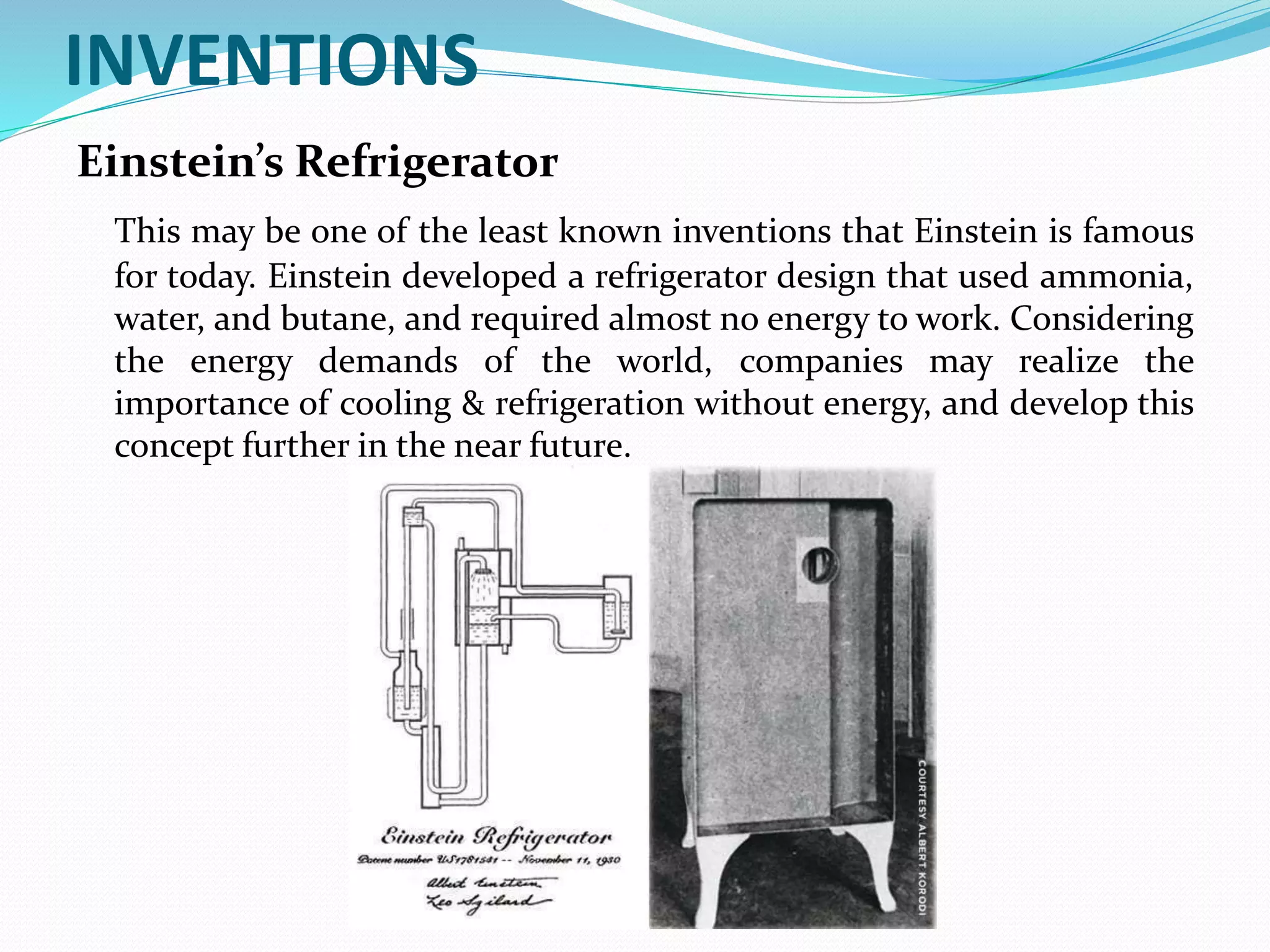
Albert Einstein, born March 14, 1879, and died April 18, 1955, made groundbreaking contributions to physics, including the quantum theory of light, the equation E=mc², and the theory of general relativity. His discoveries helped prove the existence of atoms, explained the photoelectric effect, and led to the development of the atomic bomb through the Manhattan Project. Additionally, he invented an energy-efficient refrigerator design, highlighting his influence on both scientific and practical advancements.