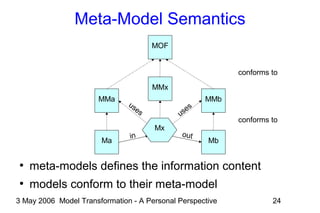
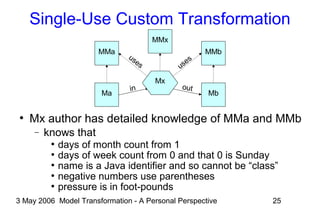
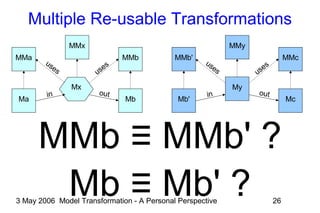
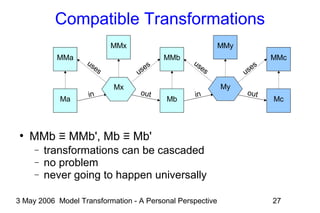
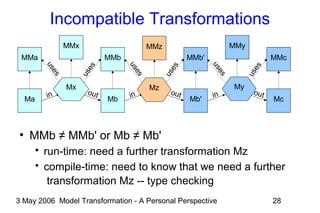
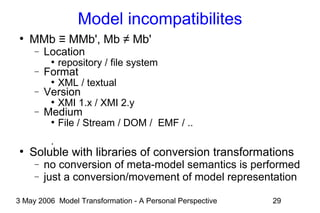
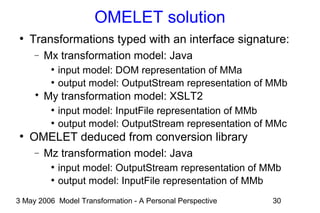
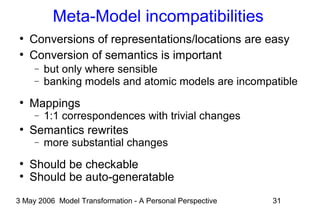
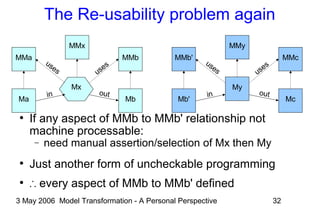
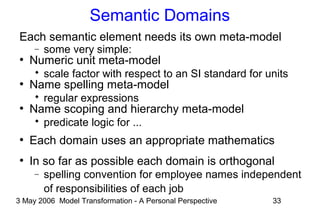
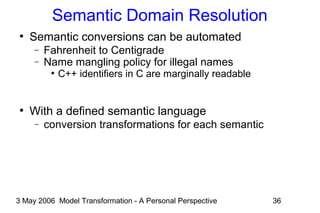
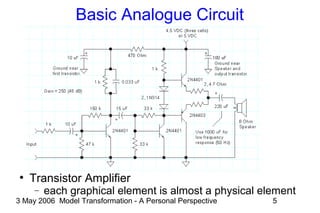
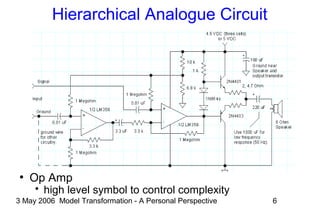
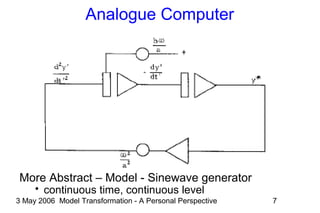
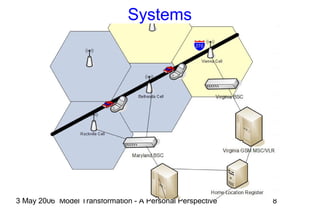
The document discusses model transformation from the perspective of the author's background in embedded systems and digital signal processing. It outlines the author's experience with diagrams and models from analog circuits to block diagrams to functional modeling. It then discusses the challenges of model transformation, including dealing with meta-model semantics, managing multiple meta-models, and improving transformation efficiency through techniques like combining multiple transformation passes. The document argues that achieving widespread re-usable transformations will require formalizing the relationships between meta-models and their semantics.





![3 May 2006 Model Transformation - A Personal Perspective 14
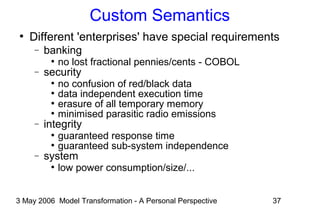
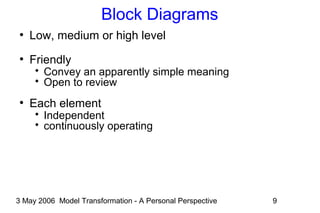
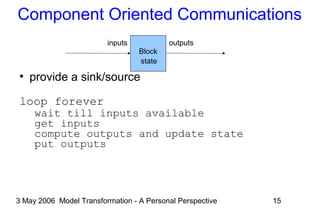
Transformations as Program Steps
●
Generic state-based transaction
state state'
Mx
inputs outputs
state state'
inputs[constraint]/outputs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ammamdatalk-130623130118-phpapp01/85/Model-Transformation-A-Personal-Perspective-14-320.jpg)

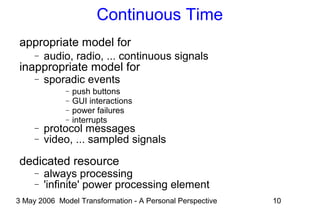
![3 May 2006 Model Transformation - A Personal Perspective 22
Transformations Everywhere
[... from requirements
via vague specification
to executable specification]
●
Hundreds of transformations from:
− executable specification to implementation (code)
●
Code to executable
− currently hidden inside compilers
− could be exposed as hundreds of transformations
●
could then be customised for special purposes
●
could be optimised one transformation at a time](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ammamdatalk-130623130118-phpapp01/85/Model-Transformation-A-Personal-Perspective-22-320.jpg)