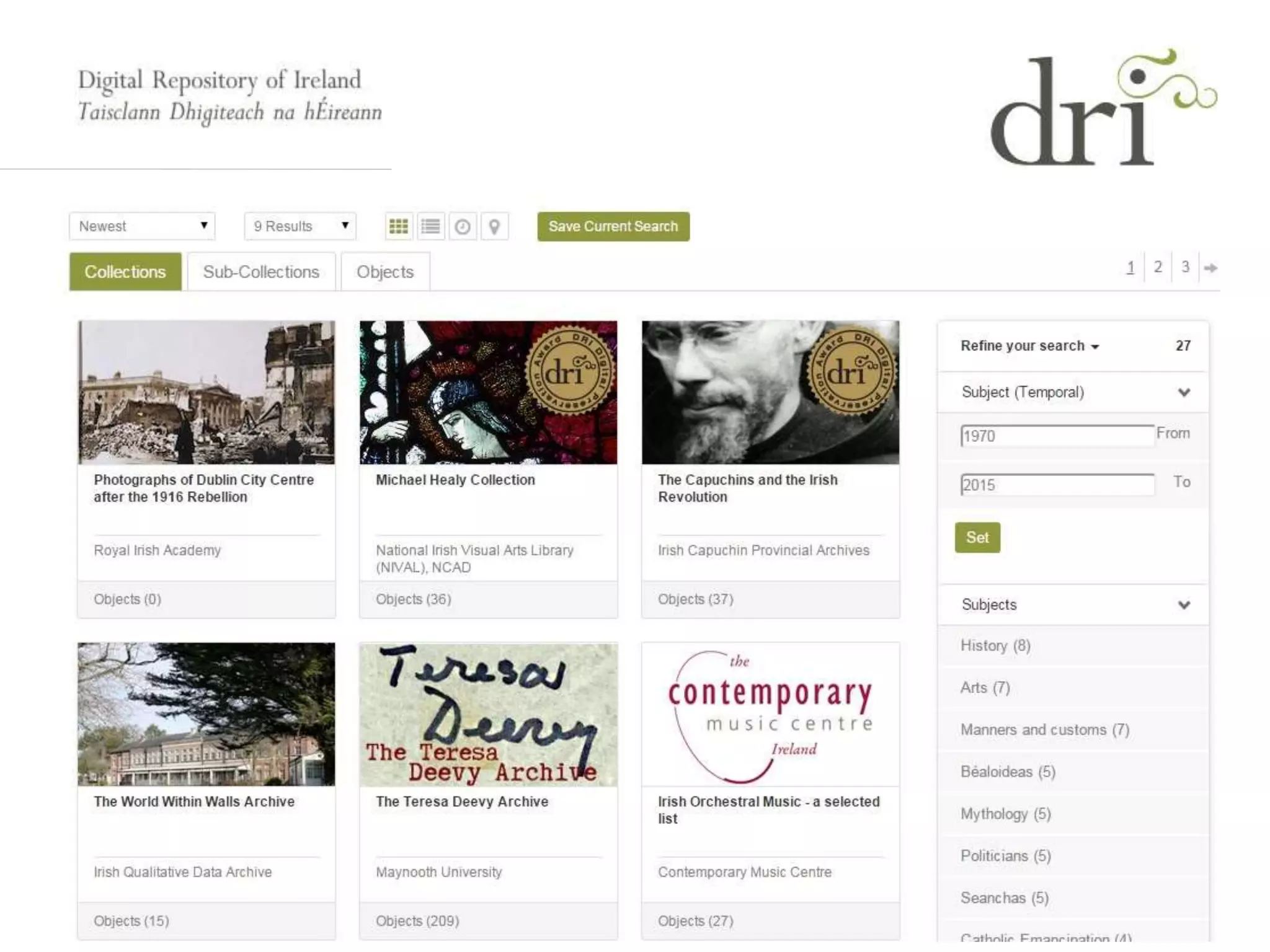
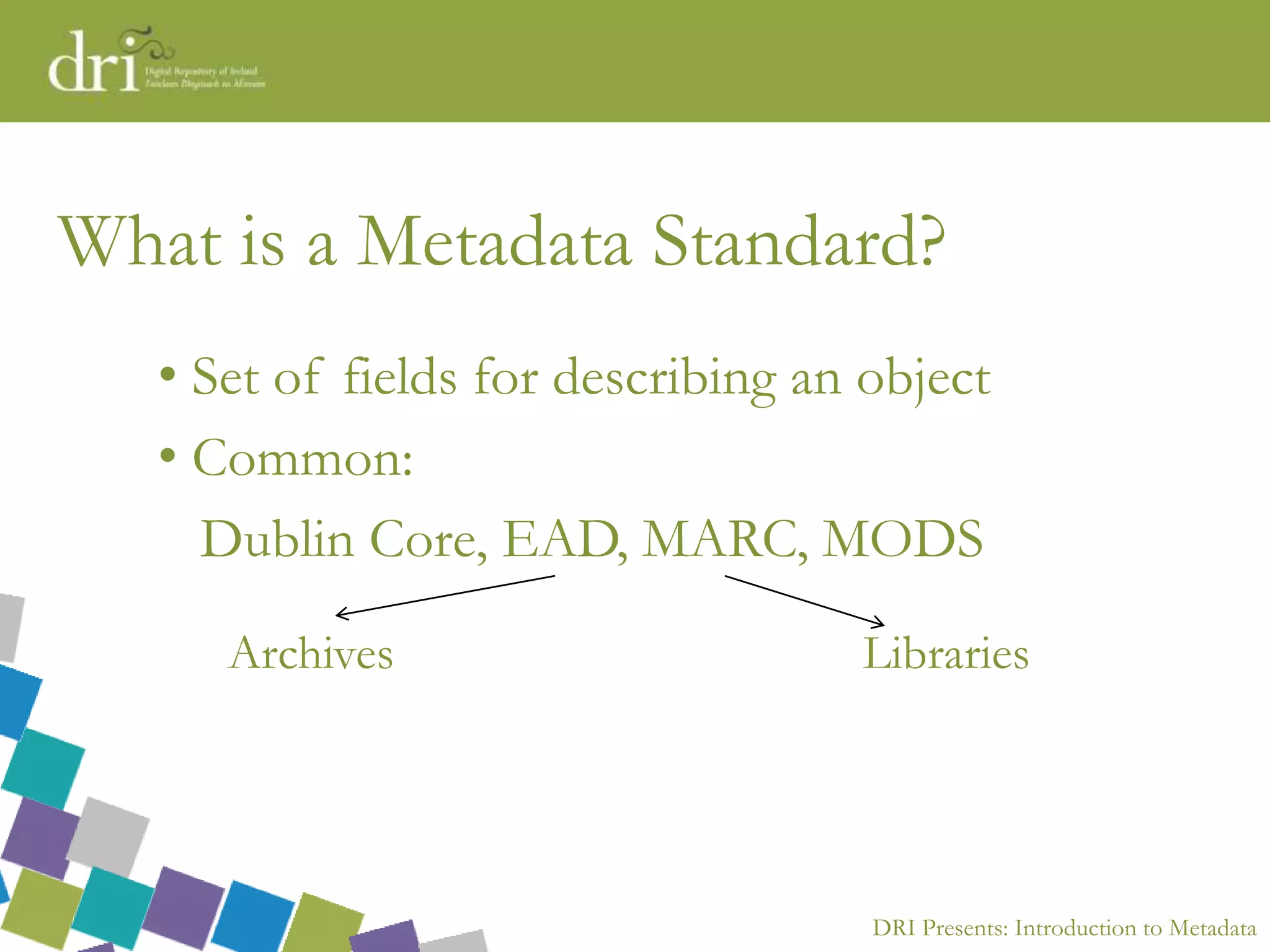
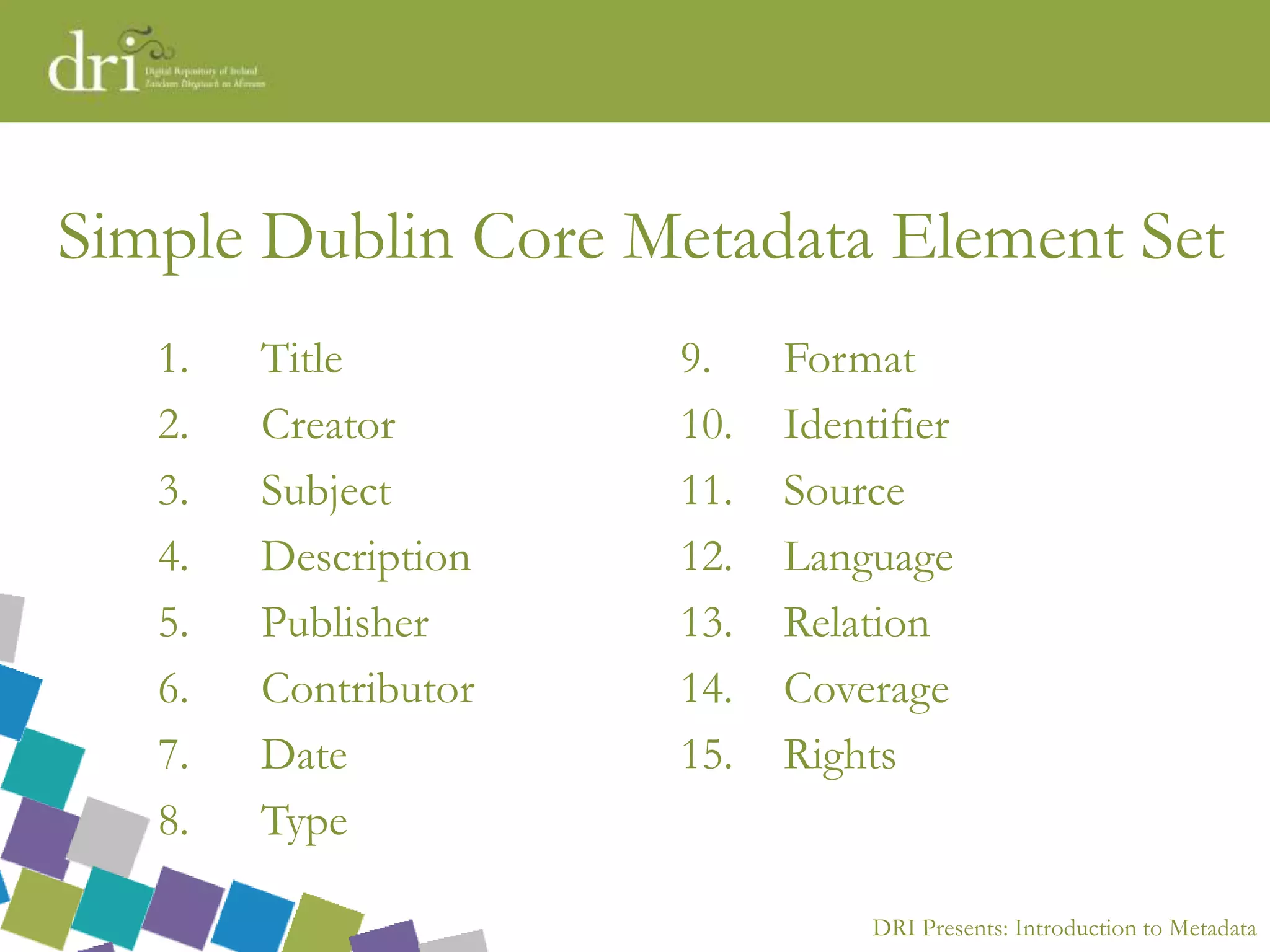
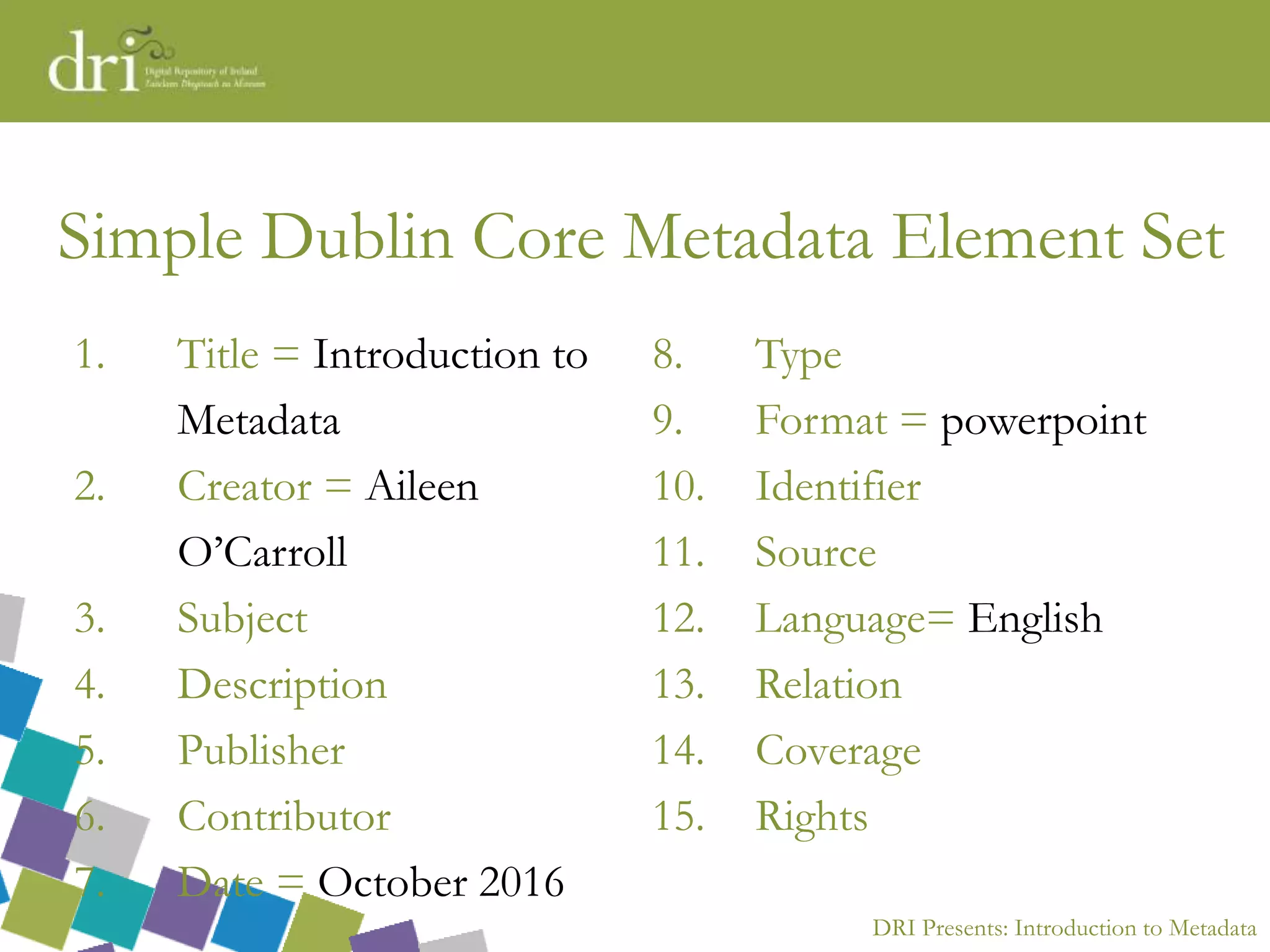
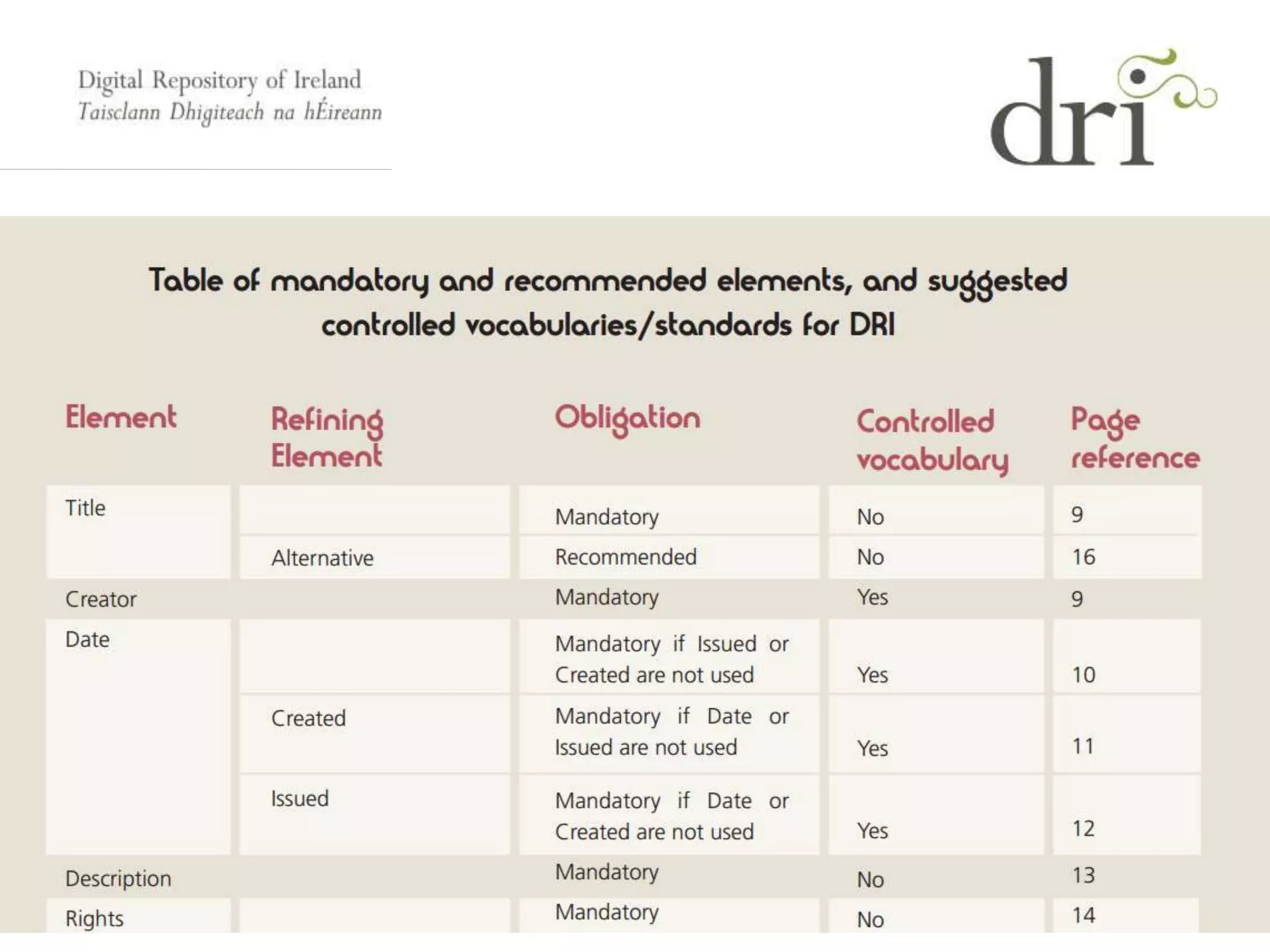
The document introduces metadata, explaining its importance as data about data that enhances searchability, discoverability, and sharing. It outlines different types of metadata (technical, preservation, structural, and descriptive), the qualities of good metadata, and various metadata standards like Dublin Core. The presentation emphasizes that good metadata should be accurate, rich, and consistent, and highlights the role of controlled vocabularies in achieving consistency and interoperability.