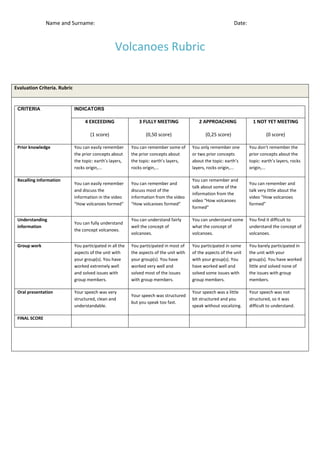
Here are the steps to create a baking soda and vinegar volcano:
1. Place some baking soda in a container to represent the volcano's interior.
2. Slowly pour vinegar into the baking soda volcano's opening.
3. Watch as the chemical reaction between the baking soda and vinegar causes the volcano to erupt with fizzing and bubbling, simulating a real volcanic eruption.
The baking soda and vinegar reaction produces carbon dioxide gas that allows students to observe chemical changes in an exciting visual way. It's a fun science experiment kids will enjoy!