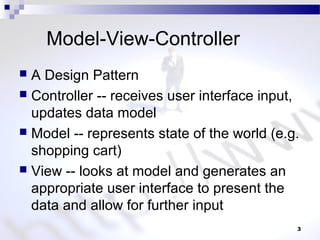
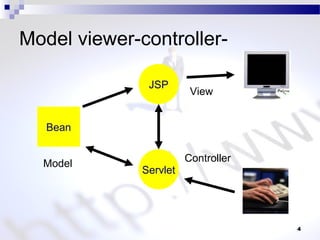
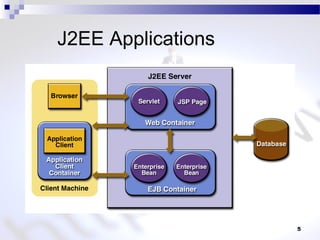
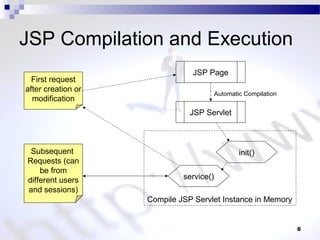
This document discusses JSP processing and elements. It states that JSP pages have a .jsp extension and are organized like HTML files. A JSP page is compiled to a servlet class when first requested or modified. The document also briefly mentions the MVC design pattern and describes common JSP elements like scriptlets, expressions, declarations, and directives.




![9
Expression
A shortcut to print out a value or an
expression
<%= [expression]%>
Expression can be a variable, formula, object
property, string concatenation, method with
return value, or anything that returns a value
See example “expression-example.jsp”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/9c4djsp-140809031853-phpapp01/85/JSP-Processing-9-320.jpg)