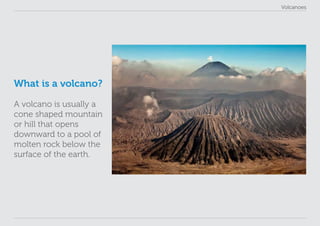
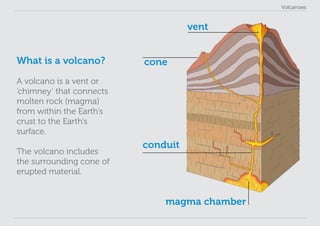
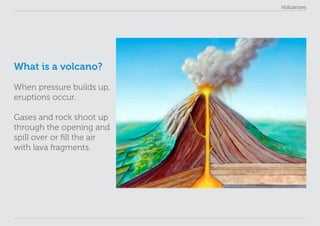
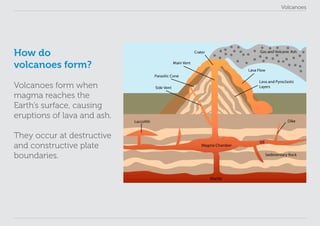
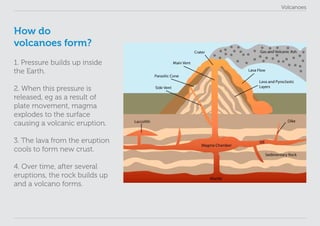
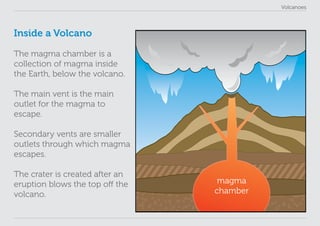
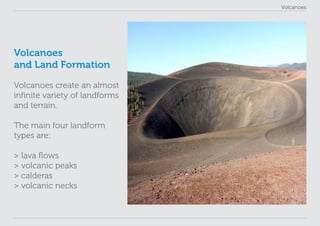
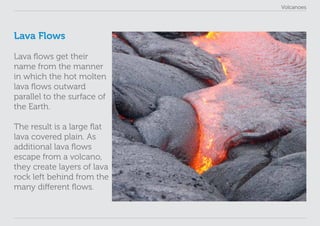
This lesson plan provides materials to teach students about volcanoes over one 60 minute session. Students will gain an understanding of volcano formation and types, learn to identify volcanic features, view images of active volcanoes, and locate 12 notable volcanoes on a map. The lesson involves a presentation to impart key points about volcanoes, followed by an activity where students discover information about volcanoes in their worksheet. The lesson aims to help students develop research, classification, communication and observation skills.