This document provides information about albumin, the major protein in human plasma. It discusses albumin's structure, function, measurement, and causes of hypoalbuminemia and hyperalbuminemia. Key points include:
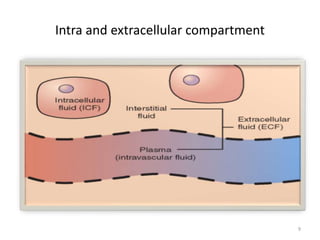
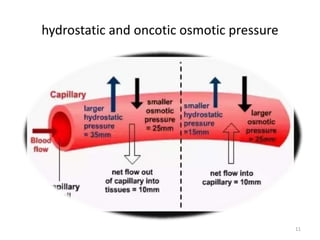
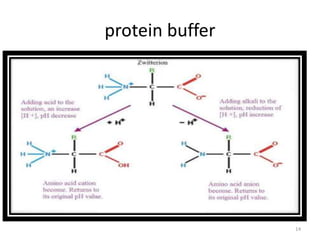
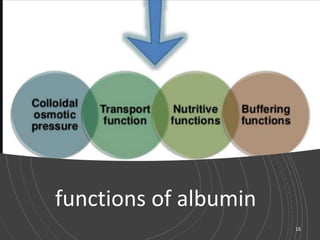
- Albumin is produced by the liver and has a molecular weight of 65,000 Daltons. Its main function is to regulate colloid osmotic pressure in blood.
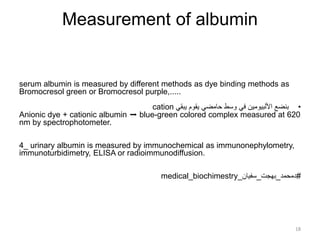
- Serum albumin levels are normally between 3.5-5.5 g/dL and can be measured using dye binding or immunochemical methods.
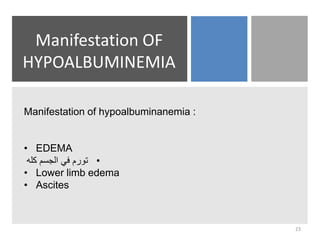
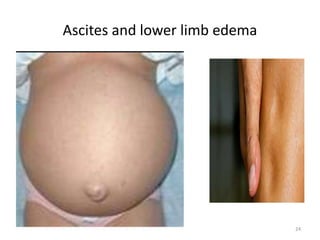
- Causes of low albumin include liver disease impairing synthesis, increased loss through the kidneys or intestines, infections, malnutrition, and hemodilution.