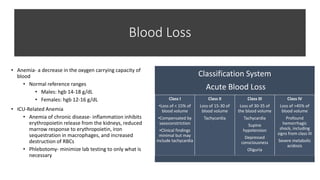
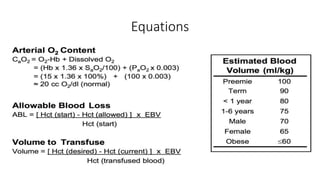
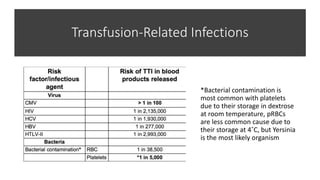
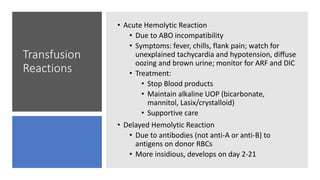
This document discusses anemia, blood transfusions, and transfusion reactions. It defines anemia as a decrease in oxygen-carrying capacity of blood and notes normal hemoglobin ranges. It also describes different types of blood products including packed red blood cells, platelets, fresh frozen plasma, and cryoprecipitate. The document outlines indications for transfusing each product and notes storage requirements. It discusses potential transfusion complications such as hemolytic, febrile, allergic, and circulatory overload reactions. The document also covers massive transfusion protocols.