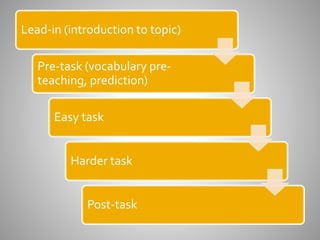
The document describes different types of listening texts and tasks. It lists 8 examples of text types: 1) a news broadcast, 2) directions to a home, 3) a missing person description, 4) an embarrassing anecdote, 5) a shopping dialogue, 6) a pop song, 7) entertainment information, and 8) a weather forecast. It then lists 11 examples of tasks: a) answering wh- questions, b) putting pictures in order, c) ticking items on a list, d) drawing on a map, e) filling in a grid/table, f) choosing a picture, g) taking notes, h) choosing an adjective, i) writing exact words, j) drawing a picture