This document summarizes and analyzes various approaches to studying skills for language learning, including:
1. The need to teach thought processes alongside language to develop students' ability to perform required tasks.
2. The development of functional-notional approaches in line with communicative language teaching and needs analysis.
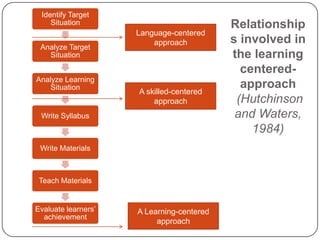
3. The learning-centered approach aims to maximize learning potential by considering student learning needs and motivation. It emphasizes using skills gained outside class and group/pair work.