RDSO is the research and standards organization for Indian Railways, formed in 1957. It has laboratories for developing and testing railway equipment. RDSO's functions include developing new designs, technologies, and standards.
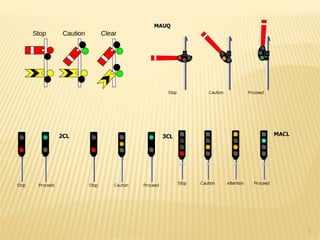
Railway signaling controls train movements safely to prevent collisions. It uses systems like block signaling and train detection to determine track occupancy. Fixed signals like semaphore and color light signals convey aspects to drivers.
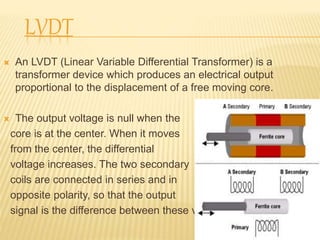
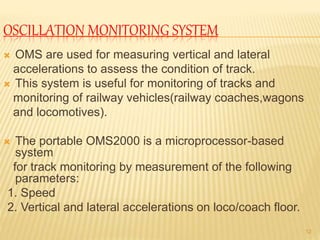
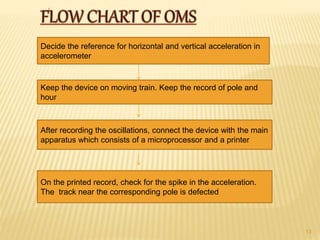
Transducers like LVDTs and accelerometers are used in railway applications such as track monitoring. LVDTs produce electrical outputs from core displacement. Accelerometers detect vibration. Oscillation monitoring systems use accelerometers to assess track conditions. Other systems detect wheel and brake overheating issues