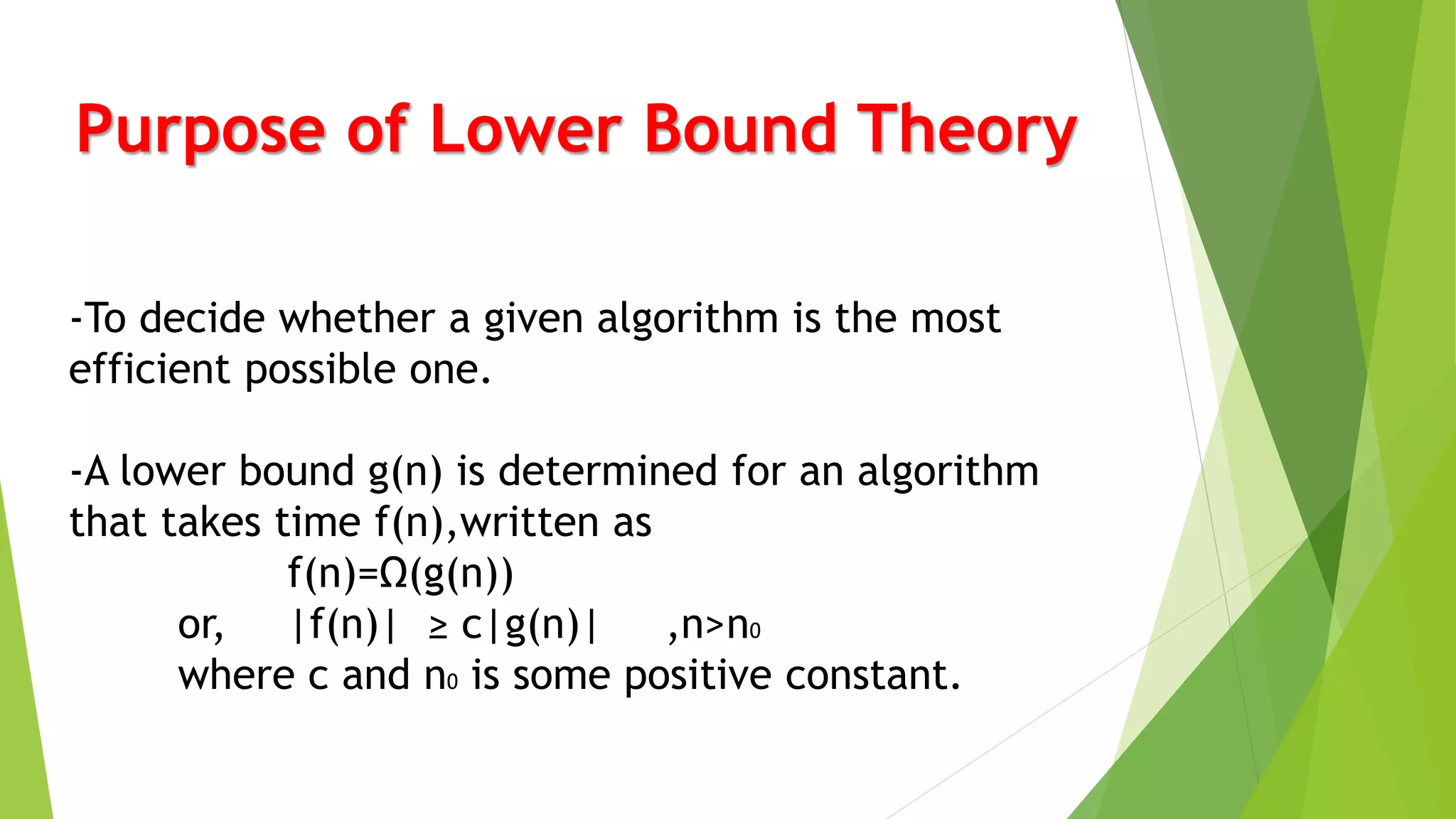
1) The lower bound theory is used to determine if an algorithm is the most efficient possible by comparing its time complexity f(n) to a lower bound complexity g(n).
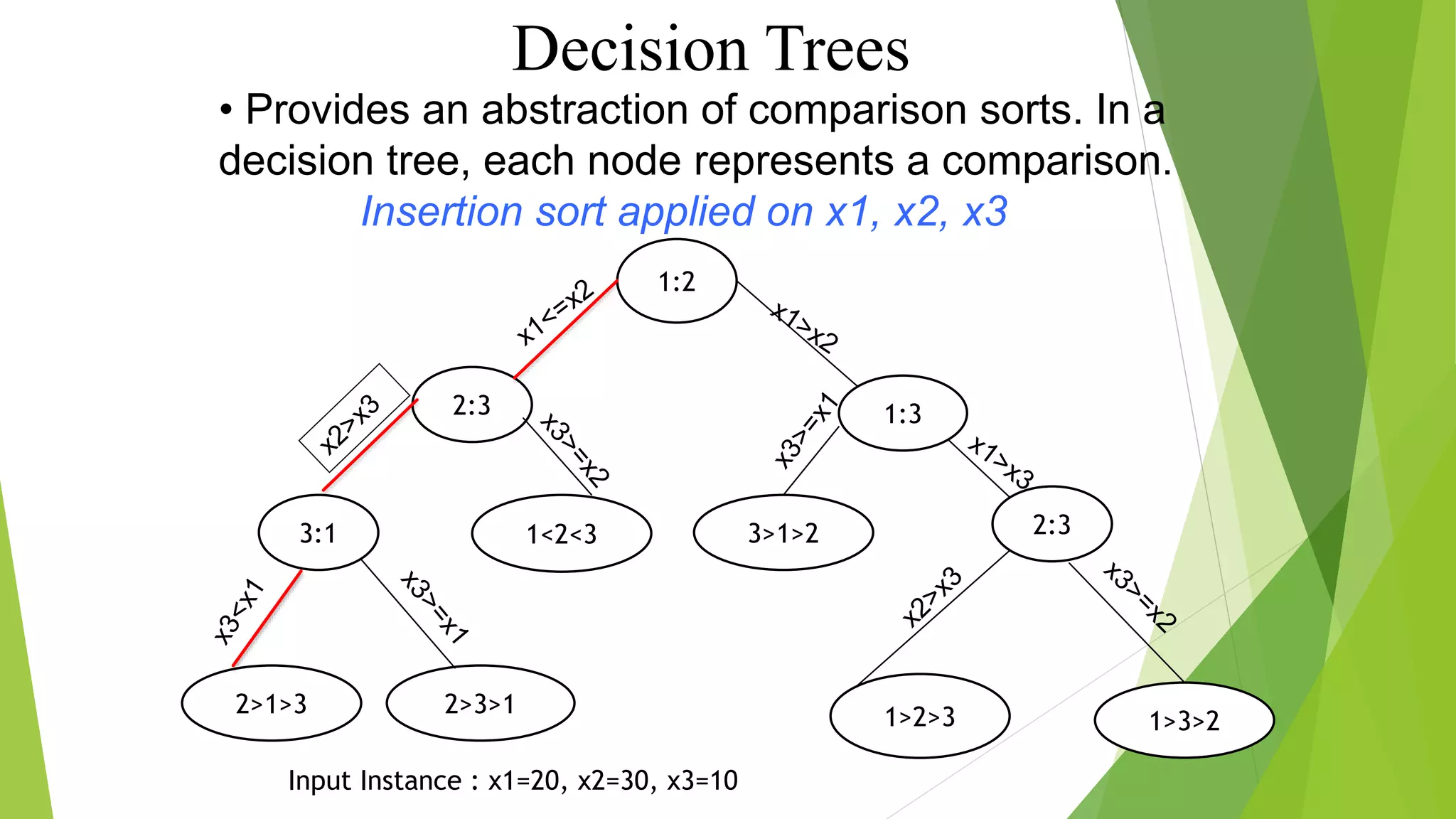
2) For comparison-based sorting algorithms, the decision tree model shows that any sorting algorithm requires at least O(nlogn) comparisons in the worst case.
3) This lower bound of O(nlogn) time complexity for comparison-based sorting algorithms means that no algorithm can sort faster than nlogn time using only element comparisons.

![Lower Bound in Sorting
-A technique to show the permutation of integers
from 1 to n for an array A[1…n] of n distinct values
in the form of a tree following a particular sorted
order.
-The algorithm used here is called comparison-
based algorithm and the sorting procedure as
comparison sort.
Decision Tree(Comparison Tree)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithms-150522092934-lva1-app6892/75/Algorithms-3-2048.jpg)


![Let T(n) be the minimum number of comparisons that are
sufficient to sort n items in the worst case.
Now,we know that in a binary tree,if all the internal nodes are at
levels less than k,then there are at most 2^k external nodes(one
more than the number of internal nodes).
Therefore,
k=T(n)
Since,T(n) is an integer, we get the lower bound
T(n) ≥ log2 n! [as k ≥ log2 n!]
By Stirling’s approximaton,
e(n/e)^n ≤ n! < e(n+1/e)^n+1
or, n! ≈ ((2∏n)^1/2)(n/e)^n
Using this relation,
log n!=nlogn-n/ln2+(1/2)logn+O(1)
Therefore,
T(n)=Ω(nlogn)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithms-150522092934-lva1-app6892/75/Algorithms-7-2048.jpg)



