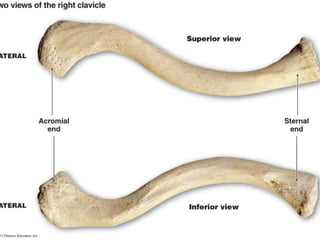
The clavicle is a modified long bone located horizontally between the sternum and acromion process. Its medial end articulates with the manubrium to form the sternoclavicular joint and its lateral end articulates with the acromion process to form the acromioclavicular joint. It serves to support the shoulder girdle and allows the arm to swing freely from the trunk while also transmitting the weight of the upper limb through both joints.