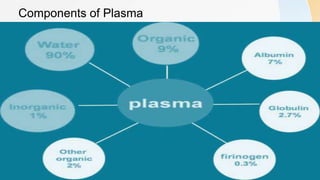
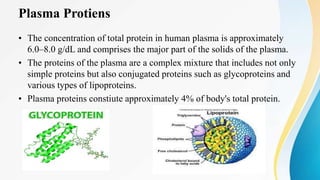
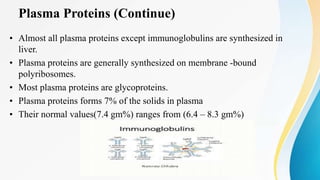
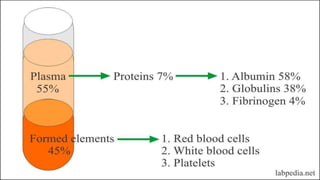
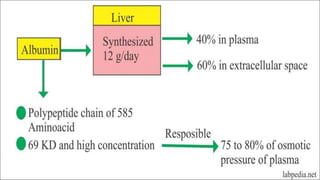
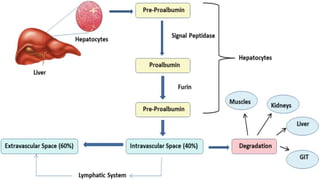
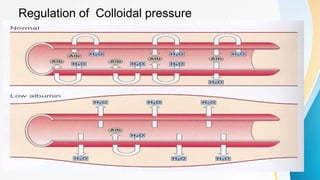
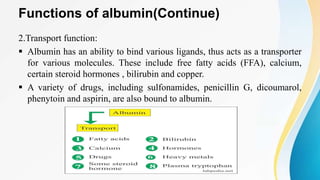
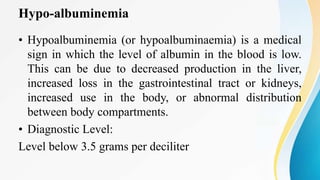
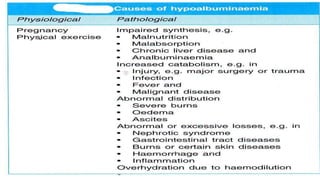
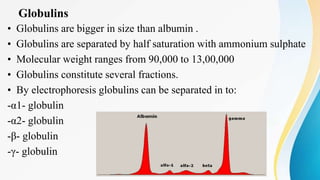
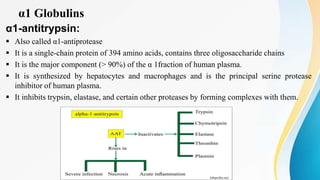
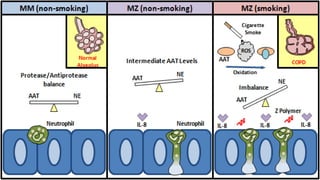
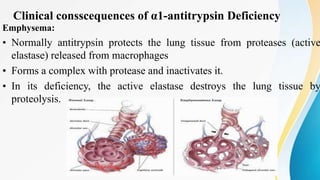
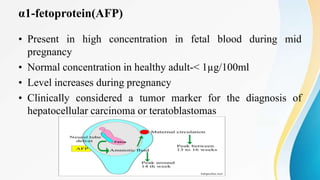
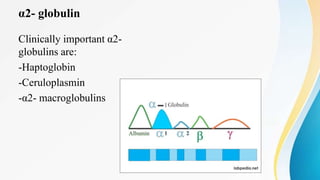
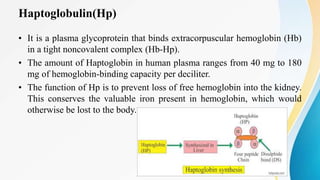
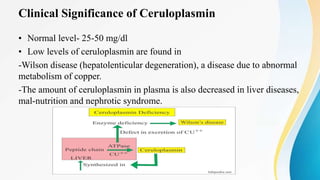
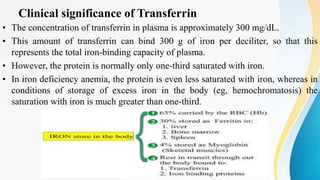
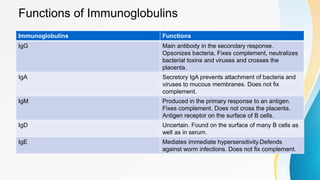
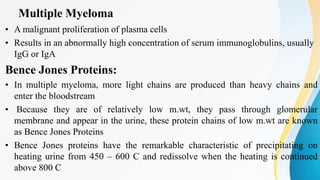
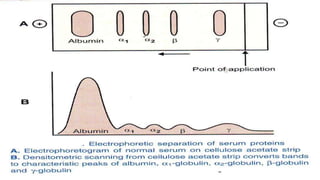
Plasma is the liquid portion of blood that remains after red and white blood cells are removed. It contains water, salts, enzymes, antibodies, and proteins. The major plasma proteins are albumin, globulins, and fibrinogen. Albumin is the most abundant plasma protein and plays important roles in maintaining colloidal osmotic pressure and transporting molecules like fatty acids, hormones, and bilirubin. Low albumin levels can cause edema. Globulins are divided into alpha, beta, and gamma classes, and include proteins like ceruloplasmin, transferrin, C-reactive protein, and haptoglobin that have clinical significance as markers of disease states.