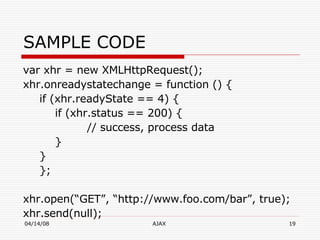
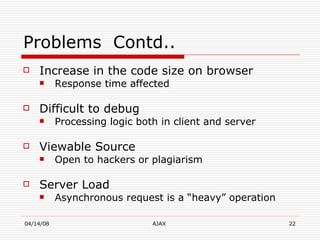
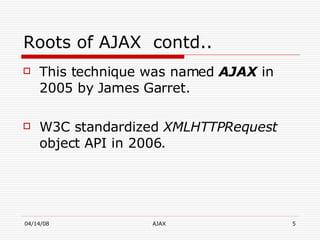
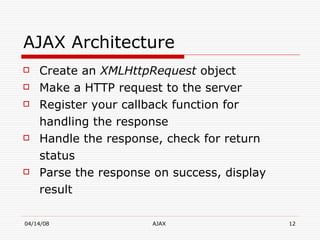
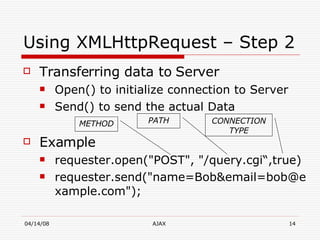
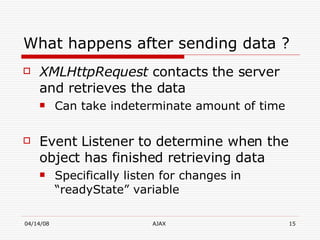
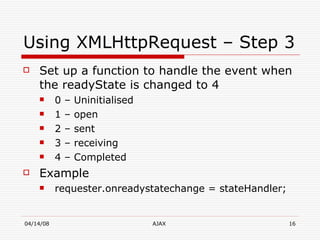
AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) is a development technique for building interactive web applications. It allows web pages to be updated asynchronously by exchanging data with a web server behind the scenes, without interfering with the display and behavior of the existing page. Some key uses of AJAX include real-time form validation, auto-completion of form fields, loading additional data without page refreshes, and implementing rich user interfaces with progress indicators and other controls. The core components that enable AJAX include HTML/XHTML for content display, CSS for presentation, DOM for dynamic display of information, XMLHttpRequest object for asynchronous data retrieval from the server, and JavaScript to bind everything together.







![Using XMLHttpRequest – Step 4 Parse and display data responseXML responseText Example var nameNode = requester.responseXML.getElementsByTagName("name")[0]; var nameTextNode = nameNode.childNodes[0]; var name = nameTextNode.nodeValue;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/a-1208155892089001-8/85/AJAX-18-320.jpg)