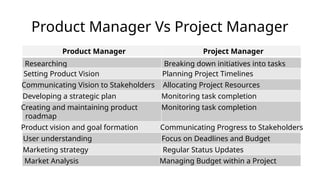
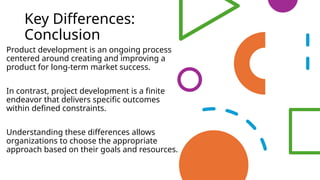
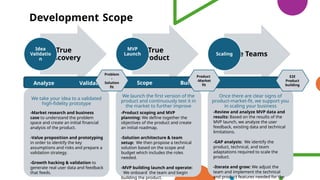
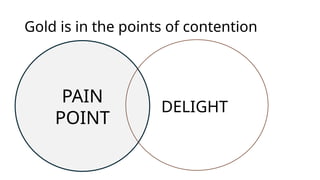
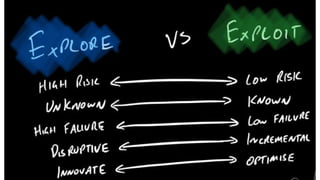
The document presents a session led by Peter Ward on the distinctions between Microsoft 365 product development and project development, focusing on their definitions, objectives, and methodologies. It emphasizes the ongoing nature of product development contrasted with the finite scope of projects, highlighting the importance of agile methodologies for adaptability and user-centric approaches. Key issues in product development include challenges such as scope creep and resource management, while benefits are noted in terms of collaboration, product quality, and flexibility.