negative - and like charges repel while opposite charges attract. An electric field is a vector quantity that describes the force that would be experienced by a hypothetical positive test charge placed at a point in space. The electric field near a point charge is calculated using the equation E = kQ/r^2, where k is a constant, Q is the charge producing the field, and r is the distance from the charge. The direction of the electric field points away from a positive charge and toward a negative charge.