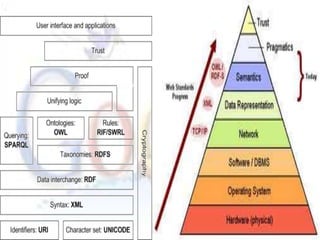
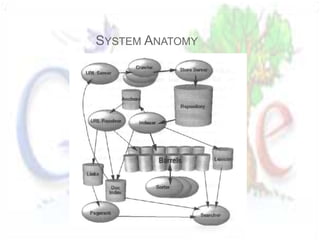
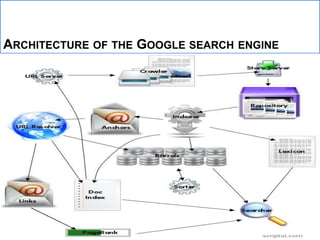
The document describes the anatomy and architecture of Google's large-scale search engine. It discusses how Google crawls the web to index pages, calculates page ranks, and uses its index to return relevant search results. Key components include distributed crawlers that gather page content, a URL server that directs crawlers, storage servers that house the repository, an indexer that processes pages into searchable hits, and a searcher that handles user queries using the index and page ranks.