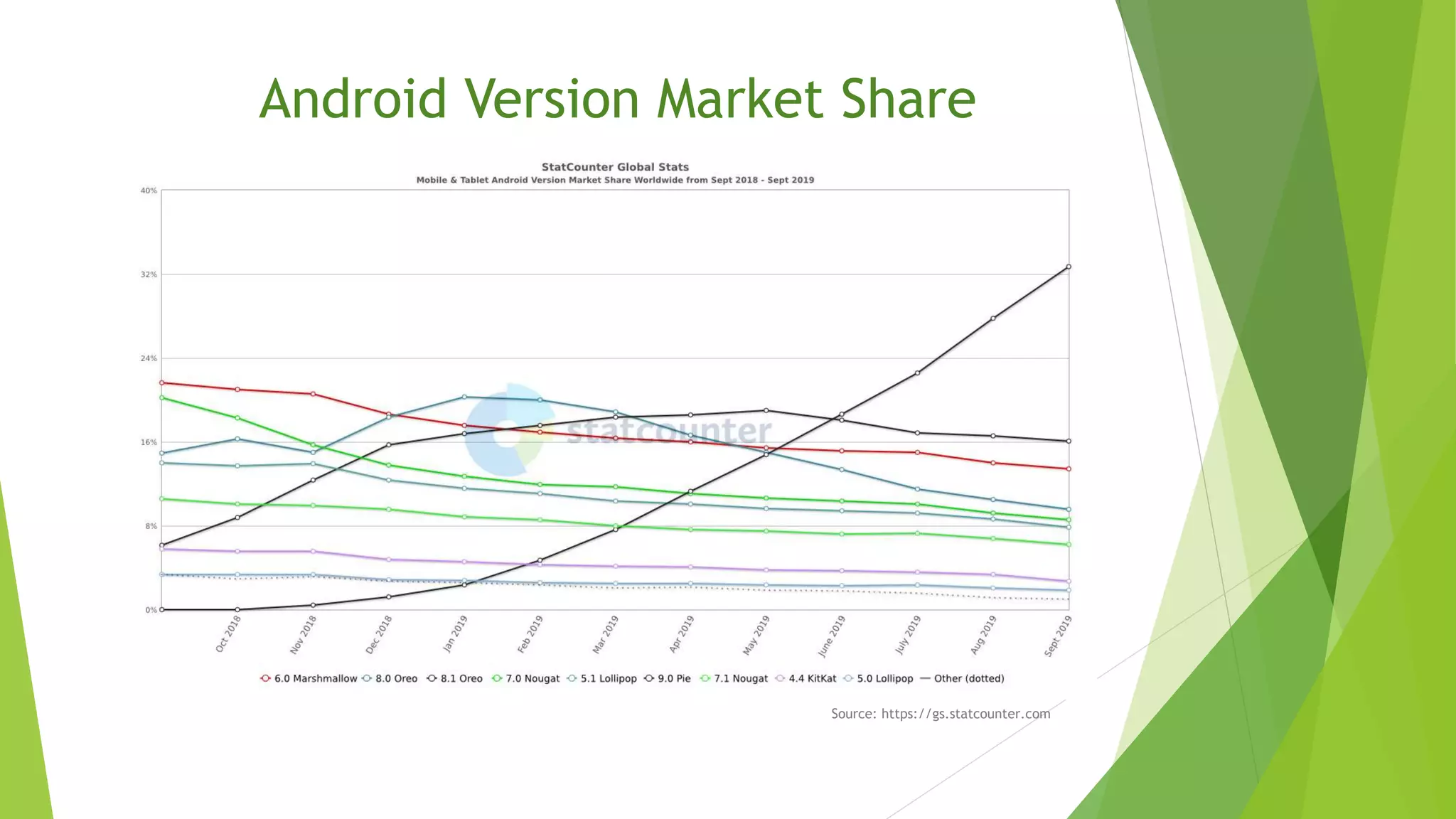
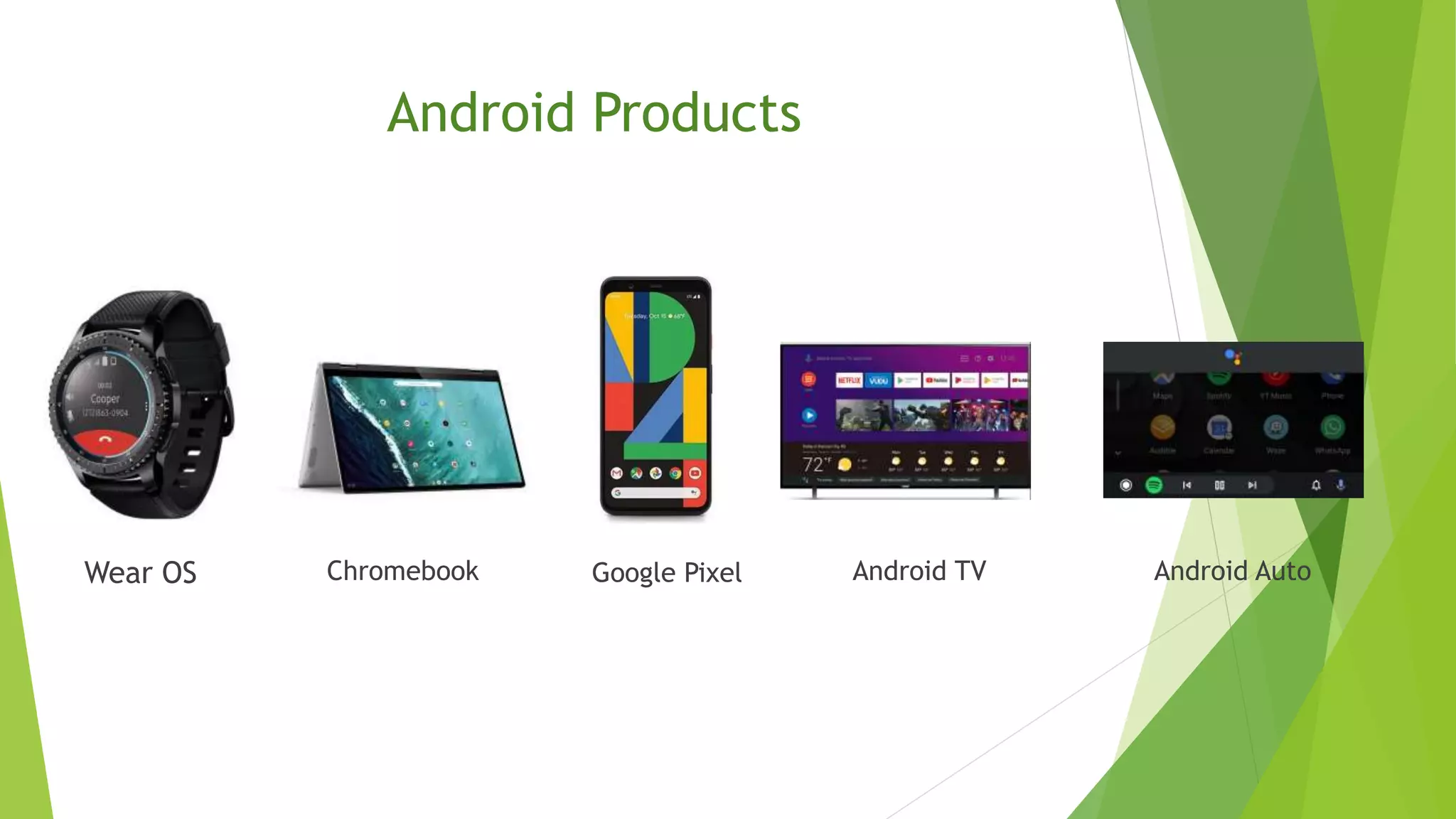
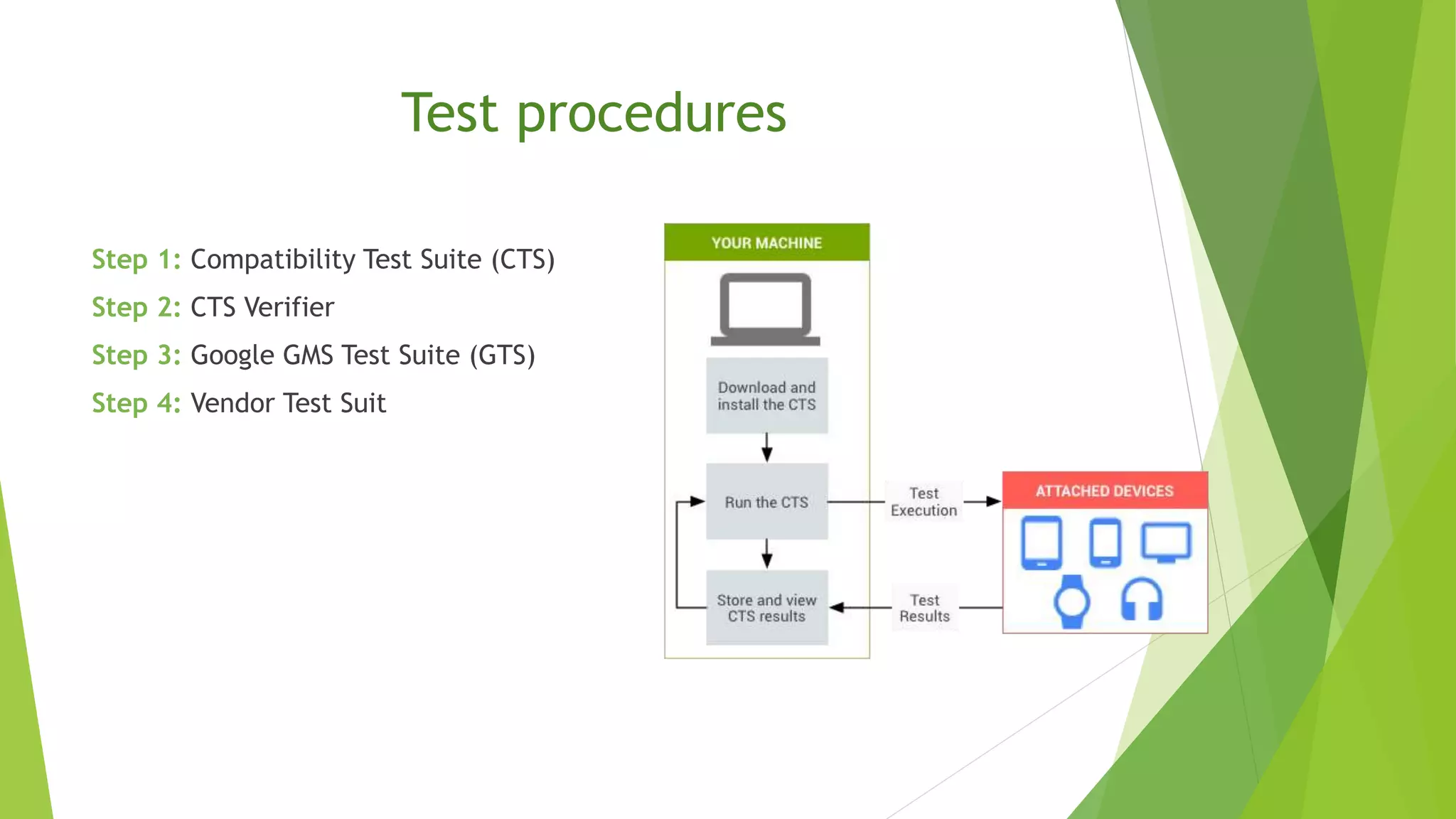
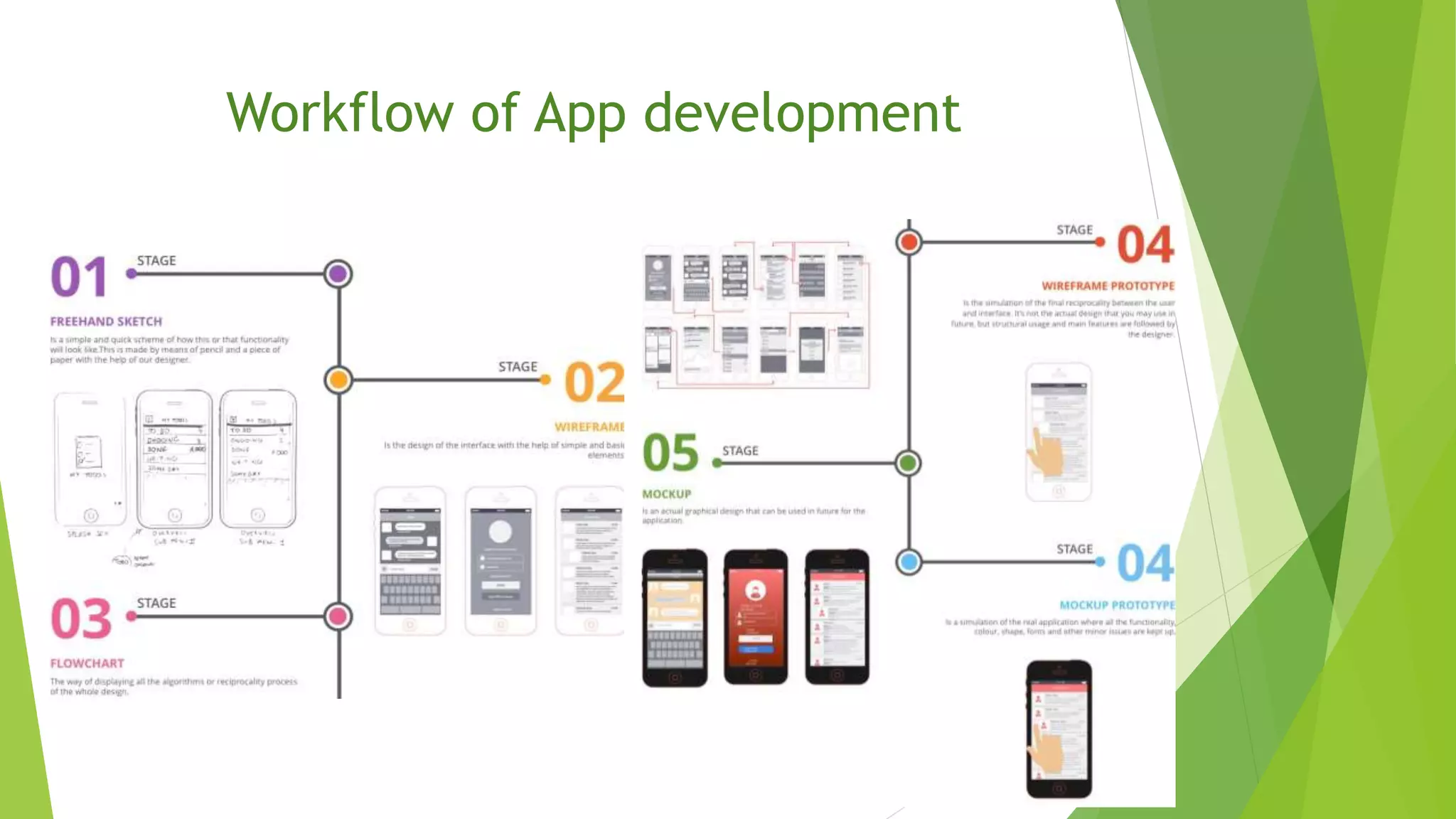
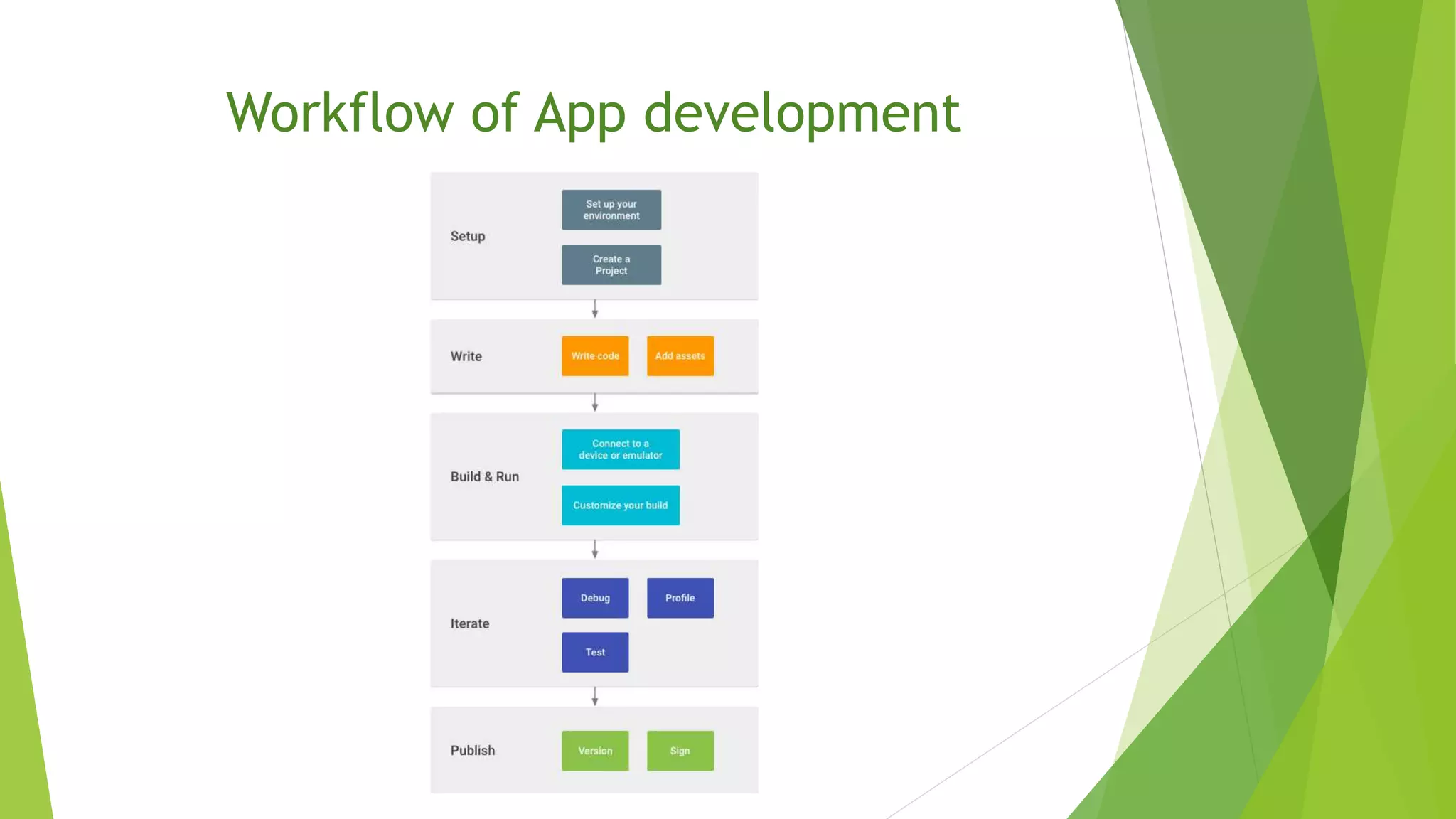
The document provides an overview of the Android operating system, detailing its development by Google and the Open Handset Alliance, as well as the benefits of choosing Android for developers and users. It discusses various Android products, custom skins created by OEMs, and the significance of Google Mobile Services (GMS) for app functionality. Additionally, it outlines the app development workflow, different types of apps, and concludes with the advantages that have contributed to Android's dominance in the smartphone market.