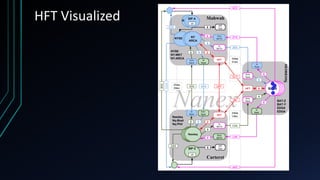
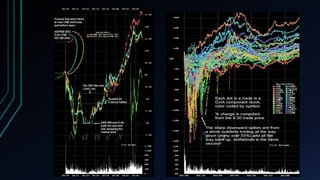
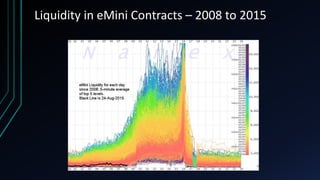
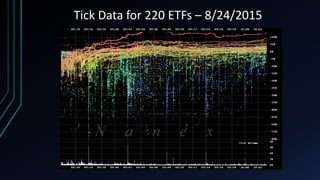
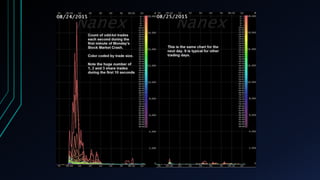
This document discusses the centralization of markets through the Securities Information Processor (SIP) and National Best Bid and Offer (NBBO), which consolidate market data like bid/ask quotes and trades from various trading venues. It also describes high-frequency and algorithmic trading strategies, like latency arbitrage and index arbitrage, and how they provide liquidity but can also harm other investors. Dark pools are mentioned as markets that hide liquidity. The document analyzes market data from an event on August 24, 2015 and questions whether high-frequency traders exacerbated volatility.