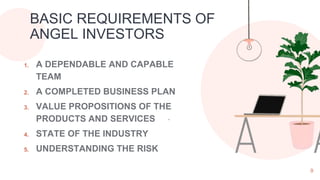
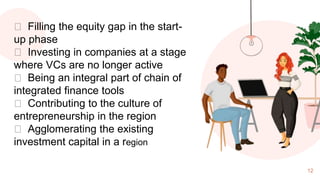
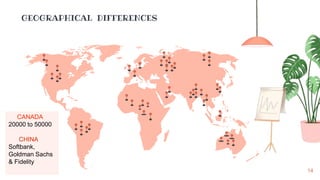
Angel investors are individuals who provide capital for business start-ups, typically in exchange for equity or convertible debt, and focus on supporting businesses rather than maximizing profits. They evaluate potential investments based on various factors, including the founder's knowledge, the disruptiveness of the idea, and customer viability. Unlike venture capitalists, angel investors usually work independently and mainly invest in early-stage companies, although their involvement can come with trade-offs like reduced control over the business.