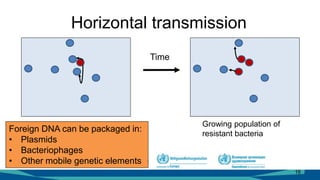
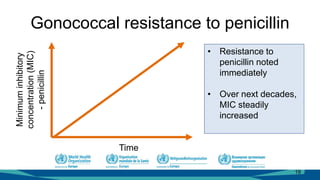
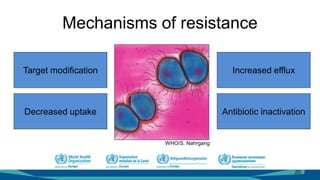
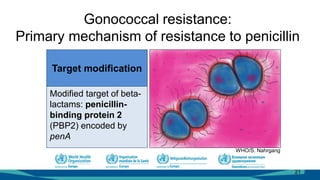
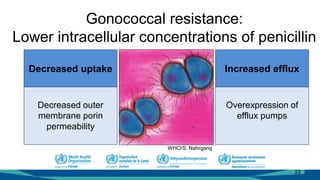
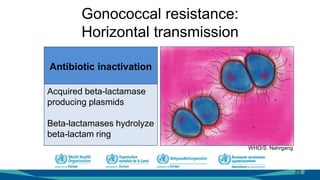
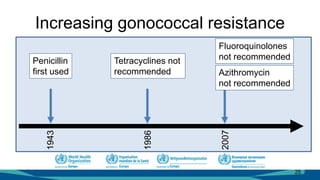
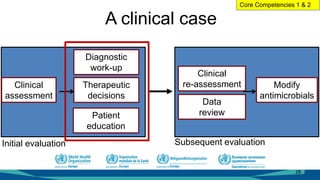
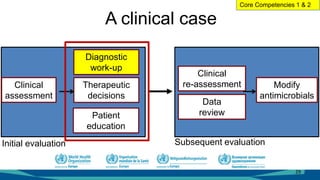
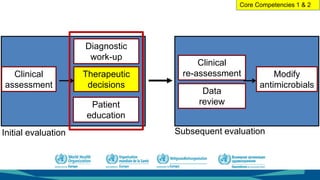
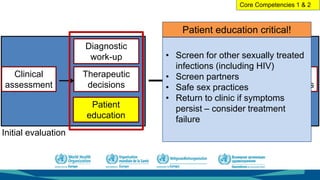
The document outlines a course on antimicrobial resistance aimed at clinicians, emphasizing the urgent need to address drug-resistant pathogens. It highlights core competencies for appropriate antimicrobial prescribing, mechanisms of resistance, and the implications of resistance for patient outcomes. Clinical case evaluations and guidelines for treatment illustrate the importance of evidence-based practices in combating antimicrobial resistance.