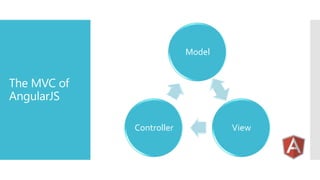
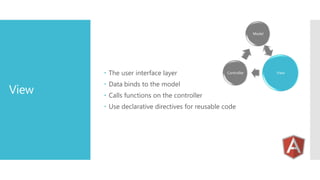
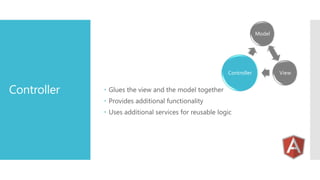
AngularJS is an MVC framework for building client-side web applications. It uses two-way data binding between models and views, dependency injection to decouple modules, and directives to extend HTML. Key features include routing for single-page applications, services for reusable logic, and tools for testing AJAX code. AngularJS provides standard directives, services, and routing capabilities to build complete applications in the browser.