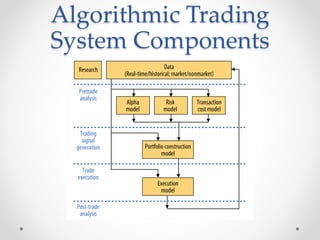
This document provides an overview of algorithmic trading, including:
- Algorithmic trading uses computer programs to automate trading processes like analysis, signal generation, and execution. Profits drive these systems through cost savings, commissions, or proprietary trading.
- For broker trading, the objective is to minimize costs, while proprietary trading aims to maximize profits. Trading firms that take on risk stand to gain the largest share of profits.
- The trade process involves pretrade analysis using fundamental, technical, or quantitative methods, generating trading signals based on entry and exit strategies and risk management, and then executing trades.