Angular 2.0 was released on September 14th, 2016 by Google. It is a total rewrite from Angular 1.x and uses TypeScript as its default language. Some key features include components, templates, modules, services, dependency injection and routing. Components control views through templates. Modules allow grouping and metadata. Templates use data binding syntax. Services provide reusable business logic. Dependency injection provides services to components. Routing enables navigation between views.








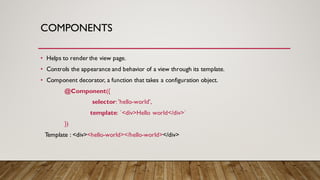


![TEMPLATES
• One way data binding
• {{ }} => Interpolation.Display a component property,
• [ ] => Property binding. Bind the value to the property.
• ( ) => Event binding.
• [()] =>Two way data binding](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-160926101527/85/Angular2-12-320.jpg)


![DATA BINDING
• BindingType (Divided based on the direction in which data flows)
1. Interpolation | property | attribute
One way from source to target.Data source =>View target.
{{expression}} => <h2>{{title}}</h2>
[target] = "expression" => <span [hidden] = “isSet” ></span>
2. Event
One way from target to source.View target => Data source.
(target) = "statement” => (click) = ‘callMe’
3. Two way
[(target)] = "expression” => [(ngModel)] = ‘callMe’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-160926101527/85/Angular2-15-320.jpg)



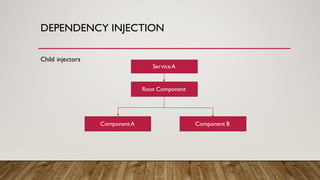
![DEPENDENCY INJECTION
@Component({
providers:[ProductService]
})
class ProductComponent {
product:Product;
constructor(private productService: ProductService) {
this.product = this.productService.getProduct();
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-160926101527/85/Angular2-20-320.jpg)



![ROUTING
<html><header></header><body>
<div id="menu”>
<a [routerLink]="['/home']" class="btn">Home</a>
<a [routerLink]="['/about']" class="btn">About</a>
</div>
<div id="container">
<router-outlet></router-outlet>
</div>
</body></html>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/angular2-160926101527/85/Angular2-24-320.jpg)




