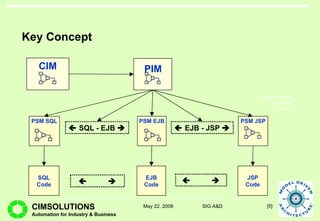
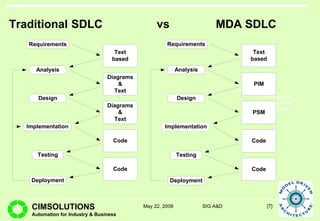
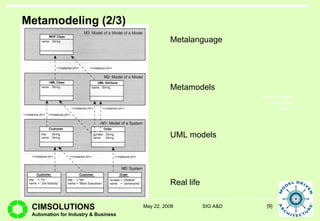
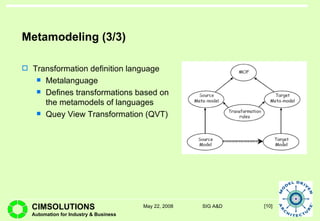
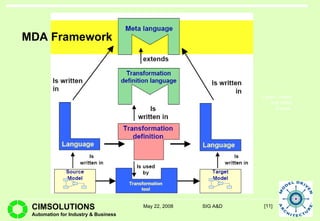
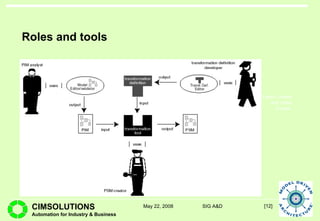
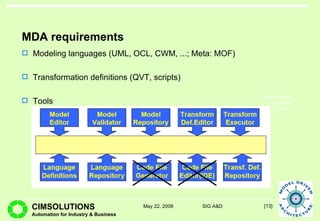
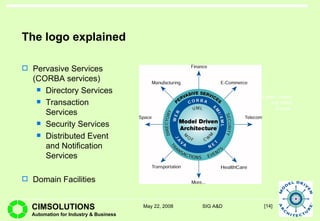
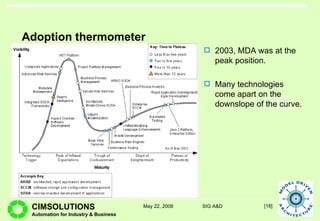
This document provides an overview of Model Driven Architecture (MDA). MDA is a framework defined by OMG that uses modeling languages as programming languages rather than just for design. It focuses on standardizing modeling to address issues with proliferated middleware solutions. MDA uses metamodeling to define modeling languages and transformations between models. It aims to improve portability, interoperability and productivity through separation of concerns between platform independent and specific models. However, challenges include limitations of existing modeling languages and lack of standardization for model transformations.