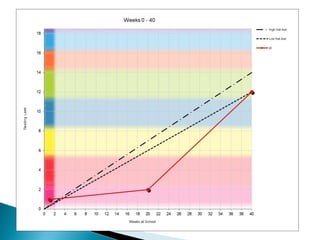
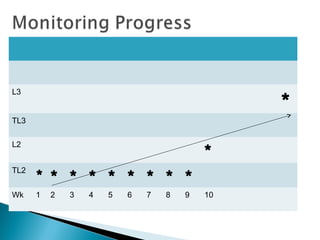
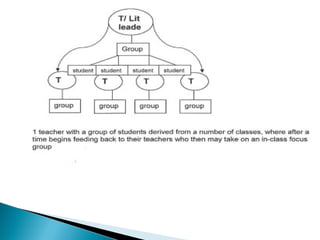
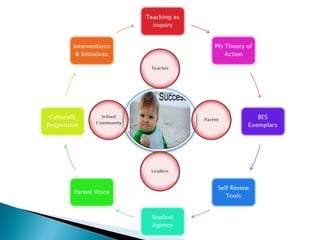
This document outlines plans for ALL mentor groups to accelerate a group of target students over 15 weeks through additional literacy interventions. It discusses aiming to build understanding of the theory of action with two expected outcomes of accelerating students and developing a curriculum and achievement action plan. The intervention will be a minimum of 4 sessions per week supported by regular meetings. It will consider relevant research, known levers of change, and identify pathways of progress for each learner. There will be built in reviews of student progress and engagement with student and family voice. The approach will be based on the learners, teacher strengths, resources, and fit with other interventions.