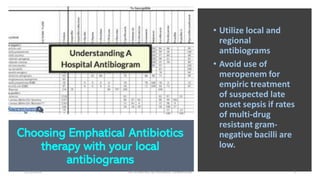
The document discusses antibiotic stewardship and strategies to combat antibiotic resistance. It outlines how inappropriate antibiotic use has led to increased antibiotic resistant organisms and how antimicrobial stewardship aims to optimize antibiotic use and minimize unintended consequences. The document provides numerous examples of antibiotic stewardship strategies including obtaining cultures before prescribing antibiotics, using local antibiotic resistance data to guide treatment, reviewing culture results to modify prescriptions, restricting broad-spectrum antibiotics, and monitoring treatment response and duration. It stresses the importance of education, guidelines, surveillance, and metrics to evaluate antibiotic stewardship programs.