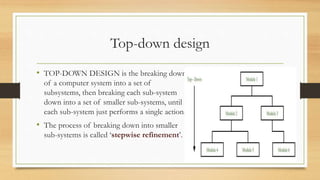
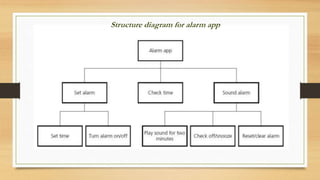
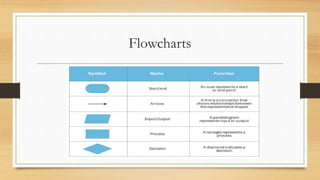
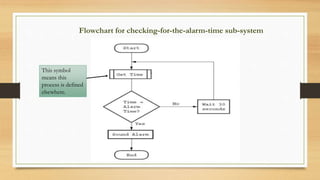
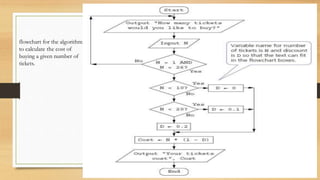
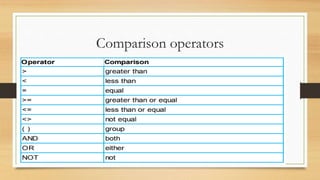
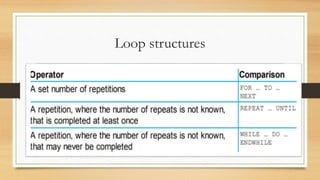
This document introduces algorithms and problem solving. It discusses what a computer system is and provides examples. It also covers tools and techniques for designing algorithms like top-down design, structure diagrams, flowcharts, pseudocode, library routines, and standard problem solving methods like totaling, counting, finding max/min/average, and linear searching. Standard pseudocode constructs are also defined like variables, input/output, loops, and conditional statements.






















![Psuedo code for finding max,min and average
marks from the class.
MaxMarks StudentMarks[1]
MinMarks StudentMarks[1]
For Counter 2 TO ClassSize
IF StudentMarks[Counter] > MaxMArks
THEN
MaxMarks StudentMarks[Counter]
End if
IF StudentMark[Counter] < MinMarks
THEN
MinMarks StudentMark[Counter]
ENDIF
NEXT Counter
Total 0
For Counter 1 TO ClassSize
Total Total +
StudentMArks[Counter]
NEXT Counter
Average Total / ClassSize](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmdesignandproblemsolvingautosaved-230525024624-6a6fb3b2/85/Algorithm-Design-and-Problem-Solving-Autosaved-pptx-31-320.jpg)
![Pseudocode for linear search
OUTPUT: “Please enter name to find”
INPUT : Name
Found FALSE
Counter 1
REPEAT
IF Name = StudentName[Counter]
THEN
Found TRUE
ELSE
Counter Counter + 1
ENDIF
UNTIL Found OR Counter > ClassSize
THEN
OUTPUT Name “ Found at
position”, Counter,” in the list.”
ELSE
OTPUT NAME ,’Not found”
ENDIF](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/algorithmdesignandproblemsolvingautosaved-230525024624-6a6fb3b2/85/Algorithm-Design-and-Problem-Solving-Autosaved-pptx-32-320.jpg)