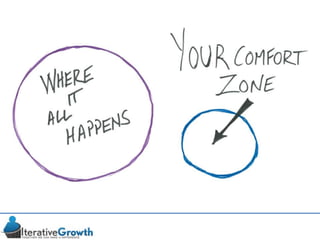
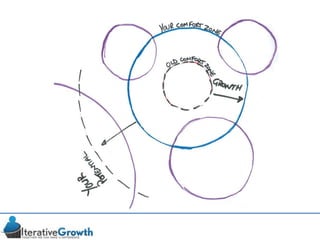
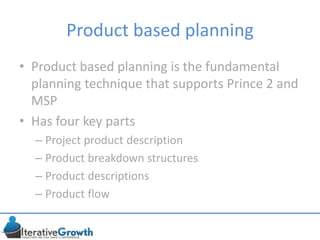
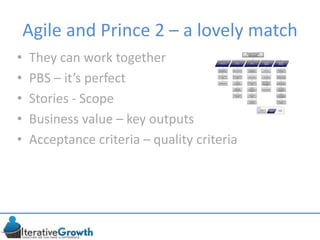
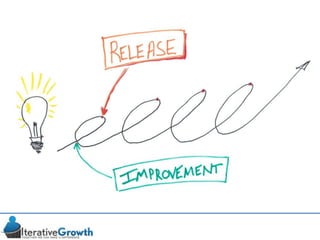
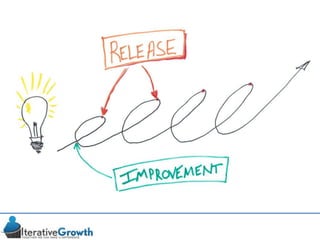
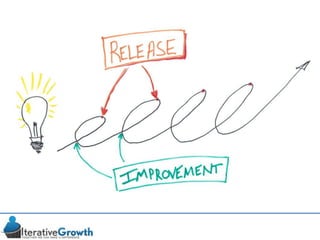
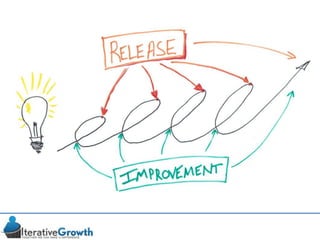
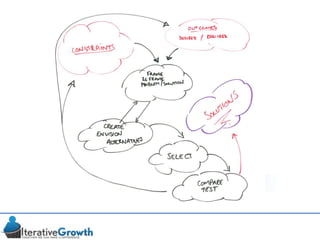
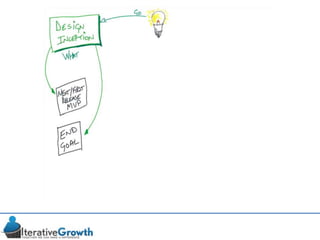
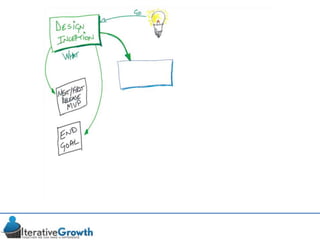
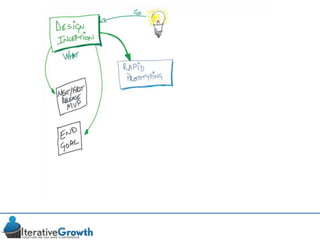
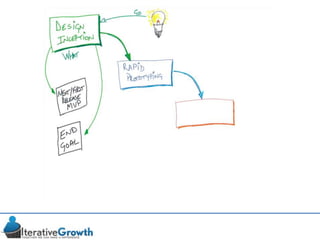
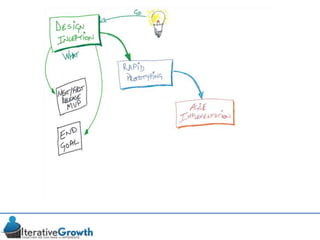
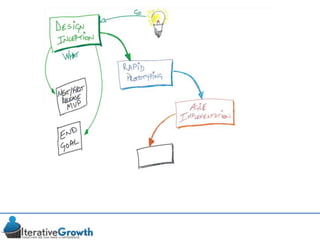
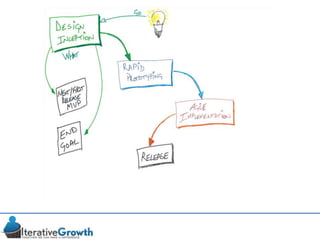
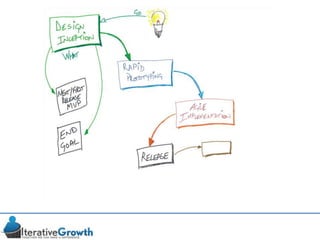
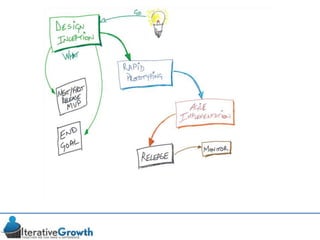
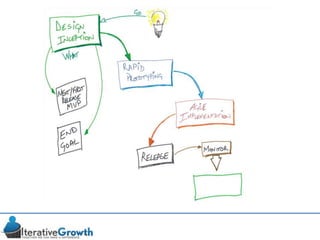
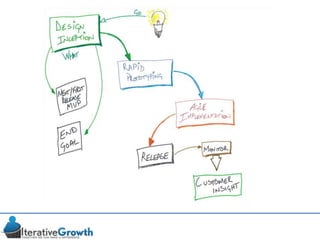
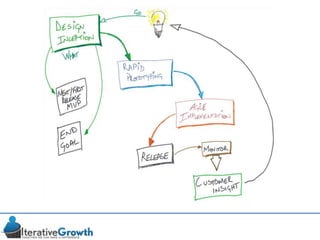
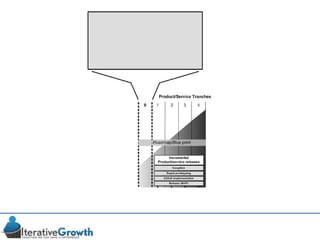
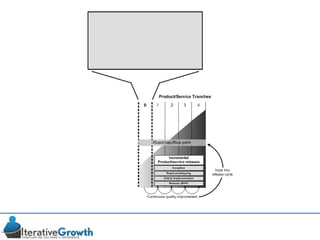
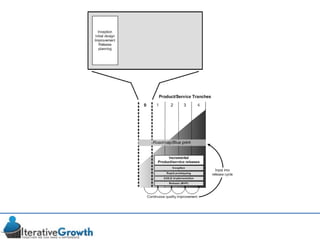
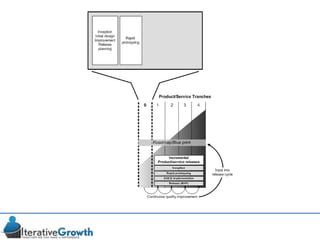
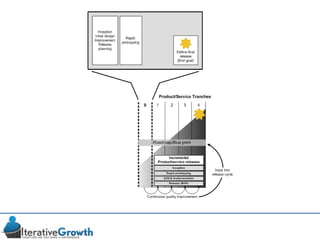
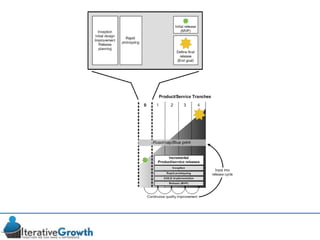
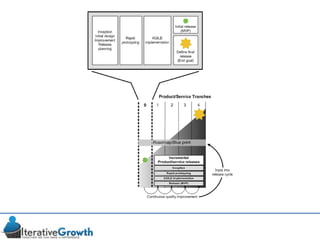
This document discusses an iterative approach to digital product development using agile principles. It advocates taking a product-based rather than project-based approach, with continuous quality improvement and refinement of the product over time based on feedback. Agile practices like having very structured but flexible processes, visual transparency, and failing fast are recommended. While agile has risks if not implemented properly, following principles like minimum viable products and iterative design allows products to be informed by measurement and to evolve as needed.