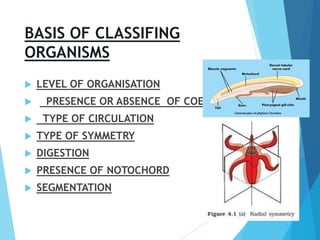
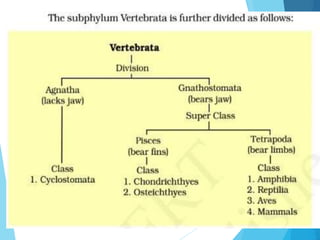
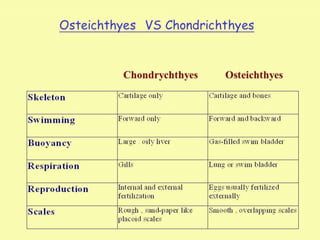
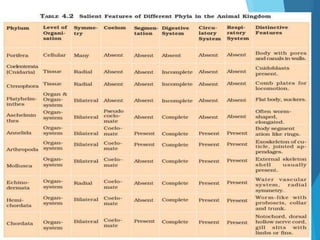
This document provides information on different animal kingdoms and phyla. It discusses key characteristics of porifera, cnidaria, ctenophora, platyhelminthes, aschelminths, annelida, arthropoda, mollusca, echinodermata, hemichordata, chordata, cyclostomata, chondrichthyes, osteichthyes, amphibians, reptiles, aves, and mammalia. For each group, example organisms are given and distinguishing features such as body plan, symmetry, digestive system, and more are described.