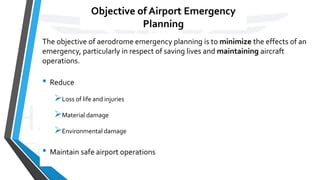
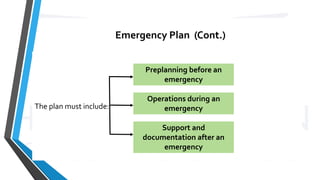
The document discusses airport emergency planning, outlining the types of emergencies that can occur at an airport, the roles of different agencies in responding to emergencies, and components of an airport emergency plan. It describes types of aircraft and non-aircraft emergencies, the objectives of emergency planning to minimize impacts and maintain operations, and agencies that should be involved like air traffic services, rescue and fire fighting, and medical services. It provides details on developing mutual aid agreements and sample outlines for airport emergency plans.