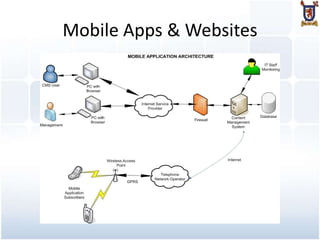
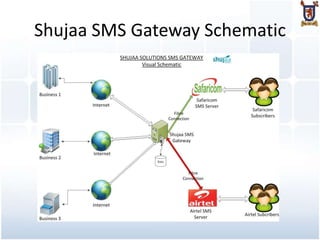
The document provides an overview of mobile technologies, including definitions and examples of SMS, USSD, mobile applications, and mobile websites. It discusses how mobile users interact with these technologies and the infrastructure required for services like bulk SMS and mobile banking. The document also highlights best practices for mobile website development and mentions various mobile technologies such as IVR and SIM toolkit programming.