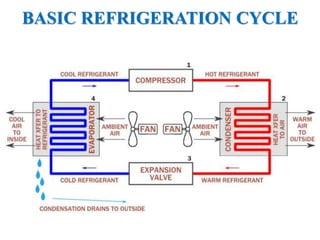
HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems are used to control indoor air quality by regulating temperature, humidity, and air quality. An HVAC system generally includes a furnace, air conditioner, ducts, vents and thermostat. It can heat or cool spaces through convection, conduction, or radiation and distributes heated or cooled air through ductwork or piping for water systems. Proper ventilation and filtration are also important for improving indoor air quality.