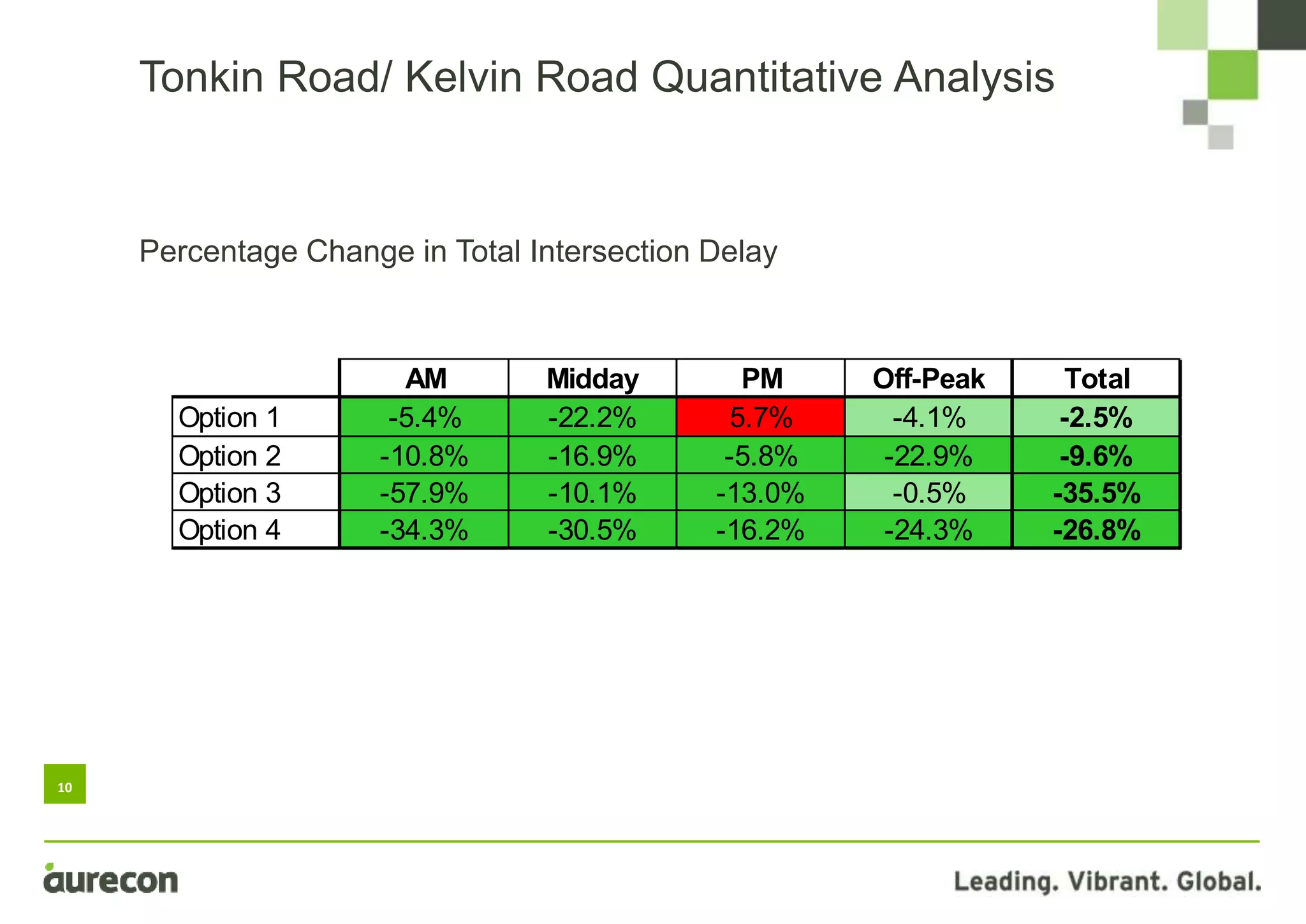
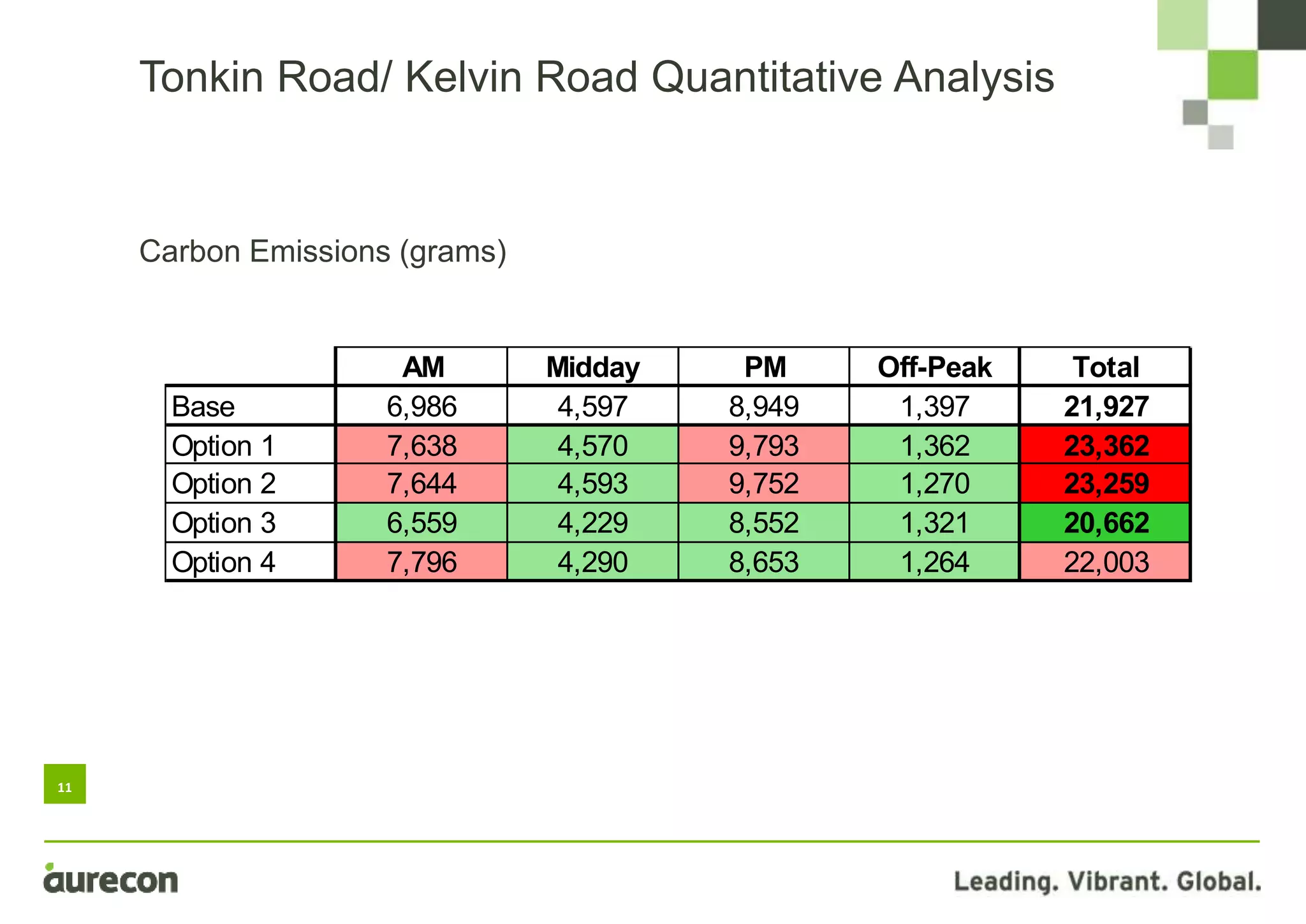
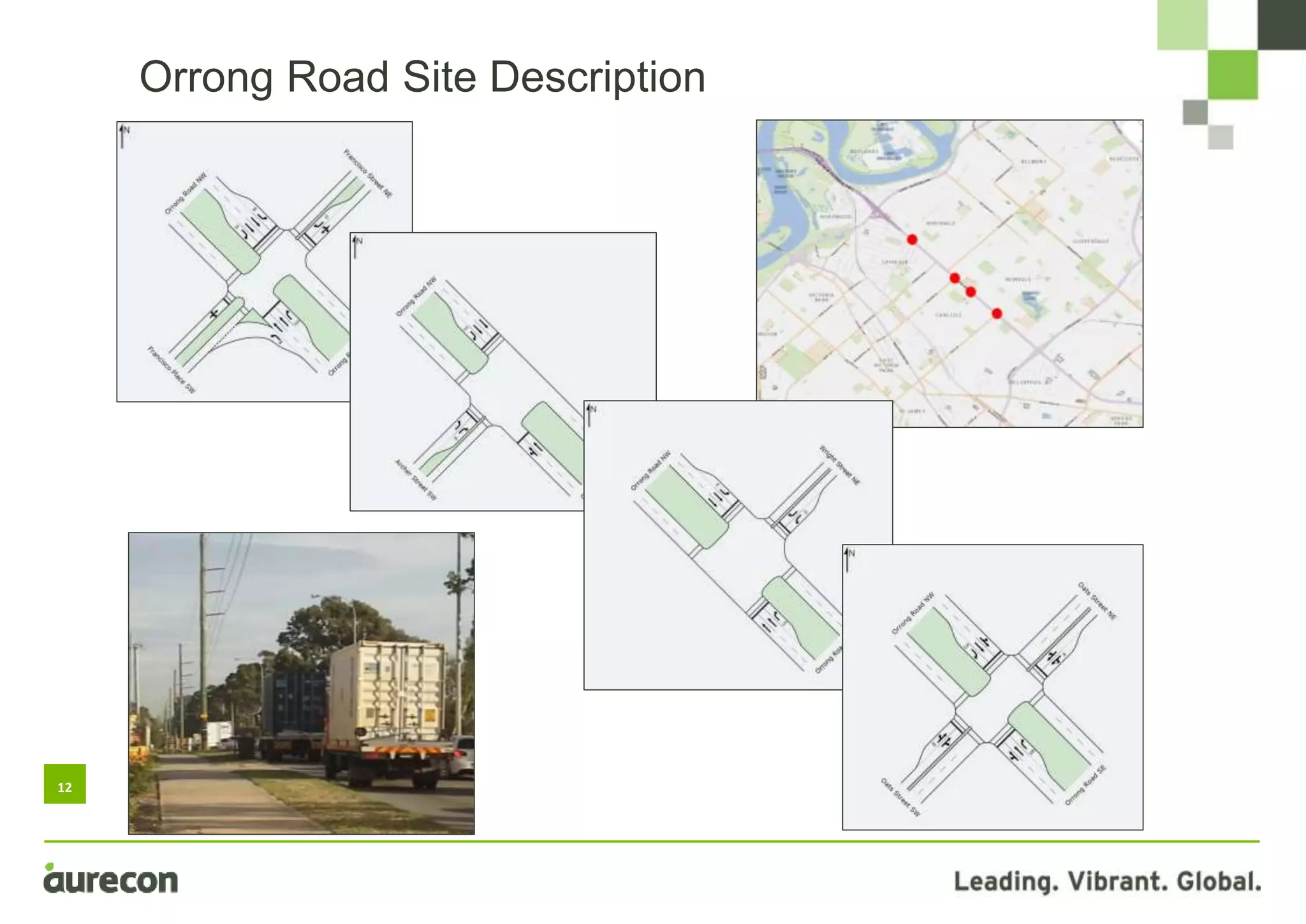
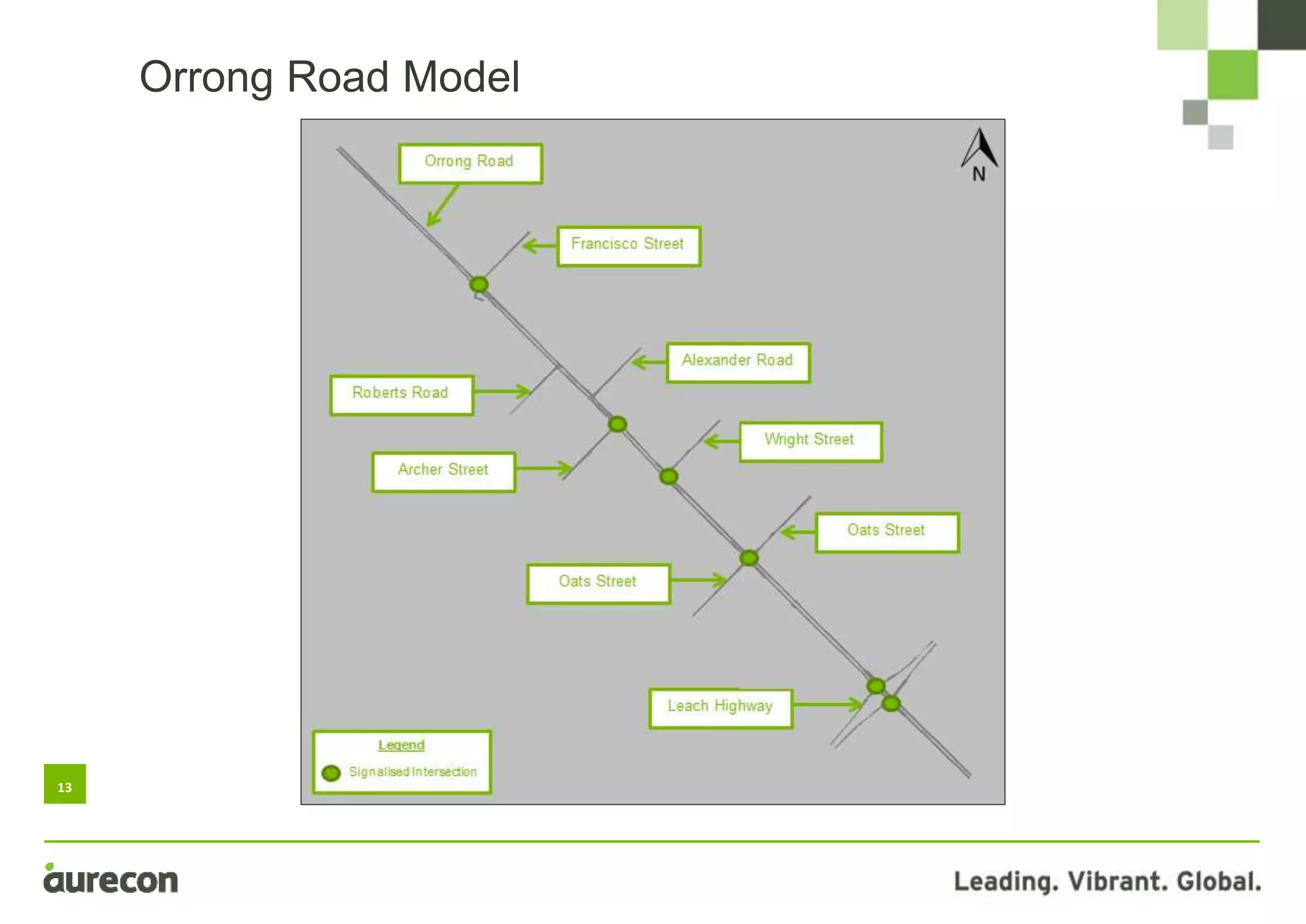
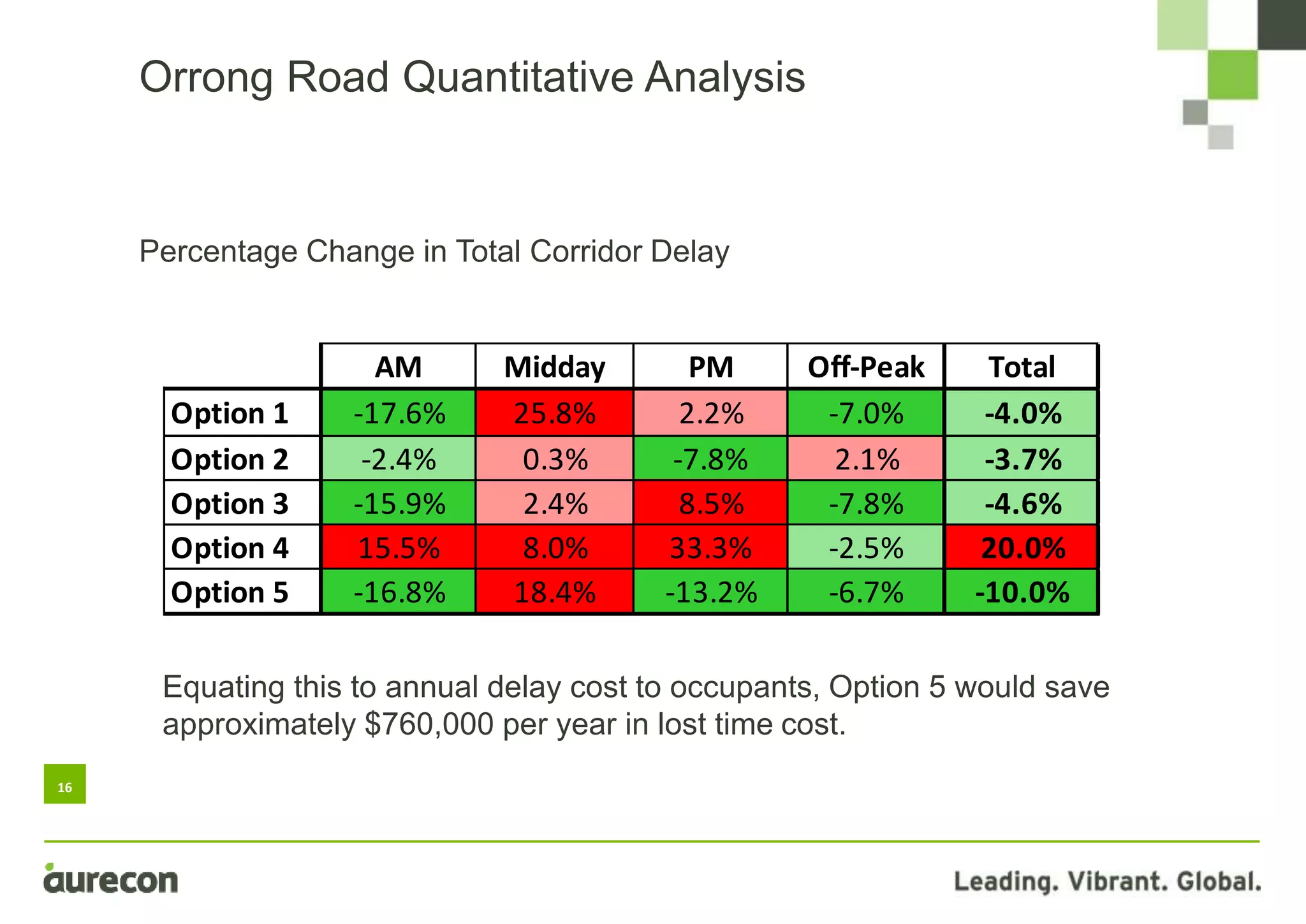
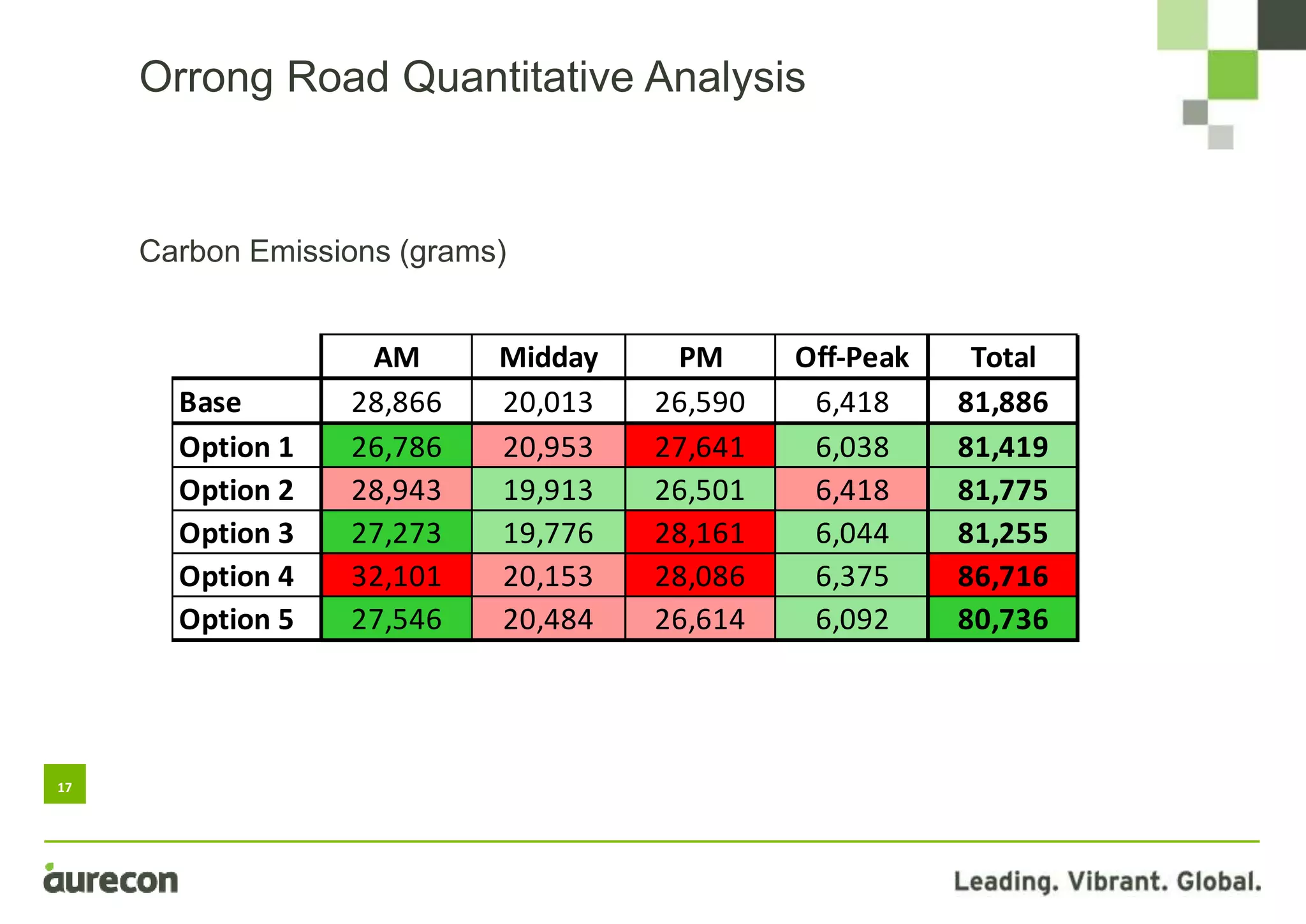
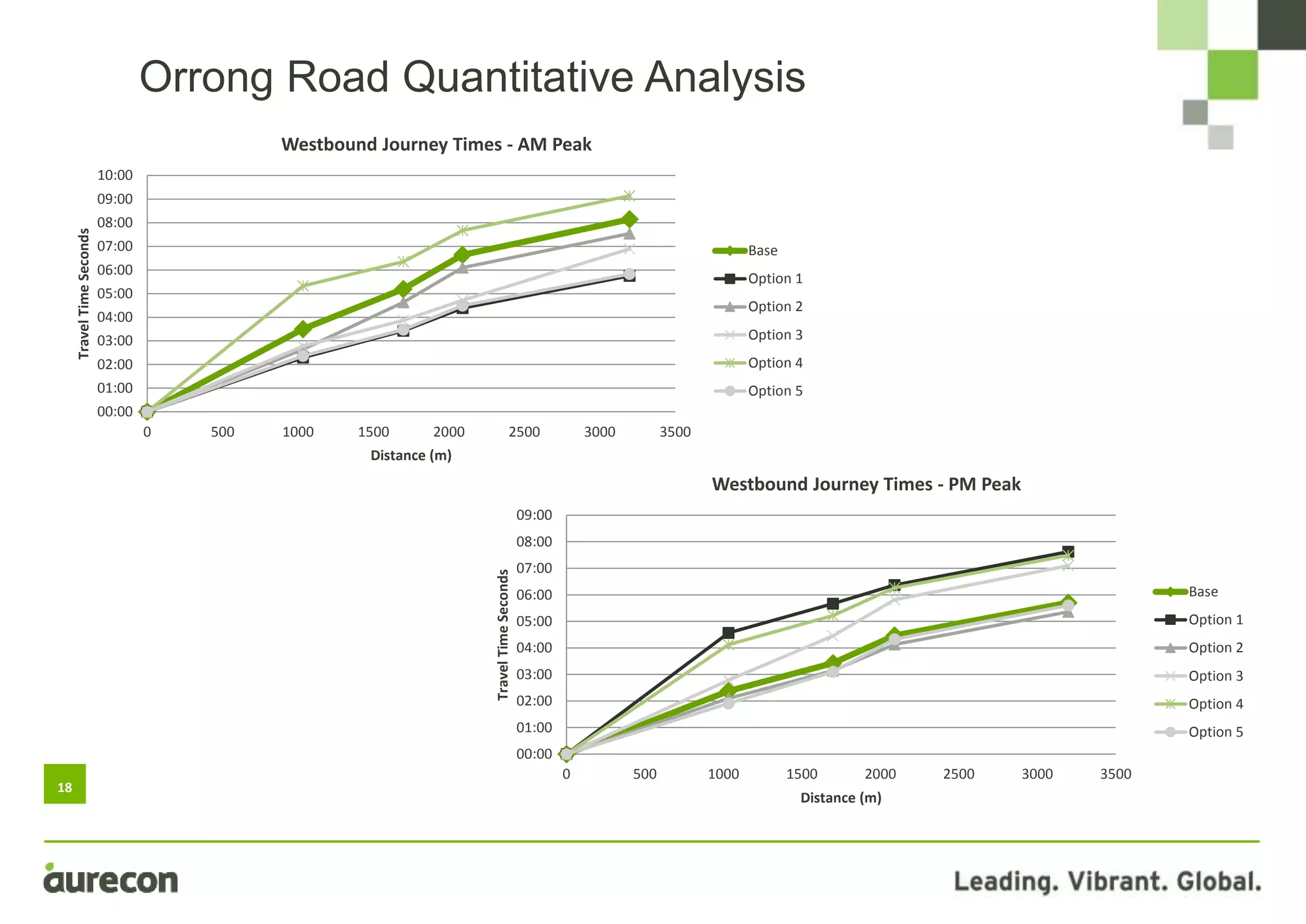
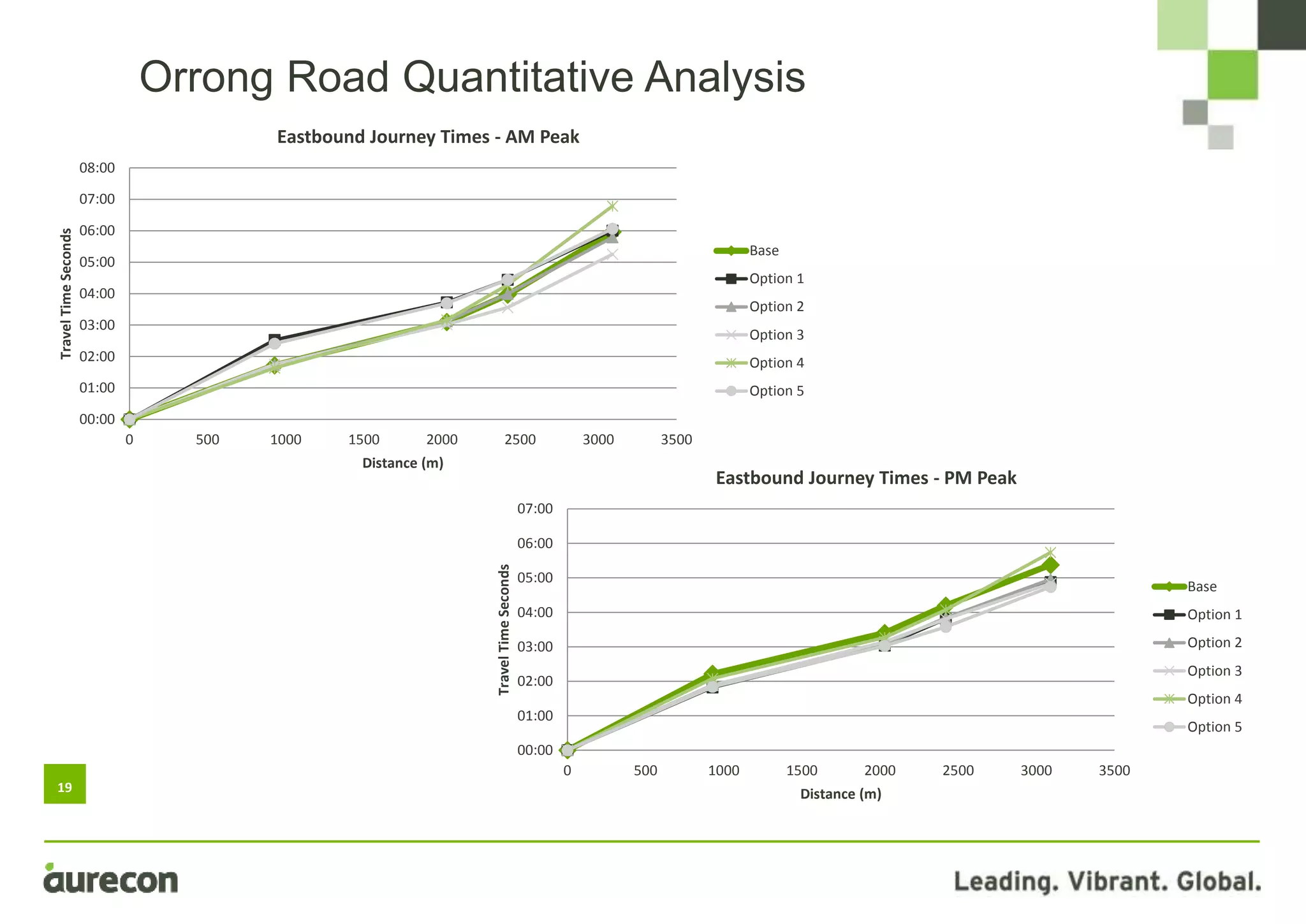
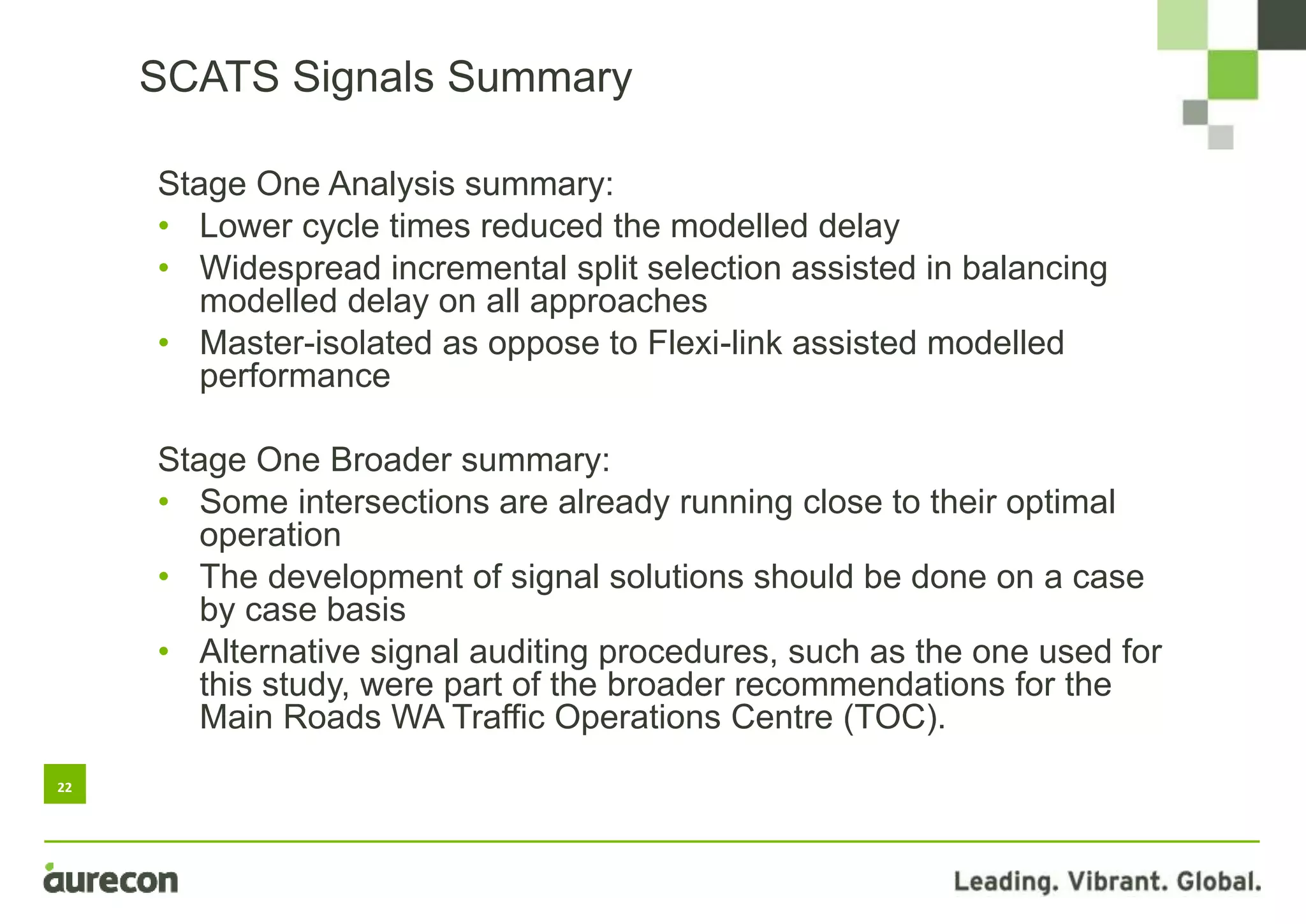
This document summarizes a study conducted on optimizing traffic signal timing in Western Australia using SCATS (Sydney Coordinated Adaptive Traffic System). Two sites - Tonkin Highway/Kelvin Road intersection and Orrong Road corridor - were modeled with various SCATS timing options. Modeling found options that reduced delay up to 57% and carbon emissions. Option 5 for Orrong Road, involving widespread incremental split selection and optimal cycle times, showed the largest delay and speed improvements. The study recommends considering signal timing solutions on a case-by-case basis and alternative auditing procedures to further optimize intersections using SCATS.