An introduction to chemical equilibria
•Download as DOCX, PDF•
1 like•250 views
This document introduces the concept of chemical equilibrium through reversible reactions. It explains that in a closed system where a reversible reaction occurs, the reaction will reach a dynamic equilibrium where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. At this point, the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant, though the reaction continues at the molecular level. The term "position of equilibrium" refers to the distribution of substances between reactants and products at equilibrium. If conditions change in a way that alters the reaction rates, it shifts the position of equilibrium toward more products or reactants.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Recommended
Le chatelier principles in dynamic equilibrium reactions

It includes le-chatelier principle and how it affect the dynamic equilibrium reactions corresponds concentration ,pressure ,volume ,temperature change with an example.
Final Presentation Ideal Solution 2

The document analyzes deviations from ideality in a methanol-water solution through measurements of heat of mixing, volume of mixing, and partial pressures of mixing. The heat of mixing was exothermic and deviations increased near a 1:1 ratio. Volume upon mixing did not equal the sum of individual volumes. Partial pressures deviated from ideality due to increased vaporization from exothermic mixing. Modifications varying temperature and substituting isopropanol showed more ideal behavior at higher temperatures and with isopropanol.
States of matter

The document discusses the three states of matter - solids, liquids, and gases. It describes their characteristic properties at a microscopic level, including that particles in solids are locked in place, liquids flow freely but maintain a fixed volume, and gases spread freely and assume the shape of their container. It also discusses intermolecular and intramolecular forces, different types of intermolecular forces, gas laws, the kinetic molecular theory of gases, behavior of real gases, and properties of liquids.
Brief concepts of chemical equilibrium 

This document provides an overview of key concepts related to chemical equilibrium. It defines reversible reactions and explains that chemical equilibrium is reached when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, resulting in no further change in reactant and product concentrations over time. The document also discusses homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium, factors that affect equilibrium such as temperature, pressure, and concentration, Le Chatelier's principle, and examples of industrial processes that utilize chemical equilibrium concepts.
Third law of td from wikipedia

The document discusses the third law of thermodynamics in several paragraphs. It begins by stating the third law - that the entropy of a system at absolute zero is a well-defined constant. It then provides several alternative formulations of the third law. The document goes on to discuss the mathematical formulation and consequences of the third law, including that absolute zero cannot be reached in a finite number of steps and that specific heat, vapor pressure, latent heat of melting, and thermal expansion coefficient must approach zero as temperature approaches absolute zero.
Fugacity & fugacity coefficient

Introduction
Concepts of Fugacity
Effect of Temperature & pressure on Fugacity
Important relation of Fugacity Coefficient
Vapour Liquid Equilibrium for pure species
Fugacity & Fugacity coefficient: Species in solution
Reference
New chm 152 unit 2 power points sp13

The document discusses chemical equilibrium. It begins by defining chemical equilibrium as a dynamic state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, such that there is no net change in concentrations. It then discusses concepts such as the equilibrium constant K, reaction quotient Q, Le Chatelier's principle, and factors that affect equilibrium like concentration, pressure, temperature, and catalysts. In summary, (1) chemical equilibrium is a dynamic state with equal forward and reverse reaction rates, (2) the equilibrium constant K relates concentrations at equilibrium, and (3) systems at equilibrium will shift in response to changes to reduce stress and reestablish equilibrium.
Unit 5 Part 6 The Mole

The document discusses how chemists measure and count substances at the atomic level. It introduces the mole as the unit chemists use to count representative particles like atoms and molecules. The mole is based on Avogadro's number, which states that one mole of a substance contains 6.02 x 1023 representative particles. Examples are given for calculating the number of atoms or moles of a substance using its formula and Avogadro's number.
Recommended
Le chatelier principles in dynamic equilibrium reactions

It includes le-chatelier principle and how it affect the dynamic equilibrium reactions corresponds concentration ,pressure ,volume ,temperature change with an example.
Final Presentation Ideal Solution 2

The document analyzes deviations from ideality in a methanol-water solution through measurements of heat of mixing, volume of mixing, and partial pressures of mixing. The heat of mixing was exothermic and deviations increased near a 1:1 ratio. Volume upon mixing did not equal the sum of individual volumes. Partial pressures deviated from ideality due to increased vaporization from exothermic mixing. Modifications varying temperature and substituting isopropanol showed more ideal behavior at higher temperatures and with isopropanol.
States of matter

The document discusses the three states of matter - solids, liquids, and gases. It describes their characteristic properties at a microscopic level, including that particles in solids are locked in place, liquids flow freely but maintain a fixed volume, and gases spread freely and assume the shape of their container. It also discusses intermolecular and intramolecular forces, different types of intermolecular forces, gas laws, the kinetic molecular theory of gases, behavior of real gases, and properties of liquids.
Brief concepts of chemical equilibrium 

This document provides an overview of key concepts related to chemical equilibrium. It defines reversible reactions and explains that chemical equilibrium is reached when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, resulting in no further change in reactant and product concentrations over time. The document also discusses homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium, factors that affect equilibrium such as temperature, pressure, and concentration, Le Chatelier's principle, and examples of industrial processes that utilize chemical equilibrium concepts.
Third law of td from wikipedia

The document discusses the third law of thermodynamics in several paragraphs. It begins by stating the third law - that the entropy of a system at absolute zero is a well-defined constant. It then provides several alternative formulations of the third law. The document goes on to discuss the mathematical formulation and consequences of the third law, including that absolute zero cannot be reached in a finite number of steps and that specific heat, vapor pressure, latent heat of melting, and thermal expansion coefficient must approach zero as temperature approaches absolute zero.
Fugacity & fugacity coefficient

Introduction
Concepts of Fugacity
Effect of Temperature & pressure on Fugacity
Important relation of Fugacity Coefficient
Vapour Liquid Equilibrium for pure species
Fugacity & Fugacity coefficient: Species in solution
Reference
New chm 152 unit 2 power points sp13

The document discusses chemical equilibrium. It begins by defining chemical equilibrium as a dynamic state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, such that there is no net change in concentrations. It then discusses concepts such as the equilibrium constant K, reaction quotient Q, Le Chatelier's principle, and factors that affect equilibrium like concentration, pressure, temperature, and catalysts. In summary, (1) chemical equilibrium is a dynamic state with equal forward and reverse reaction rates, (2) the equilibrium constant K relates concentrations at equilibrium, and (3) systems at equilibrium will shift in response to changes to reduce stress and reestablish equilibrium.
Unit 5 Part 6 The Mole

The document discusses how chemists measure and count substances at the atomic level. It introduces the mole as the unit chemists use to count representative particles like atoms and molecules. The mole is based on Avogadro's number, which states that one mole of a substance contains 6.02 x 1023 representative particles. Examples are given for calculating the number of atoms or moles of a substance using its formula and Avogadro's number.
Equilibrium cheat sheet

This document provides an overview of key concepts in equilibrium chemistry including reversible reactions, equilibrium constants, Le Chatelier's principle, and techniques for solving equilibrium problems using ICE charts and calculating reaction quotients. It defines equilibrium as a state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. ICE charts are introduced as a method to organize information about initial concentrations, changes, and equilibrium concentrations in solving equilibrium problems. The document also discusses writing and using equilibrium constant expressions, solubility products, and reaction quotients to determine if a system is at equilibrium or not.
Unit 5 Part 7 Moles Grams And Liters

This document discusses several key concepts related to moles, grams, and liters in chemistry:
1) The gram atomic mass is the mass of one mole of an element in grams, and the gram formula mass is the mass of one mole of a compound by adding the gram atomic masses of its elements.
2) Conversions between moles and grams use the gram atomic/formula mass - moles are multiplied by mass to get grams, and grams are divided by mass to get moles.
3) One mole of any gas occupies 22.4 liters at standard temperature and pressure (0°C and 1 atmosphere). Volume can be converted to moles by dividing liters by 22.
Chemical equilibrium

This document discusses chemical equilibrium, which occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction in a closed system. It defines the equilibrium constant (Kc) and explains that a high Kc value means a high product yield, while a low Kc means a low product yield. It also describes Le Chatelier's Principle, which states that applying stress to a system in equilibrium will cause the equilibrium to shift to reduce the effect of the stress, and discusses how temperature, concentration, and pressure influence the position and value of equilibrium constants.
الكيمياء الحركية Kinetic Chemistry

الكيمياء الحركية
Kinetic Chemistry
Chemical kinetics
حركية التفاعل أو الحركية الكيميائية هو العلم الذي يهتم ويختص بدراسة معدل التغير في سرعة التفاعلات الكيميائية والعوامل المؤثرة فيها مثل الضغط ودرجة الحرارة والتركيز وطبيعة العوامل المتفاعلة والعوامل الحفازة أو المثبطة، كما أنها تقوم بوضع نماذج رياضياتية التي توصف خواص التفاعلات الكيميائية.
Equilibrium

The document discusses chemical equilibrium and Le Chatelier's principle. It explains that chemical equilibrium occurs when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, and the concentrations of reactants and products remain unchanged. Le Chatelier's principle states that if a system at equilibrium experiences a change in concentration, temperature, or pressure, the equilibrium will shift to counteract the applied stress. The document provides examples of how changing temperature, concentration, or pressure would cause the equilibrium of a reaction to shift left or right.
Le Chatelier's Principle 

Le Chatelier's Principle states that if conditions of a system at equilibrium are changed, the equilibrium will shift to counteract the imposed change. Specifically:
- Increasing the concentration of a reactant will shift the equilibrium towards products.
- Decreasing the concentration of a reactant will shift equilibrium towards reactants.
- Increasing pressure of a gaseous reaction will shift equilibrium towards the side with fewer moles of gas.
- Increasing temperature of an endothermic reaction shifts equilibrium towards reactants, while an exothermic reaction shifts towards products.
Chem 2 - Third Law of Thermodynamics and Standard Molar Entropy V

This document discusses the Third Law of Thermodynamics and how it relates to standard molar entropy (S°). The Third Law states that the entropy of a substance at 0 K is zero, meaning it is in a perfectly ordered state with one microstate. This allows the absolute entropies and standard molar entropies (S°) of substances to be calculated. S° values are provided in tables and can be used to calculate the entropy change (ΔS°) of chemical reactions based on the standard molar entropies of the reactants and products.
Chapter 1 some basic concepts of chemistry class 11 UPDATED PPT

The document summarizes several important concepts and laws in chemistry:
1) The law of conservation of mass states that matter is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions.
2) The law of definite proportions states that a chemical compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions by mass.
3) Gay-Lussac's law of gaseous volumes describes how gases combine or are produced in simple volume ratios in chemical reactions at the same temperature and pressure.
4) Avogadro's law states that equal volumes of gases under the same conditions contain an equal number of molecules.
Rates ofreactionandequilibrium cheat sheet

This document summarizes key concepts relating to reaction rates, equilibrium, and factors that affect them. It defines kinetics, reaction rates, and activation energy. It explains collision theory, reaction coordinate diagrams, and how equilibrium is established over time as the forward and reverse reactions proceed. It also defines equilibrium constants, reaction quotients, and Le Chatelier's principle. It lists factors that affect reaction rates like surface area, concentration, and temperature. Finally, it summarizes how changing conditions like concentration, temperature, and pressure can shift the position of equilibrium according to Le Chatelier's principle.
CHM023L - B06 Final Report Group 3 Experiment 3 (Chemical Equilibrium: Le Cha...

This document describes the results of 5 experiments on chemical equilibriums. In Experiment 1, adding KSCN or FeCl3 shifted the iron complex ion equilibrium forward by making the solution darker red. Adding heat shifted it backward and making it lighter, indicating the reaction is exothermic. Experiment 2 examined the chromate/dichromate ion equilibrium, finding that acid and base addition shifted the equilibrium in opposite directions. Experiment 3 showed that adding ammonia or acid shifted the copper complex ion equilibrium left or right, respectively. Experiment 4 showed that adding water to a saturated NaCl solution shifted the equilibrium left. Experiment 5 showed that adding ions shifted the ammonium hydroxide or acetic acid equilibriums left.
Chapter 5 states of matter class 11 cbse

This document discusses intermolecular forces and the behavior of gases. It describes three types of intermolecular forces - London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and dipole-induced dipole forces. It also explains the gas laws of Boyle, Charles, Gay-Lussac, Avogadro, Dalton and the ideal gas equation. Real gases deviate from ideal behavior at high pressures due to molecular interactions. The van der Waals equation accounts for these interactions through correction terms.
Chem 2 - Chemical Equilibrium VII: The Reaction Quotient Q for Non-equilbrium...

This document discusses the reaction quotient Q and how it can be used to determine if a chemical reaction is at equilibrium or not. It explains that Q is calculated the same way as the equilibrium constant K, but Q can be calculated for any reaction conditions, while K only applies at equilibrium. If Q equals K, the reaction is at equilibrium. If Q is greater than K, there are too many products and the reaction will shift towards the reactants. If Q is less than K, there are too many reactants and the reaction will shift towards the products. An example problem demonstrates calculating Q and comparing it to K to determine the direction a reaction needs to shift.
Lewis-Randall Rule ,Excess property,Excess Gibbs Energy &Activity Coefficient 

Detail Explanation of Lewis-Randall Rule ,Excess property,Excess Gibbs Energy &Activity Coefficient and u will find some expressions and relations
le chatelier's principle

Le Chatelier's Principle describes how chemical equilibriums respond to changes in conditions. When volume decreases, pressure increases, so the equilibrium shifts to reduce pressure by producing more products from fewer reactants. When temperature increases, the equilibrium shifts to absorb the extra heat by moving left to favor the endothermic reaction of reactants forming products.
G11 s lequilibria

The document discusses the position of equilibrium in chemical reactions. It states that if a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed, the position of equilibrium will move to counteract the change according to Le Chatelier's principle. Specifically, it provides examples of how the equilibrium position would change if ammonia, hydrogen, or nitrogen were removed from the ammonia synthesis reaction, or if pressure or temperature were increased. It also notes that while catalysts speed up the rate of the reaction, they do not change the equilibrium position.
Ch 06 chemical composition

This document discusses methods for determining the chemical composition of compounds including:
1) Counting atoms by converting between grams and moles using molar masses from the periodic table.
2) Calculating the mass of molecules from the masses of their constituent atoms.
3) Using molecular formulas as conversion factors between moles of atoms and molecules or grams of atoms and molecules.
Class xi chemistry (chapter 1) converted

Chemistry is the study of matter and its composition, structure, properties, and interactions. [1] Some key concepts introduced in the document include the classification of matter as elements, compounds, or mixtures based on its chemical and physical properties. [2] Five important laws governing chemical combinations are also outlined: the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite proportions, the law of multiple proportions, Gay-Lussac's law of gaseous volumes, and Avogadro's law. [3]
Industrial preparation of ammonia 

The Haber process produces ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen gases under high pressure, temperature, and in the presence of an iron catalyst. Temperature and pressure conditions are carefully balanced - high pressure favors the reaction but too high a temperature slows it down. The equilibrium position is influenced by Le Chatelier's principle - increasing pressure favors the side with fewer moles of gas, lowering temperature favors the exothermic forward reaction. Recycling unreacted gases and optimizing conditions allows high ammonia yields from this industrially important process.
Industrial preparation of ammonia 1

The Haber process produces ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen gases under high pressure, temperature, and in the presence of an iron catalyst. Temperature and pressure conditions are carefully balanced - high enough for a reasonable reaction rate but not so high that most gases remain unreacted. The process involves continually recycling unreacted gases through the reactor until nearly full conversion to ammonia is achieved. Le Chatelier's principle and considerations of reaction rates and equilibrium guide the optimization of temperature, pressure, and proportions of gases for maximum economical ammonia production.
Chemical Equilibrium

This document contains information about chemical equilibrium from Ranada Prasad Shaha University student Swarup Saha. It defines chemical equilibrium as a state where forward and reverse reactions occur simultaneously at the same rate. It describes characteristics of chemical equilibrium such as stability with constant conditions, attainment through catalysis, and dynamic rather than static nature. The document also covers the law of mass action and Le Châtelier's principle.
Chemical-Equilibrium-Class-10-notes.pdf

The document discusses chemical equilibrium, which occurs when a reversible reaction reaches a state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. It provides examples of reversible reactions using double-headed arrows and explains that at equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. The document also discusses how equilibrium can be determined through techniques like titration and spectroscopy, and how the equilibrium constant Kc is calculated based on the concentrations of reactants and products in the balanced chemical equation.
Equilibrium in Physical Processes Class 11 Free Study Material PDF

Unlock the intricacies of Equilibrium in Physical Processes Class 11 Chemistry study notes. Delve into phase transitions, solubility equilibria, and acid-base ionization, mastering key concepts like Le Chatelier's Principle and equilibrium constants. Build a solid foundation for understanding and applying these principles in real-world scenarios.
For more information, visit- www.vavaclasses.com
More Related Content
What's hot
Equilibrium cheat sheet

This document provides an overview of key concepts in equilibrium chemistry including reversible reactions, equilibrium constants, Le Chatelier's principle, and techniques for solving equilibrium problems using ICE charts and calculating reaction quotients. It defines equilibrium as a state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. ICE charts are introduced as a method to organize information about initial concentrations, changes, and equilibrium concentrations in solving equilibrium problems. The document also discusses writing and using equilibrium constant expressions, solubility products, and reaction quotients to determine if a system is at equilibrium or not.
Unit 5 Part 7 Moles Grams And Liters

This document discusses several key concepts related to moles, grams, and liters in chemistry:
1) The gram atomic mass is the mass of one mole of an element in grams, and the gram formula mass is the mass of one mole of a compound by adding the gram atomic masses of its elements.
2) Conversions between moles and grams use the gram atomic/formula mass - moles are multiplied by mass to get grams, and grams are divided by mass to get moles.
3) One mole of any gas occupies 22.4 liters at standard temperature and pressure (0°C and 1 atmosphere). Volume can be converted to moles by dividing liters by 22.
Chemical equilibrium

This document discusses chemical equilibrium, which occurs when the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction in a closed system. It defines the equilibrium constant (Kc) and explains that a high Kc value means a high product yield, while a low Kc means a low product yield. It also describes Le Chatelier's Principle, which states that applying stress to a system in equilibrium will cause the equilibrium to shift to reduce the effect of the stress, and discusses how temperature, concentration, and pressure influence the position and value of equilibrium constants.
الكيمياء الحركية Kinetic Chemistry

الكيمياء الحركية
Kinetic Chemistry
Chemical kinetics
حركية التفاعل أو الحركية الكيميائية هو العلم الذي يهتم ويختص بدراسة معدل التغير في سرعة التفاعلات الكيميائية والعوامل المؤثرة فيها مثل الضغط ودرجة الحرارة والتركيز وطبيعة العوامل المتفاعلة والعوامل الحفازة أو المثبطة، كما أنها تقوم بوضع نماذج رياضياتية التي توصف خواص التفاعلات الكيميائية.
Equilibrium

The document discusses chemical equilibrium and Le Chatelier's principle. It explains that chemical equilibrium occurs when the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, and the concentrations of reactants and products remain unchanged. Le Chatelier's principle states that if a system at equilibrium experiences a change in concentration, temperature, or pressure, the equilibrium will shift to counteract the applied stress. The document provides examples of how changing temperature, concentration, or pressure would cause the equilibrium of a reaction to shift left or right.
Le Chatelier's Principle 

Le Chatelier's Principle states that if conditions of a system at equilibrium are changed, the equilibrium will shift to counteract the imposed change. Specifically:
- Increasing the concentration of a reactant will shift the equilibrium towards products.
- Decreasing the concentration of a reactant will shift equilibrium towards reactants.
- Increasing pressure of a gaseous reaction will shift equilibrium towards the side with fewer moles of gas.
- Increasing temperature of an endothermic reaction shifts equilibrium towards reactants, while an exothermic reaction shifts towards products.
Chem 2 - Third Law of Thermodynamics and Standard Molar Entropy V

This document discusses the Third Law of Thermodynamics and how it relates to standard molar entropy (S°). The Third Law states that the entropy of a substance at 0 K is zero, meaning it is in a perfectly ordered state with one microstate. This allows the absolute entropies and standard molar entropies (S°) of substances to be calculated. S° values are provided in tables and can be used to calculate the entropy change (ΔS°) of chemical reactions based on the standard molar entropies of the reactants and products.
Chapter 1 some basic concepts of chemistry class 11 UPDATED PPT

The document summarizes several important concepts and laws in chemistry:
1) The law of conservation of mass states that matter is neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions.
2) The law of definite proportions states that a chemical compound always contains the same elements in the same proportions by mass.
3) Gay-Lussac's law of gaseous volumes describes how gases combine or are produced in simple volume ratios in chemical reactions at the same temperature and pressure.
4) Avogadro's law states that equal volumes of gases under the same conditions contain an equal number of molecules.
Rates ofreactionandequilibrium cheat sheet

This document summarizes key concepts relating to reaction rates, equilibrium, and factors that affect them. It defines kinetics, reaction rates, and activation energy. It explains collision theory, reaction coordinate diagrams, and how equilibrium is established over time as the forward and reverse reactions proceed. It also defines equilibrium constants, reaction quotients, and Le Chatelier's principle. It lists factors that affect reaction rates like surface area, concentration, and temperature. Finally, it summarizes how changing conditions like concentration, temperature, and pressure can shift the position of equilibrium according to Le Chatelier's principle.
CHM023L - B06 Final Report Group 3 Experiment 3 (Chemical Equilibrium: Le Cha...

This document describes the results of 5 experiments on chemical equilibriums. In Experiment 1, adding KSCN or FeCl3 shifted the iron complex ion equilibrium forward by making the solution darker red. Adding heat shifted it backward and making it lighter, indicating the reaction is exothermic. Experiment 2 examined the chromate/dichromate ion equilibrium, finding that acid and base addition shifted the equilibrium in opposite directions. Experiment 3 showed that adding ammonia or acid shifted the copper complex ion equilibrium left or right, respectively. Experiment 4 showed that adding water to a saturated NaCl solution shifted the equilibrium left. Experiment 5 showed that adding ions shifted the ammonium hydroxide or acetic acid equilibriums left.
Chapter 5 states of matter class 11 cbse

This document discusses intermolecular forces and the behavior of gases. It describes three types of intermolecular forces - London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and dipole-induced dipole forces. It also explains the gas laws of Boyle, Charles, Gay-Lussac, Avogadro, Dalton and the ideal gas equation. Real gases deviate from ideal behavior at high pressures due to molecular interactions. The van der Waals equation accounts for these interactions through correction terms.
Chem 2 - Chemical Equilibrium VII: The Reaction Quotient Q for Non-equilbrium...

This document discusses the reaction quotient Q and how it can be used to determine if a chemical reaction is at equilibrium or not. It explains that Q is calculated the same way as the equilibrium constant K, but Q can be calculated for any reaction conditions, while K only applies at equilibrium. If Q equals K, the reaction is at equilibrium. If Q is greater than K, there are too many products and the reaction will shift towards the reactants. If Q is less than K, there are too many reactants and the reaction will shift towards the products. An example problem demonstrates calculating Q and comparing it to K to determine the direction a reaction needs to shift.
Lewis-Randall Rule ,Excess property,Excess Gibbs Energy &Activity Coefficient 

Detail Explanation of Lewis-Randall Rule ,Excess property,Excess Gibbs Energy &Activity Coefficient and u will find some expressions and relations
le chatelier's principle

Le Chatelier's Principle describes how chemical equilibriums respond to changes in conditions. When volume decreases, pressure increases, so the equilibrium shifts to reduce pressure by producing more products from fewer reactants. When temperature increases, the equilibrium shifts to absorb the extra heat by moving left to favor the endothermic reaction of reactants forming products.
G11 s lequilibria

The document discusses the position of equilibrium in chemical reactions. It states that if a dynamic equilibrium is disturbed, the position of equilibrium will move to counteract the change according to Le Chatelier's principle. Specifically, it provides examples of how the equilibrium position would change if ammonia, hydrogen, or nitrogen were removed from the ammonia synthesis reaction, or if pressure or temperature were increased. It also notes that while catalysts speed up the rate of the reaction, they do not change the equilibrium position.
Ch 06 chemical composition

This document discusses methods for determining the chemical composition of compounds including:
1) Counting atoms by converting between grams and moles using molar masses from the periodic table.
2) Calculating the mass of molecules from the masses of their constituent atoms.
3) Using molecular formulas as conversion factors between moles of atoms and molecules or grams of atoms and molecules.
Class xi chemistry (chapter 1) converted

Chemistry is the study of matter and its composition, structure, properties, and interactions. [1] Some key concepts introduced in the document include the classification of matter as elements, compounds, or mixtures based on its chemical and physical properties. [2] Five important laws governing chemical combinations are also outlined: the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite proportions, the law of multiple proportions, Gay-Lussac's law of gaseous volumes, and Avogadro's law. [3]
What's hot (17)
Chem 2 - Third Law of Thermodynamics and Standard Molar Entropy V

Chem 2 - Third Law of Thermodynamics and Standard Molar Entropy V
Chapter 1 some basic concepts of chemistry class 11 UPDATED PPT

Chapter 1 some basic concepts of chemistry class 11 UPDATED PPT
CHM023L - B06 Final Report Group 3 Experiment 3 (Chemical Equilibrium: Le Cha...

CHM023L - B06 Final Report Group 3 Experiment 3 (Chemical Equilibrium: Le Cha...
Chem 2 - Chemical Equilibrium VII: The Reaction Quotient Q for Non-equilbrium...

Chem 2 - Chemical Equilibrium VII: The Reaction Quotient Q for Non-equilbrium...
Lewis-Randall Rule ,Excess property,Excess Gibbs Energy &Activity Coefficient 

Lewis-Randall Rule ,Excess property,Excess Gibbs Energy &Activity Coefficient
Similar to An introduction to chemical equilibria
Industrial preparation of ammonia 

The Haber process produces ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen gases under high pressure, temperature, and in the presence of an iron catalyst. Temperature and pressure conditions are carefully balanced - high pressure favors the reaction but too high a temperature slows it down. The equilibrium position is influenced by Le Chatelier's principle - increasing pressure favors the side with fewer moles of gas, lowering temperature favors the exothermic forward reaction. Recycling unreacted gases and optimizing conditions allows high ammonia yields from this industrially important process.
Industrial preparation of ammonia 1

The Haber process produces ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen gases under high pressure, temperature, and in the presence of an iron catalyst. Temperature and pressure conditions are carefully balanced - high enough for a reasonable reaction rate but not so high that most gases remain unreacted. The process involves continually recycling unreacted gases through the reactor until nearly full conversion to ammonia is achieved. Le Chatelier's principle and considerations of reaction rates and equilibrium guide the optimization of temperature, pressure, and proportions of gases for maximum economical ammonia production.
Chemical Equilibrium

This document contains information about chemical equilibrium from Ranada Prasad Shaha University student Swarup Saha. It defines chemical equilibrium as a state where forward and reverse reactions occur simultaneously at the same rate. It describes characteristics of chemical equilibrium such as stability with constant conditions, attainment through catalysis, and dynamic rather than static nature. The document also covers the law of mass action and Le Châtelier's principle.
Chemical-Equilibrium-Class-10-notes.pdf

The document discusses chemical equilibrium, which occurs when a reversible reaction reaches a state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. It provides examples of reversible reactions using double-headed arrows and explains that at equilibrium, the concentrations of reactants and products remain constant. The document also discusses how equilibrium can be determined through techniques like titration and spectroscopy, and how the equilibrium constant Kc is calculated based on the concentrations of reactants and products in the balanced chemical equation.
Equilibrium in Physical Processes Class 11 Free Study Material PDF

Unlock the intricacies of Equilibrium in Physical Processes Class 11 Chemistry study notes. Delve into phase transitions, solubility equilibria, and acid-base ionization, mastering key concepts like Le Chatelier's Principle and equilibrium constants. Build a solid foundation for understanding and applying these principles in real-world scenarios.
For more information, visit- www.vavaclasses.com
Core & Extension - Chemical Rxns - Reversible Rxns I.pptx

1. The document discusses reversible chemical reactions and chemical equilibrium.
2. It explains that some reactions can go in both the forward and reverse directions under certain conditions, and that at equilibrium the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal.
3. The document describes how changing conditions like temperature, pressure, or concentration can shift the equilibrium position by favoring the endothermic or exothermic direction.
Chemical-Equilibrium-Class-10-important-questions.pdf

The document contains questions and answers related to chemical equilibrium. It defines terms like active mass, law of mass action, irreversible and reversible reactions, and chemical equilibrium. It also describes Le Chatelier's principle, stating that changing concentration, temperature, or pressure causes the equilibrium of a reaction to shift in the direction that counteracts the applied stress. Examples are provided to explain how increasing or decreasing temperature, pressure, or concentration affects the yield of products in endothermic and exothermic reactions.
Equilibrium class 11 cbse NCERT

This document discusses chemical equilibriums, including:
1) Equilibriums can be physical (phase changes) or chemical (reactions). At equilibrium, the forward and reverse rates are equal and concentrations/properties remain constant.
2) Equilibrium constants (K) describe the position of equilibrium. Factors like concentration, temperature, and catalysts affect the equilibrium position according to Le Chatelier's principle.
3) Acid-base equilibriums involve acid/base ionization constants (Ka/Kb). Strong acids fully ionize in water while weak acids only partially ionize. The strength of an acid/base depends on how easily it donates/accepts protons.
ch 7 equilibrium 1.pdf

English chapter we are going to discuss about the reduction in the oxidation their heat evolution changes occurrence and about their reducing agent and oxidization
equilibrium-160117190305.pdf

(1) The document discusses various types of equilibriums including physical and chemical equilibriums. It explains concepts such as homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibriums, law of chemical equilibrium, and factors that affect equilibrium.
(2) Key aspects of acids and bases are also summarized such as Arrhenius, Brønsted-Lowry, and Lewis theories of acids and bases. Ionization of acids and bases is explained through ionization constants.
(3) Relationships between ionization constants Ka and Kb and calculations of pH for weak acids and bases are also covered in the document.
Equilibrium-class 12 chemistry

Equilibrium in physical and chemical processes, dynamic nature of equilibrium, law of mass
action, equilibrium constant, factors affecting equilibrium ‐ Le Chatelier's principle, ionic
equilibrium‐ ionization of acids and bases, strong and weak electrolytes, degree of ionization,
ionization of poly basic acids, acid strength, concept of pH, buffer solution, solubility product,
common ion effect , Arrhenius concept, brownsted lowry concept, acidic buffer, basic buffer, dissociation constant, equilibrium constant, see saw game, equilibrium in solid, liquid and gaseous state, solubility product.
B.1 Collision Theory.pptx

The document discusses collision theory, which states that for a chemical reaction to occur, reactant particles must collide with sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy barrier. It explains that temperature, concentration, surface area, and catalysts can affect the rate of reaction by increasing the frequency or effectiveness of collisions between reactants. Catalysts specifically provide an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy.
New chm-152-unit-2-power-points-sp13-140227172047-phpapp01

This document discusses the concept of chemical equilibrium. Some key points:
1. Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, so concentrations of reactants and products no longer change.
2. The equilibrium constant, Kc, relates concentrations of products and reactants at equilibrium. When the reaction quotient, Q, equals Kc the system is at equilibrium.
3. Le Chatelier's principle states that if a system at equilibrium experiences a change, it will shift in a way to counteract the change and reestablish equilibrium. Changes in concentration, pressure, and temperature can disturb equilibrium.
3. Increasing temperature favors the endothermic reaction, while
Chemical reactions and equations class 10

The document discusses various physical and chemical changes that occur in everyday life. It provides examples of physical changes such as changes in state from liquid to gas, and chemical changes where new substances are formed. The key differences between physical and chemical changes are explained, with chemical changes resulting in the formation of new substances with different properties compared to the original reactants. Specific chemical reactions and observations that indicate chemical changes, such as gas evolution, temperature change, and color change, are also outlined.
Chemistryppt chemical equilibrium

The document discusses chemical equilibrium. It defines equilibrium as a state where the rates of the forward and reverse reactions of a chemical process are equal, resulting in no net change in the concentrations or properties of the system. It provides examples of physical and chemical equilibrium processes. It describes key characteristics of equilibrium like dynamic nature, constant concentrations and temperatures, and the relationship between reaction rates and equilibrium constants.
B.1 Collision Theory PHYSICAL SCIENCE.pptx

The document discusses collision theory, which explains that for a chemical reaction to occur, reactant particles must collide with sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy barrier. It explains how factors like concentration, temperature, surface area, and catalysts affect the rate of reaction by influencing the frequency and success of collisions between reactants. Catalysts specifically provide an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy.
200910ch3b0handout.ppt

This document provides an overview of a university course on organic synthesis. It covers topics like pericyclic reactions, electrocyclizations, sigmatropic rearrangements, and the Woodward-Hoffmann rules for predicting stereochemistry. Examples are given of reaction mechanisms and how the rules explain stereochemical outcomes. The document also lists additional reading materials and notes that attending all lectures is essential since not all material is covered in the handout.
Chemical Equilibrium-8.pptx

This document outlines key concepts about chemical equilibria, including:
1. Reversible reactions can reach a state of dynamic equilibrium where the forward and reverse reaction rates are equal.
2. The position of equilibrium can shift if concentration, temperature, or pressure changes, according to Le Chatelier's principle which states the equilibrium shifts to minimize the effect of the change.
3. Increasing the concentration of reactants shifts the equilibrium right, while increasing products shifts it left. Temperature and pressure changes also shift the equilibrium according to whether reactions are endothermic/exothermic or have more gas molecules on one side.
Exothermic Reactions

This document discusses chemical reactions and different types of reactions. It begins by defining a chemical reaction as a process where the atoms in reactants are rearranged to form new substances known as products. It describes the key components of a chemical reaction as reactants, products, and activation energy. It then provides examples of the six main types of chemical reactions: synthesis, combustion, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and acid-base reactions. It explains the basic mechanisms and components of each type of reaction.
Similar to An introduction to chemical equilibria (19)
Equilibrium in Physical Processes Class 11 Free Study Material PDF

Equilibrium in Physical Processes Class 11 Free Study Material PDF
Core & Extension - Chemical Rxns - Reversible Rxns I.pptx

Core & Extension - Chemical Rxns - Reversible Rxns I.pptx
Chemical-Equilibrium-Class-10-important-questions.pdf

Chemical-Equilibrium-Class-10-important-questions.pdf
New chm-152-unit-2-power-points-sp13-140227172047-phpapp01

New chm-152-unit-2-power-points-sp13-140227172047-phpapp01
More from ashok koori
Carcass charcteristics of different meat anima

This document summarizes the carcass characteristics of different meat animals. It describes the typical age at slaughter, color of meat, carcass yield, bone percentage, and meat yield for common meats including cattle, buffalo, sheep, goat, pig, poultry, rabbit, and deer. For each type of meat, key details are provided on color, fat content, texture, and other distinguishing qualities.
Indian standards regulations of food safety

The document discusses several Indian regulations and standards related to food safety. It describes the objectives and functions of the Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI), which regulates and sets standards for food in India. It also discusses standards set by the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) for microbiological limits in foods like milk and meat. Other acts mentioned include the Agricultural Produce Grading and Marketing Act, Meat Food Products Order, Milk and Milk Products Order, and the Prevention of Food Adulteration Act.
Lymphatic organs of body

Lymphatic organs of body
• Lymphoid organs are the organs, in which lymphocytes can differentiate and proliferate.
• They are part of lymphatic system.
• The lymphatic system is part of circulatory system and a vital part of the immune system, comprising a network of lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph (from Latin, lympha meaning "water" directionally towards the heart.
• Unlike the cardiovascular system, the lymphatic system is not a closed system.
• HISTORY –
• Hippocrates and Aristotle described lymph as white fluid.
• Gasparo aselli an Italian anatomist discovered lymphatic vessels in 1622.
• Van hook in 1652 demonstrated the presence of cisterna chyli and thoracic duct in humans.
• William hunter in the late 18th century was the first to describe the functions of lymphatic system.
• Olof Rudbeck of Swedish university described that lymphatic system constitute a circulatory system separate from blood circulation and this fact was accepted by Royal society of London.
Adrenalin gland 

Adrenal gland
The paired adrenal glands lie against roof of the abdomen near the thoracolumbar junction .They are retroperitoneal and usually located craniomedial to the corresponding kidney (more directly medial in the horse ).They are closely connected with in aorta on the left ,caudal vena cava on the right
Although generally elongated ,the glands are often asymmetrical and quite irregular ,It is difficult to specify their size since this appears to be influenced by several factors , they are relatively larger in wild animal than in related domestic forms ,in juvenile than in adult individuals .and in pregnant and lactating females than in those reproductively inactive .
Adrenal glands are firm ,solid bodies, that fractured surface expose the division of the interior in to an outer cortex and inner medulla ,The cortex is mesodermal and produces mineralocorticoids hormone.
The medulla is a ectodermal origin. And produces epinephrine and non epinephrine .
Digestive system ashok

digestive system diagrammatic representation by Dr.Ashok Koori which including mouth parts about
lips
palate - there are two types
1).Shoft palate
2) hard palate
hard palate is formed by maxilla,pre maxilla and pallatie bone
cheek
tooth
salivary glands
there are the types (Usually) of salivary glands present in mouth which are
1) Perotid salivary gland
2)sublingual Salivary gland
and third is sub maxillary salivary gland
-Pharynx --there is divided into 3 part
1) Nesopharynx
2)Oropharynx
3) Leryngopharynx
-Stomach
Small Intestine
Large Intestine
Rectum and anus
Assesory glands are pancrease salivary gland liver
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Compose By Dr

This document summarizes the key components and functions of the human digestive system. It outlines the major structures of the alimentary canal including the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anal canal. It also describes the major digestive glands that include the salivary glands, gastric gland, intestinal gland, liver and gallbladder, and pancreas. Functions of specific structures like the lips, teeth, tongue, and salivary glands in the mouth are highlighted.
Handbook of-good-dairy-husbandry-practices

This section discusses the importance of properly inducting newly purchased animals into the herd to prevent disease transmission. It recommends quarantining new animals separately for 3 weeks, performing deworming, vaccinations, and disease testing during this period. Key tests include mastitis screening and testing for Brucellosis, TB, and Johne's disease. New animals should only be introduced if negative on all tests, and strict biosecurity measures like attending quarantined animals last and cleaning/disinfecting between groups should be followed. Proper purchasing, transportation, and quarantine practices are essential to maintain herd health.
Document

This textbook on Organic Chemistry was prepared for teaching B.Sc students in India according to the curriculum approved by the Central Board of Secondary Education. The book is also suitable for students of IIT and AIIMS and provides various methods for exam preparation. The authors are Dr. Ashok K. Koor, from the College of Veterinary Science in MHOW, Indore, India, who can be contacted by email or phone for further details.
New Micros

Success requires actively pursuing your goals rather than passively waiting for opportunities. While achieving success may seem impossible, maintaining a positive mindset that focuses on what is possible can help you overcome challenges and achieve your ambitions. Remain determined and do not give up on your dreams, as hard work and perseverance are necessary to transform "impossible" into reality.
powepoint 313

The document provides information about laboratory mice and rats. It describes their key physical characteristics including small size and high fecundity for mice and larger size for rats. It also outlines their taxonomy, common uses in research, physiological norms and development stages, breeding cycles, housing and identification. Common diseases and euthanasia methods are also mentioned.
More from ashok koori (10)
Recently uploaded
Connect to Grow: The power of building networks

In the intricate tapestry of life, connections serve as the vibrant threads that weave together opportunities, experiences, and growth. Whether in personal or professional spheres, the ability to forge meaningful connections opens doors to a multitude of possibilities, propelling individuals toward success and fulfillment.
Eirini is an HR professional with strong passion for technology and semiconductors industry in particular. She started her career as a software recruiter in 2012, and developed an interest for business development, talent enablement and innovation which later got her setting up the concept of Software Community Management in ASML, and to Developer Relations today. She holds a bachelor degree in Lifelong Learning and an MBA specialised in Strategic Human Resources Management. She is a world citizen, having grown up in Greece, she studied and kickstarted her career in The Netherlands and can currently be found in Santa Clara, CA.
Community Skills Building Workshop | PMI Silver Spring Chapter | June 12, 2024

Community Skills Building Workshop | PMI Silver Spring Chapter | June 12, 2024Hector Del Castillo, CPM, CPMM
We recently hosted the much-anticipated Community Skill Builders Workshop during our June online meeting. This event was a culmination of six months of listening to your feedback and crafting solutions to better support your PMI journey. Here’s a look back at what happened and the exciting developments that emerged from our collaborative efforts.
A Gathering of Minds
We were thrilled to see a diverse group of attendees, including local certified PMI trainers and both new and experienced members eager to contribute their perspectives. The workshop was structured into three dynamic discussion sessions, each led by our dedicated membership advocates.
Key Takeaways and Future Directions
The insights and feedback gathered from these discussions were invaluable. Here are some of the key takeaways and the steps we are taking to address them:
• Enhanced Resource Accessibility: We are working on a new, user-friendly resource page that will make it easier for members to access training materials and real-world application guides.
• Structured Mentorship Program: Plans are underway to launch a mentorship program that will connect members with experienced professionals for guidance and support.
• Increased Networking Opportunities: Expect to see more frequent and varied networking events, both virtual and in-person, to help you build connections and foster a sense of community.
Moving Forward
We are committed to turning your feedback into actionable solutions that enhance your PMI journey. This workshop was just the beginning. By actively participating and sharing your experiences, you have helped shape the future of our Chapter’s offerings.
Thank you to everyone who attended and contributed to the success of the Community Skill Builders Workshop. Your engagement and enthusiasm are what make our Chapter strong and vibrant. Stay tuned for updates on the new initiatives and opportunities to get involved. Together, we are building a community that supports and empowers each other on our PMI journeys.
Stay connected, stay engaged, and let’s continue to grow together!
About PMI Silver Spring Chapter
We are a branch of the Project Management Institute. We offer a platform for project management professionals in Silver Spring, MD, and the DC/Baltimore metro area. Monthly meetings facilitate networking, knowledge sharing, and professional development. For more, visit pmissc.org.欧洲杯投注-欧洲杯投注投注官方网站-欧洲杯投注买球投注官网|【网址🎉ac99.net🎉】

【网址🎉ac99.net🎉】在欧洲杯投注,你会发现数之不尽的在线博彩机会,包括世界各地的精彩体育赛事以及绝佳的赔率。此外,欧洲杯投注还会为你提供诸如赌场、宾果和扑克等在线游戏以及各种各样的奖金优惠,包括欧洲杯投注的免费投注。无论你是忠实的足球迷,或者是二十一点的专业玩家,在这里都可以找到你最感兴趣的投注市场或游戏。
欧洲杯外围-欧洲杯外围赛程-欧洲杯外围压注|【网址🎉ac99.net🎉】

【网址🎉ac99.net🎉】欧洲杯外围是爱尔兰的博彩公司,成立于1988年,位于爱尔兰的都柏林。欧洲杯外围通过在爱尔兰和英国的一系列持牌博彩商店以及经营爱尔兰最大的电话博彩服务来开展业务。在互联网上,欧洲杯外围提供体育博彩,在线扑克,在线宾果游戏,在线赌场和在线游戏。
一比一原版布拉德福德大学毕业证(bradford毕业证)如何办理

一模一样【微信:A575476】【布拉德福德大学毕业证(bradford毕业证)成绩单Offer】【微信:A575476】(留信学历认证永久存档查询)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作(包括:隐形水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠,文字图案浮雕,激光镭射,紫外荧光,温感,复印防伪)行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备,十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,业务范围有加拿大、英国、澳洲、韩国、美国、新加坡,新西兰等学历材料,包您满意。
【业务选择办理准则】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理一份就读学校的毕业证【微信:A575476】文凭即可
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理一份毕业证【微信:A575476】即可
三、进国企,银行,事业单位,考公务员等等,这些单位是必需要提供真实教育部认证的,办理教育部认证所需资料众多且烦琐,所有材料您都必须提供原件,我们凭借丰富的经验,快捷的绿色通道帮您快速整合材料,让您少走弯路。
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
→ 【关于价格问题(保证一手价格)
我们所定的价格是非常合理的,而且我们现在做得单子大多数都是代理和回头客户介绍的所以一般现在有新的单子 我给客户的都是第一手的代理价格,因为我想坦诚对待大家 不想跟大家在价格方面浪费时间
对于老客户或者被老客户介绍过来的朋友,我们都会适当给一些优惠。
选择实体注册公司办理,更放心,更安全!我们的承诺:可来公司面谈,可签订合同,会陪同客户一起到教育部认证窗口递交认证材料,客户在教育部官方认证查询网站查询到认证通过结果后付款,不成功不收费!
美洲杯投注-美洲杯投注比分-美洲杯投注比分投注|【网址🎉ac44.net🎉】

【网址🎉ac44.net🎉】美洲杯投注是世界上最大的网上博彩公司之一,于直布罗陀注册,在200个国家拥有超过3500万客户。在国际上都可以称得上是极其优秀的博彩公司。总部位于英国Stoke-on-Trent,美洲杯投注在世界各地的雇员超过600名。该公司登录亚洲市场多年,近年针对亚洲的市场拓展的很快。它的特点是投注赔率富于变化,同时对于冷门赛事,赔率变化幅度会大于其它博彩公司。美洲杯投注在终赔阶段往往向立博、韦德等靠拢,一旦差异很大,往往会出现问题。
按照学校原版(ArtEZ文凭证书)ArtEZ艺术学院毕业证快速办理

官方原版办理【(ArtEZ毕业证书)ArtEZ艺术学院毕业证】【176555708微信号】海外认证成绩单、外壳、offer、留信学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作(包括:隐形水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠,文字图案浮雕,激光镭射,紫外荧光,温感,复印防伪)行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备,十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,业务范围有加拿大、英国、澳洲、韩国、美国、新加坡,新西兰等学历材料,包您满意。
【我们承诺采用的是学校原版纸张(纸质、底色、纹路),我们拥有全套进口原装设备,特殊工艺都是采用不同机器制作,仿真度基本可以达到100%,所有工艺效果都可提前给客户展示,不满意可以根据客户要求进行调整,直到满意为止!】
【业务选择办理准则】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理一份就读学校的毕业证【微信176555708】文凭即可
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理一份毕业证【微信176555708】即可
三、进国企,银行,事业单位,考公务员等等,这些单位是必需要提供真实教育部认证的,办理教育部认证所需资料众多且烦琐,所有材料您都必须提供原件,我们凭借丰富的经验,快捷的绿色通道帮您快速整合材料,让您少走弯路。
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
留信网服务项目:
1、留学生专业人才库服务(留信分析)
2、国(境)学习人员提供就业推荐信服务
3、留学人员区块链存储服务
→ 【关于价格问题(保证一手价格)】
我们所定的价格是非常合理的,而且我们现在做得单子大多数都是代理和回头客户介绍的所以一般现在有新的单子 我给客户的都是第一手的代理价格,因为我想坦诚对待大家 不想跟大家在价格方面浪费时间
对于老客户或者被老客户介绍过来的朋友,我们都会适当给一些优惠。
选择实体注册公司办理,更放心,更安全!我们的承诺:客户在留信官方认证查询网站查询到认证通过结果后付款,不成功不收费!
一比一原版坎特伯雷大学毕业证(UC毕业证书)学历如何办理

制做办理【微信号:176555708】【制做办理(UC毕业证书)】【微信号:176555708】《成绩单、外壳、offer、真实留信官方学历认证(永久存档/真实可查)》采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作(包括:隐形水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠,文字图案浮雕,激光镭射,紫外荧光,温感,复印防伪)行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备,十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,业务范围有加拿大、英国、澳洲、韩国、美国、新加坡,新西兰等学历材料,包您满意。
【我们承诺采用的是学校原版纸张(纸质、底色、纹路)我们拥有全套进口原装设备,特殊工艺都是采用不同机器制作,仿真度基本可以达到100%,所有工艺效果都可提前给客户展示,不满意可以根据客户要求进行调整,直到满意为止!】
【业务选择办理准则】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理一份就读学校的毕业证【微信号:176555708】文凭即可
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理一份毕业证【微信号:176555708】即可
三、进国企,银行,事业单位,考公务员等等,这些单位是必需要提供真实教育部认证的,办理教育部认证所需资料众多且烦琐,所有材料您都必须提供原件,我们凭借丰富的经验,快捷的绿色通道帮您快速整合材料,让您少走弯路。
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
留信网服务项目:
1、留学生专业人才库服务(留信分析)
2、国(境)学习人员提供就业推荐信服务
3、留学人员区块链存储服务
【关于价格问题(保证一手价格)】
我们所定的价格是非常合理的,而且我们现在做得单子大多数都是代理和回头客户介绍的所以一般现在有新的单子 我给客户的都是第一手的代理价格,因为我想坦诚对待大家 不想跟大家在价格方面浪费时间
对于老客户或者被老客户介绍过来的朋友,我们都会适当给一些优惠。
选择实体注册公司办理,更放心,更安全!我们的承诺:客户在留信官方认证查询网站查询到认证通过结果后付款,不成功不收费!
一比一原版(surrey毕业证书)英国萨里大学毕业证成绩单修改如何办理

原版定制【微信:741003700】《(surrey毕业证书)英国萨里大学毕业证学位证成绩单》【微信:741003700】成绩单 、雅思、外壳、留信学历认证永久存档查询,采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作(包括:隐形水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠,文字图案浮雕,激光镭射,紫外荧光,温感,复印防伪)行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备,十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,业务范围有加拿大、英国、澳洲、韩国、美国、新加坡,新西兰等学历材料,包您满意。
【业务选择办理准则】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理一份毕业证【Q微信741003700】文凭即可
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理一份毕业证【Q微信741003700】即可
三、进国企,银行,事业单位,考公务员等等,这些单位是必需要提供真实教育部认证的,办理教育部认证所需资料众多且烦琐,所有材料您都必须提供原件,我们凭借丰富的经验,快捷的绿色通道帮您快速整合材料,让您少走弯路。
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
【关于价格问题(保证一手价格)】
我们所定的价格是非常合理的,而且我们现在做得单子大多数都是代理和回头客户介绍的所以一般现在有新的单子 我给客户的都是第一手的代理价格,因为我想坦诚对待大家 不想跟大家在价格方面浪费时间
对于老客户或者被老客户介绍过来的朋友,我们都会适当给一些优惠。
欧洲杯足彩-欧洲杯足彩体育投注-欧洲杯足彩投注网站|【网址🎉ac99.net🎉】

【网址🎉ac99.net🎉】欧洲杯足彩是世界上历史最悠久的博彩公司之一。其历史可以追溯到十九世纪末,确切时间是1886年。这家英国公司拥有超过15000名员工,是博彩行业规模最大的公司。欧洲杯足彩是英国最受欢迎的实体博彩公司之一,其排名仅次于欧洲杯足彩,旗下2800家投注站遍布全英国。
一比一原版美国西北大学毕业证(NWU毕业证书)学历如何办理

原版办理【微信号:BYZS866】【美国西北大学毕业证(NWU毕业证书)】【微信号:BYZS866】《成绩单、外壳、雅思、offer、真实留信官方学历认证(永久存档/真实可查)》采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作(包括:隐形水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠,文字图案浮雕,激光镭射,紫外荧光,温感,复印防伪)行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备,十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,业务范围有加拿大、英国、澳洲、韩国、美国、新加坡,新西兰等学历材料,包您满意。
【我们承诺采用的是学校原版纸张(纸质、底色、纹路)我们拥有全套进口原装设备,特殊工艺都是采用不同机器制作,仿真度基本可以达到100%,所有工艺效果都可提前给客户展示,不满意可以根据客户要求进行调整,直到满意为止!】
【业务选择办理准则】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理一份就读学校的毕业证【微信号BYZS866】文凭即可
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理一份毕业证【微信号BYZS866】即可
三、进国企,银行,事业单位,考公务员等等,这些单位是必需要提供真实教育部认证的,办理教育部认证所需资料众多且烦琐,所有材料您都必须提供原件,我们凭借丰富的经验,快捷的绿色通道帮您快速整合材料,让您少走弯路。
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
留信网服务项目:
1、留学生专业人才库服务(留信分析)
2、国(境)学习人员提供就业推荐信服务
3、留学人员区块链存储服务
【关于价格问题(保证一手价格)】
我们所定的价格是非常合理的,而且我们现在做得单子大多数都是代理和回头客户介绍的所以一般现在有新的单子 我给客户的都是第一手的代理价格,因为我想坦诚对待大家 不想跟大家在价格方面浪费时间
对于老客户或者被老客户介绍过来的朋友,我们都会适当给一些优惠。
选择实体注册公司办理,更放心,更安全!我们的承诺:客户在留信官方认证查询网站查询到认证通过结果后付款,不成功不收费!
按照学校原版(UofT文凭证书)多伦多大学毕业证快速办理

快速办理【(UofT毕业证书)多伦多大学毕业证】【176555708微信号】硕士毕业证成绩单、外壳、offer、留信学历认证(永久存档真实可查)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作(包括:隐形水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠,文字图案浮雕,激光镭射,紫外荧光,温感,复印防伪)行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备,十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,业务范围有加拿大、英国、澳洲、韩国、美国、新加坡,新西兰等学历材料,包您满意。
【我们承诺采用的是学校原版纸张(纸质、底色、纹路),我们拥有全套进口原装设备,特殊工艺都是采用不同机器制作,仿真度基本可以达到100%,所有工艺效果都可提前给客户展示,不满意可以根据客户要求进行调整,直到满意为止!】
【业务选择办理准则】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理一份就读学校的毕业证【微信176555708】文凭即可
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理一份毕业证【微信176555708】即可
三、进国企,银行,事业单位,考公务员等等,这些单位是必需要提供真实教育部认证的,办理教育部认证所需资料众多且烦琐,所有材料您都必须提供原件,我们凭借丰富的经验,快捷的绿色通道帮您快速整合材料,让您少走弯路。
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
留信网服务项目:
1、留学生专业人才库服务(留信分析)
2、国(境)学习人员提供就业推荐信服务
3、留学人员区块链存储服务
→ 【关于价格问题(保证一手价格)】
我们所定的价格是非常合理的,而且我们现在做得单子大多数都是代理和回头客户介绍的所以一般现在有新的单子 我给客户的都是第一手的代理价格,因为我想坦诚对待大家 不想跟大家在价格方面浪费时间
对于老客户或者被老客户介绍过来的朋友,我们都会适当给一些优惠。
选择实体注册公司办理,更放心,更安全!我们的承诺:客户在留信官方认证查询网站查询到认证通过结果后付款,不成功不收费!
Gabrielle M. A. Sinaga Portfolio, Film Student (2024)

My portfolio as a highly motivated film student pursuing a career in Yogyakarta.
体育博彩论坛-十大体育博彩论坛-体育博彩论坛|【网址🎉ac55.net🎉】

在体育博彩论坛,你会发现数之不尽的在线博彩机会,包括世界各地的精彩体育赛事以及绝佳的赔率。此外,体育博彩论坛还会为你提供诸如赌场、宾果和扑克等在线游戏以及各种各样的奖金优惠,包括体育博彩论坛的免费投注。无论你是忠实的足球迷,或者是二十一点的专业玩家,在这里都可以找到你最感兴趣的投注市场或游戏。
美洲杯买球-美洲杯买球下注平台-美洲杯买球投注平台|【网址🎉ac55.net🎉】

【网址🎉ac55.net🎉】美洲杯买球是爱尔兰的博彩公司,成立于1988年,位于爱尔兰的都柏林。美洲杯买球通过在爱尔兰和英国的一系列持牌博彩商店以及经营爱尔兰最大的电话博彩服务来开展业务。在互联网上,美洲杯买球提供体育博彩,在线扑克,在线宾果游戏,在线赌场和在线游戏。
一比一原版(EUR毕业证)鹿特丹伊拉斯姆斯大学毕业证如何办理

原件一模一样【微信:95270640】【鹿特丹伊拉斯姆斯大学毕业证EUR学位证成绩单】【微信:95270640】(留信学历认证永久存档查询)采用学校原版纸张、特殊工艺完全按照原版一比一制作(包括:隐形水印,阴影底纹,钢印LOGO烫金烫银,LOGO烫金烫银复合重叠,文字图案浮雕,激光镭射,紫外荧光,温感,复印防伪)行业标杆!精益求精,诚心合作,真诚制作!多年品质 ,按需精细制作,24小时接单,全套进口原装设备,十五年致力于帮助留学生解决难题,业务范围有加拿大、英国、澳洲、韩国、美国、新加坡,新西兰等学历材料,包您满意。
【业务选择办理准则】
一、工作未确定,回国需先给父母、亲戚朋友看下文凭的情况,办理一份就读学校的毕业证【微信:95270640】文凭即可
二、回国进私企、外企、自己做生意的情况,这些单位是不查询毕业证真伪的,而且国内没有渠道去查询国外文凭的真假,也不需要提供真实教育部认证。鉴于此,办理一份毕业证【微信:95270640】即可
三、进国企,银行,事业单位,考公务员等等,这些单位是必需要提供真实教育部认证的,办理教育部认证所需资料众多且烦琐,所有材料您都必须提供原件,我们凭借丰富的经验,快捷的绿色通道帮您快速整合材料,让您少走弯路。
留信网认证的作用:
1:该专业认证可证明留学生真实身份【微信:95270640】
2:同时对留学生所学专业登记给予评定
3:国家专业人才认证中心颁发入库证书
4:这个认证书并且可以归档倒地方
5:凡事获得留信网入网的信息将会逐步更新到个人身份内,将在公安局网内查询个人身份证信息后,同步读取人才网入库信息
6:个人职称评审加20分
7:个人信誉贷款加10分
8:在国家人才网主办的国家网络招聘大会中纳入资料,供国家高端企业选择人才
→ 【关于价格问题(保证一手价格)
我们所定的价格是非常合理的,而且我们现在做得单子大多数都是代理和回头客户介绍的所以一般现在有新的单子 我给客户的都是第一手的代理价格,因为我想坦诚对待大家 不想跟大家在价格方面浪费时间
对于老客户或者被老客户介绍过来的朋友,我们都会适当给一些优惠。
选择实体注册公司办理,更放心,更安全!我们的承诺:可来公司面谈,可签订合同,会陪同客户一起到教育部认证窗口递交认证材料,客户在教育部官方认证查询网站查询到认证通过结果后付款,不成功不收费!
办理鹿特丹伊拉斯姆斯大学毕业证毕业证offerEUR学位证【微信:95270640 】外观非常精致,由特殊纸质材料制成,上面印有校徽、校名、毕业生姓名、专业等信息。
办理鹿特丹伊拉斯姆斯大学毕业证EUR学位证毕业证offer【微信:95270640 】格式相对统一,各专业都有相应的模板。通常包括以下部分:
校徽:象征着学校的荣誉和传承。
校名:学校英文全称
授予学位:本部分将注明获得的具体学位名称。
毕业生姓名:这是最重要的信息之一,标志着该证书是由特定人员获得的。
颁发日期:这是毕业正式生效的时间,也代表着毕业生学业的结束。
其他信息:根据不同的专业和学位,可能会有一些特定的信息或章节。
办理鹿特丹伊拉斯姆斯大学毕业证毕业证offerEUR学位证【微信:95270640 】价值很高,需要妥善保管。一般来说,应放置在安全、干燥、防潮的地方,避免长时间暴露在阳光下。如需使用,最好使用复印件而不是原件,以免丢失。
综上所述,办理鹿特丹伊拉斯姆斯大学毕业证毕业证offerEUR学位证【微信:95270640 】是证明身份和学历的高价值文件。外观简单庄重,格式统一,包括重要的个人信息和发布日期。对持有人来说,妥善保管是非常重要的。
欧洲杯买球-欧洲杯买球买球推荐-欧洲杯买球买球推荐网站|【网址🎉ac10.net🎉】

【网址🎉ac10.net🎉】欧洲杯买球是一家极具特色的欧洲主流博彩公司,对于自己所擅长的赛事往往把赔率值压得很低,掩饰平局是他们一贯的手法。例如,当伟德旗帜鲜明地支持客胜,降低客胜值,提升主胜值,而平局赔率却与欧洲杯买球、欧洲杯买球的态度较吻合时,这场比赛往往以平局收场。
Learnings from Successful Jobs Searchers

Are you interested to know what actions help in a job search? This webinar is the summary of several individuals who discussed their job search journey for others to follow. You will learn there are common actions that helped them succeed in their quest for gainful employment.
A Guide to a Winning Interview June 2024

This webinar is an in-depth review of the interview process. Preparation is a key element to acing an interview. Learn the best approaches from the initial phone screen to the face-to-face meeting with the hiring manager. You will hear great answers to several standard questions, including the dreaded “Tell Me About Yourself”.
Recently uploaded (20)
Community Skills Building Workshop | PMI Silver Spring Chapter | June 12, 2024

Community Skills Building Workshop | PMI Silver Spring Chapter | June 12, 2024
Gabrielle M. A. Sinaga Portfolio, Film Student (2024)

Gabrielle M. A. Sinaga Portfolio, Film Student (2024)
An introduction to chemical equilibria
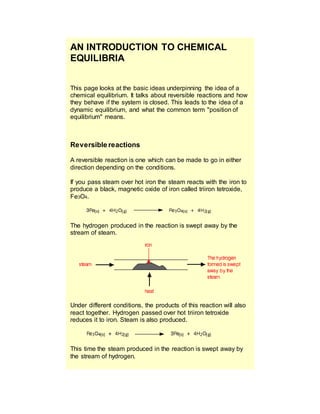
- 1. AN INTRODUCTION TO CHEMICAL EQUILIBRIA This page looks at the basic ideas underpinning the idea of a chemical equilibrium. It talks about reversible reactions and how they behave if the system is closed. This leads to the idea of a dynamic equilibrium, and what the common term "position of equilibrium" means. Reversible reactions A reversible reaction is one which can be made to go in either direction depending on the conditions. If you pass steam over hot iron the steam reacts with the iron to produce a black, magnetic oxide of iron called triiron tetroxide, Fe3O4. The hydrogen produced in the reaction is swept away by the stream of steam. Under different conditions, the products of this reaction will also react together. Hydrogen passed over hot triiron tetroxide reduces it to iron. Steam is also produced. This time the steam produced in the reaction is swept away by the stream of hydrogen.
- 2. These reactions are reversible, but under the conditions normally used, they become one-way reactions. The products aren't left in contact with each other, so the reverse reaction can't happen. Reversible reactions happening in a closed system A closed system is one in which no substances are either added to the system or lost from it. Energy can, however, be transferred in or out at will. In the example we've been looking at, you would have to imagine iron being heated in steam in a closed container. Heat is being added to the system, but none of the substances in the reaction can escape. The system is closed. As the triiron tetroxide and hydrogen start to be formed, they will also react again to give the original iron and steam. So, if you analysed the mixture after a while, what would you find? You would find that you had established what is known as adynamic equilibrium. To explain what that means, we are going to use a much simpler example . . . Dynamic equilibria Getting a visual feel for a dynamic equilibrium Imagine a substance which can exist in two forms - a blue form or an orange form - and that each form can react to give the other one. We are going to let them react in a closed system. Neither form can escape. Assume that the blue form turns into the orange one much faster than the other way round. In any given time, these are the
- 3. chances of the two changes happening: You can simulate this very easily with some coloured paper cut up into small pieces (a different colour on each side), and a dice. The following are the real results of a "reaction" I did myself. I started with 16 blue squares and looked at each one in turn and decided whether it should change colour by throwing a dice. A blue square was turned into an orange square (the bit of paper was turned over!) if I threw a 4, 5 or 6 An orange square was turned into a blue square only if I threw a 6 while I was looking at that particular square. Once I had looked at all 16 squares, I started the process all over again - but obviously with a different starting pattern. The diagrams show the results of doing this 11 times (plus the original 16 blue squares).
- 4. You can see that the "reaction" is continuing all the time. The exact pattern of orange and blue is constantly changing. However, the overall numbers of orange and of blue squares remain remarkably constant - most commonly, 12 orange ones to 4 blue ones. Note: To be honest, this was a lucky fluke, given the small number of squares I was working with. If you repeated this with much larger number of squares (say, several thousand), you would find that your patterns settled down quite reliably close to 75% orange and 25% blue. On the other hand, that would be seriously tedious! If you had the huge numbers of particles taking part in chemical reactions, the proportions would be spot on 75% to 25%. Explaining the term "dynamic equilibrium" The reaction has reached equilibrium in the sense that there is no further change in the numbers of blue and orange squares. However, the reaction is still continuing. For every orange square that turns blue, somewhere in the mixture it is replaced by a blue square turning orange. This is known as a dynamic equilibrium. The word dynamicshows that the reaction is still continuing. You can show dynamic equilibrium in an equation for a reaction by the use of special arrows. In the present case, you would write it as: It is important to realise that this doesn't just mean that the reaction is reversible. It means that you have a reversible reaction in a state of dynamic equilibrium. The "forward reaction" and the "back reaction" The change from left to right in the equation (in this case from blue to orange as it is written) is known as the forward reaction. The change from right to left is the back reaction.
- 5. Position of equilibrium In the example we've used, the equilibrium mixture contained more orange squares than blue ones. Position of equilibrium is a way of expressing this. You can say things like: "The position of equilibrium lies towards the orange." "The position of equilibrium lies towards the right-hand side." If the conditions of the experiment change (by altering the relative chances of the forward and back reactions happening), the composition of the equilibrium mixture will also change. For example, if changing the conditions produced more blue in the equilibrium mixture, you would say "The position of equilibrium has moved to the left" or "The position of equilibrium has moved towards the blue". Note: If you can be bothered, try the effect on the position of equilibrium of increasing the chances of an orange square turning blue from 1 in 6 to 2 in 6. In other words, allow it to change if you throw either a 5 or a 6 with your dice. Reaching equilibrium from the other side What happens if you started the reaction with orange squares rather than blue ones, but kept the chances of each change happening the same as in the first example? This is the result of my "reaction".
- 6. Once again, you can see that exactly the same position of equilibrium is being established as when we started with the blue squares. You get exactly the same equilibrium mixture irrespective of which side of the equation you start from - provided the conditions are the same in both cases. Remember: You can't get the numbers to work out exactly using this small number of particles. Chance fluctuations are too noticeable. Once again, if you used really large numbers of particles, the equilibrium mixture would contain 75% orange and 25% blue. Given the number of particles we're working with, the "reaction" is remarkably close to that on average. A more formal look at dynamic equilibria Thinking about reaction rates This is the equation for a general reaction which has reached dynamic equilibrium:
- 7. How did it get to that state? Let's assume that we started with A and B. At the beginning of the reaction, the concentrations of A and B were at their maximum. That means that the rate of the reaction was at its fastest. As A and B react, their concentrations fall. That means that they are less likely to collide and react, and so the rate of the forward reaction falls as time goes on. In the beginning, there isn't any C and D, so there can't be any reaction between them. As time goes on, though, their concentrations in the mixture increase and they are more likely to collide and react. With time, the rate of the reaction between C and D increases: Eventually, the rates of the two reactions will become equal. A and B will be converting into C and D at exactly the same rate as C and D convert back into A and B again.
- 8. At this point there won't be any further change in the amounts of A, B, C and D in the mixture. As fast as something is being removed, it is being replaced again by the reverse reaction. We have reached a position of dynamic equilibrium. A summary A dynamic equilibrium occurs when you have a reversible reaction in a closed system. Nothing can be added to the system or taken away from it apart from energy. At equilibrium, the quantities of everything present in the mixture remain constant, although the reactions are still continuing. This is because the rates of the forward and the back reactions are equal. If you change the conditions in a way which changes the relative rates of the forward and back reactions you will change the position of equilibrium - in other words, change the proportions of the various substances present in the equilibrium mixture. This is explored in detail on other pages in this equilibrium section.
