This document explores an experimental investigation into geopolymer concrete made from ground granulated blast furnace slag (GGBS), aimed at mitigating the environmental impact of traditional cement production by reducing carbon dioxide emissions. The study evaluates the engineering properties of the geopolymer concrete, demonstrating that it exhibits superior compressive, flexural, and tensile strengths compared to ordinary Portland cement concrete, while also being eco-friendly and more sustainable. The findings suggest that geopolymer concrete can serve as a viable alternative in construction, effectively addressing significant environmental concerns.

![IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308
__________________________________________________________________________________________
Volume: 03 Special Issue: 06 | May-2014 | RRDCE - 2014, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 314
one is the chemical process of calcining limestone into lime in
the cement kiln also produces carbon di oxide. In India about
2,069,738 thousands of metric tons of carbon di oxide is
emitted in the year of 2010. The cement industry contributes
about 5% of total global carbon dioxide emissions. The
cement is manufactured by using the raw materials such as
lime stone, clay and other minerals by procuring them by
quarrying process which also causes environmental
degradation. To produce 1 ton of cement, about 1.6 tons of
raw materials are required and the time taken to form the lime
stone is much longer than the rate at which humans use it.
On the other side, the demand of concrete is increasing day by
day for its ease of preparing and fabricating in all sorts of
convenient shapes. So to overcome this problem, the concrete
to be used should be environmental friendly. To produce
environmental friendly concrete, it is necessary to replace the
cement with the industrial by products such as fly-ash, GGBS
(Ground granulated blast furnace slag) etc. with new binding
activator to form a new product called “Geo Polymer
Concrete”.
The term geopolymer was first coined by Davidovits in 1978
to represent a broad range of materials characterized by chains
or networks of inorganic molecules. Geopolymers are chains
or networks of mineral molecules linked with co-valent bonds.
Geopolymer is produced by a polymeric reaction of alkaline
liquid with source material of geological origin or by product
material such as GGBS. Geo-polymers have the chemical
composition similar to Zeolites but they can be formed an
amorphous structure. For binding of materials the silica and
the alumina present in the source material are induced by
alkaline activators. The most common alkaline liquid used in
the geo-polymerization is the combination of Sodium
hydroxide and Sodium silicate. This combination increases the
rate of reaction. Among fifteen Alumino-silicate minerals, all
the Al-Si minerals are more soluble in sodium hydroxide
solution than in potassium hydroxide solution. Ground
granulated blast furnace slag (GGBS) is a by-product from the
blast-furnaces used to make iron. During the process, slag was
formed and it is then dried and ground to a fine powder.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 History of Geopolymers
Davidovits coined the term geopolymer in 1978 to represent a
broad range of materials characterised by chains or networks
of inorganic molecules [Davidovits, 1979, 1993, 2008][5]
, and
explained in many of his publications about the possibility of
GPs being used by Egyptians construction of pyramids, based
on microscopy, IR and NMR spectroscopy of sparse
specimens from ancient Egyptian constructions [Davidovits
and Morris, 1988; Davidovits, 1999][7]
.Demortier observed the
noticeable differences in porosities in the top and bottom
sections of pyramid blocks which were also subjected to X-ray
and NMR analyses to conclude that pyramids could be made
from „concreting‟ operations [Demortier, 2004]. Use of slurry
to form bearing courses of horizontal joints and vertical joints
between the blocks including presence of hair in the joints of
pyramids did indicate the possibility of „concrete‟ like
technology for pyramid constructions .
2.2 Fresh Geopolymer Concrete Mixes
Hardjito et al, (2002)[17]
observed that fresh geopolymer
concrete is highly viscous and cohesive with low workability
when the calcined kaolin was the source material.
2.3 Structural Usages
Davidovits and Sawyer (1985)[6]
used ground blast furnace
slag to produce geopolymer binders. This type of binders
patented in the USA under the title „Early High-Strength
Mineral Polymer‟, was used as a supplementary cementing
material in the production of precast concrete products.
2.4 Activating Medium
A combination of sodium or potassium silicate and sodium or
potassium hydroxide has been widely used as the alkaline
activator (Palomo et al, 1999; van Jaarsveld, van Deventer &
Lukey 2002; Xu & van Deventer, 2000; Swanepoel &
Strydom, 2002)[23,32]
, with the activator liquid-to-source
material ratio by mass in the range of 0.25-0.30 (Palomo,
Grutzeck & Blanco 1999; Swanepoel & Strydom 2002)[31]
.
Anurag Mishra (2008, 2009) conducted experiments on FA
based GPC by varying the concentration of NaOH and curing
time. Total nine mixes were prepared with NaOH
concentration as 8M, 12M, 16M and curing time as 24hrs,
48hrs, and 72hrs. The investigation indicated: an increase in
compressive strength with increase in NaOH concentration
and curing time, increase in compressive strength after 48hrs
curing time not significant. Compressive strength up to 46
MPa was obtained with curing at 60ºC. Water absorption
decreased with increase in NaOH concentration and curing
time.
3. SCOPE AND OBJECTIVES PRESENT WORK
3.1 Need for the Present Study
It is evident from the present facts that the production of
Ordinary Portland Cement is causing much of the
environmental hazards such as-
Emission of green house gases.
Enormous consumption of power for the manufacture
of cement.
Minimize the waste of potable water in construction
industries.
As such, a new alternate binding material is necessary in order
to address the problems, resulting in development of
geopolymer concrete.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anexperimentalinvestigationonpropertiesofggbsbasedgeopolymerconcreteforhighvolumetraffic-140824231258-phpapp02/75/An-experimental-investigation-on-properties-of-ggbs-based-geopolymer-concrete-for-high-volume-traffic-2-2048.jpg)

![IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308
__________________________________________________________________________________________
Volume: 03 Special Issue: 06 | May-2014 | RRDCE - 2014, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 316
4.4 Sodium Silicate Solution
Sodium silicate is also known as water glass or liquid glass,
available in liquid (gel) form. The sodium silicate solution is
commercially available in different grades. The sodium
silicate solution with SiO2 = 32.68%, Na2O = 15.63%, and
water = 51.69% by mass, has been used for the present study.
As per the manufacture, silicates were supplied to the
detergent company and textile industry as bonding agent.
Same sodium silicate is used for the making of geopolymer
concrete. In the present investigation sodium silicate solution
was purchased from local market.
Fig: 4.3 Sodium Silicate Solutions
5. MOLARITY CALCULATION
For 12 M NaOH calculation
NaOH solution with a concentration of 12 Molar consists of
12 x 40 = 480 grams of NaOH solids per litre of the water,
were 40 is the molecular weight of NaOH
Therefore,
0.480 kg of NaOH flakes in 1 kg of water
1.48 kg of mass of NaOH solution contains 0.480 kg of flakes
1.0 kg of mass of NaOH solution contains=1*0.48/1.48=
0.3243 kg flakes
1 kg of mass of NaOH solution contains 0.3243 kg NaOH
flakes
Table 5.1: Molarity Calculation
Molarity
NaOH flakes in
one lt of water
(kg)
NaOH flakes in
one lt of NaOH
solution (kg)
12M 0.480 0.3243
14M 0.560 0.359
16M 0.640 0.390
6. PREPARATION OF TEST SPECIMENS
6.1 Preparation of the Alkaline Solution
The Sodium hydroxide flakes were dissolved in water to make
the solution. The concentration of the NaOH solution depends
on the molarity; 12 M, 14 M, 16 M. The sodium silicate
solution was added to this NaOH solution and this mixture of
alkaline liquid was prepared one day prior to the casting of the
specimens as this is confirmed to have the better results
(Hardjito and Rangan)[18]
.The alkaline liquid was used after 24
hrs and within 36 hrs .(Hardjito and Rangan)[18]
. On the day of
casting of the specimens, the alkaline liquid was mixed to
binder and aggregates with water added (if necessary) in order
to achieve better workability.
6.2 Mixing, Casting and Curing of GPC
For mixing, conventional method used for making normal
concrete was adopted to prepare geopolymer concrete.The
solid constituents viz. GGBS and aggregates were mixed in
dry form for about 3-4 minutes. At the end of this mixing ,the
liquid component of the geopolymer concrete mixture
,i.e.,combination of the alkaline solution with extra water was
added to the solids and the mixing continued for another 3-4
minutes.The fresh GGBS based geopolymer concrete was grey
in colour and shiny in appearance. The green mix was
cohesive.The workability of the fresh concrete was measured
by means of the conventional slump test.
The fresh concrete was then poured into the moulds in three
layers immediately after mixing and compacted by hand
compaction by giving 25 strokes for each layer .After casting
the test specimens were covered with HDPE (High Density
Polyethelene) sheet, to minimise the water evoporation during
the rest period of 24hrs at room temperature. At the end of 24
hrs all the specimens along with the mould were placed inside
the hot air oven and cured at 120°c for another 24 hrs.
The specimens were taken out from the oven and kept to air-
dry at room temperature and after cooling to the room
temperature the specimens were de-moulded and tested to
determine the various strength properties.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anexperimentalinvestigationonpropertiesofggbsbasedgeopolymerconcreteforhighvolumetraffic-140824231258-phpapp02/75/An-experimental-investigation-on-properties-of-ggbs-based-geopolymer-concrete-for-high-volume-traffic-4-2048.jpg)

![IJRET: International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology eISSN: 2319-1163 | pISSN: 2321-7308
__________________________________________________________________________________________
Volume: 03 Special Issue: 06 | May-2014 | RRDCE - 2014, Available @ http://www.ijret.org 319
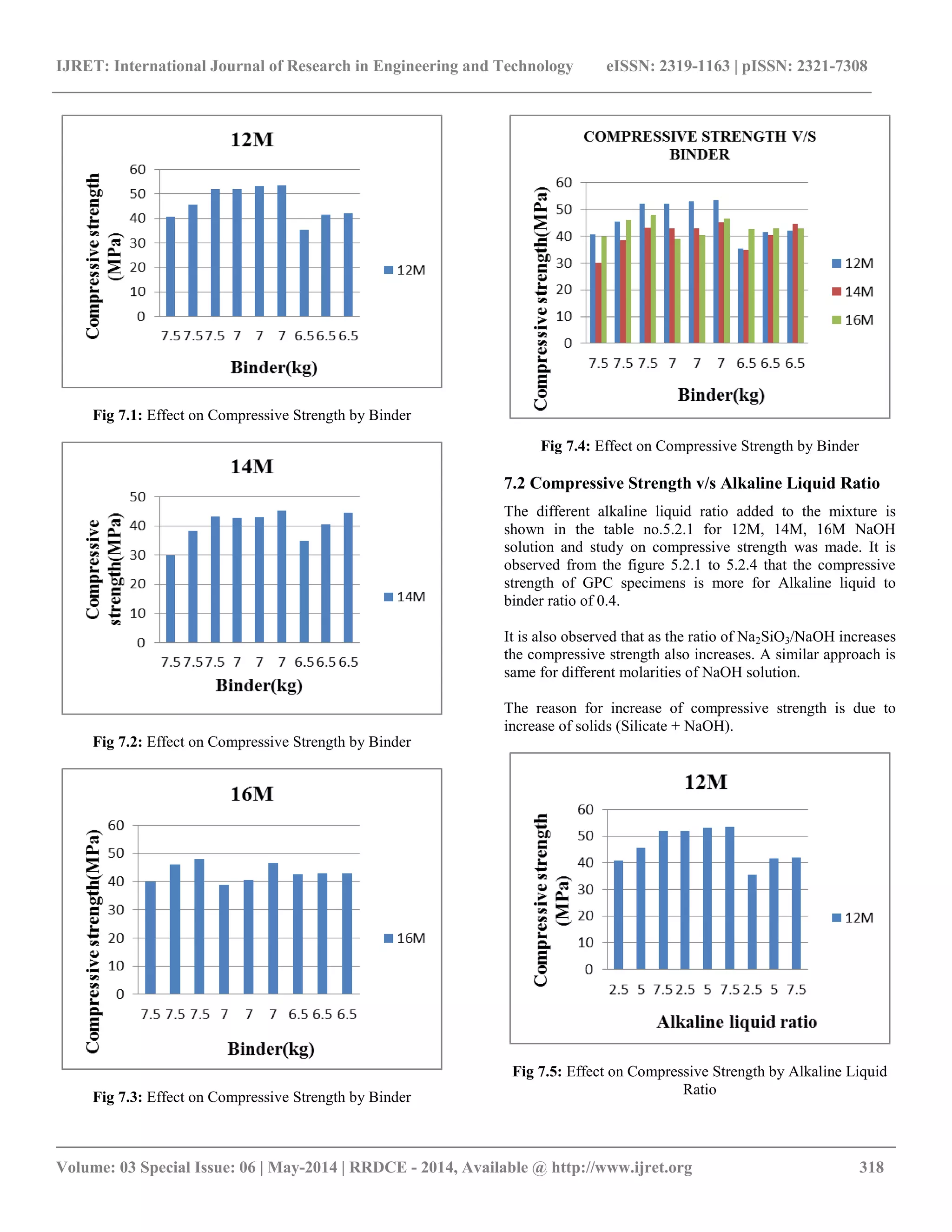
Fig 7.6: Effect on Compressive Strength by Alkaline Liquid
Ratio
Fig 7.7: Effect on Compressive Strength by Alkaline Liquid
Ratio
Fig7.8: Effect of Compressive Strength by Alkaline Liquid
Ratio
8. CONCLUSIONS
Based on the present experimental investigations the following
conclusions are drawn.
Higher concentration of sodium hydroxide in the
solution results in lower compressive strength of
GGBS based geopolymer concrete.
The compressive strength of geopolymer concrete is
more for the higher ratio of sodium silicate to sodium
hydroxide solution by mass.
The compressive strength is lower in case of higher
or lower ratio of alkaline liquid to binder.
It is evident that more the alkaline liquid
concentration (NaOH + Na2SiO3) yields lower
compressive strength.
The compressive strength increases with the
increased concentration of sodium silicate solution,
upto certain ratio.
As water binder ratio increases the compressive
strength of GGBS based geopolymer concrete
decreases.
There is marginal decrease in the density of GGBS
based geopolymer concrete compared to the
conventional OPC concrete.
The fresh GGBS based geopolymer concrete hardens
at room temperature.
REFERENCES
[1] Barbosa, V. F. F., Mackenzie, K. J. D. and
Thaumaturgo, C., (2000), “Synthesis and
characterisation of materials based on inorganic
polymers of alumina and silica: sodium polysialate
polymers”, International Journal of Inorganic
Materials, 2, 309- 317
[2] Bhikshma, V., Koti Reddy, M. and Srinivas Rao, T.,
“An Experimental Investigation on Properties of
Geopolymer Concrete (No Cement Concrete)”, Vol.
13, No. 6 (2012).
[3] Cheng, T. W. and Chiu, J. P. (2003). “Fire-resistant
Geopolymer Produced by Granulated Blast Furnace
Slag” Minerals Engineering 16(3): 205-210.
[4] Chindaprasirt, P., Chareerat, T., Siricicatnanon, V.
(2007). “Workability and Strength of Coarse High
Calcium Fly Ash Geopolymer”. Cement Concrete
Compos., 29: 224-229.
[5] Davidovits, J. 1984. “Pyramids of Egypt Made of Man-
Made Stone, Myth or Fact?” Symposium on
Archaeometry 1984. Smithsonian Institution,
Washington, DC.
[6] Davidovits, J. et al., “Process for Obtaining
Geopolymeric Alumino-Silicate and Products Thus
Obtained”, US patent USA 5, 342(1994) 595.
[7] Davidovits, J. (1999). “Chemistry of Geopolymeric
Systems, Terminology. Geopolymer” 99 International
Conference, France.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/anexperimentalinvestigationonpropertiesofggbsbasedgeopolymerconcreteforhighvolumetraffic-140824231258-phpapp02/75/An-experimental-investigation-on-properties-of-ggbs-based-geopolymer-concrete-for-high-volume-traffic-7-2048.jpg)