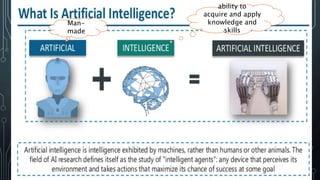
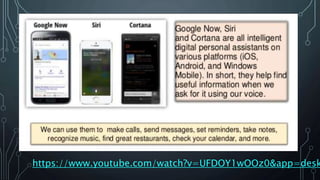
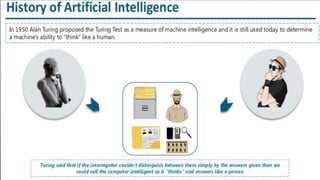
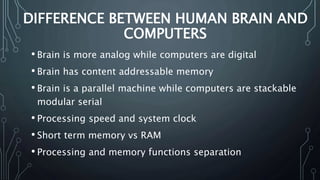
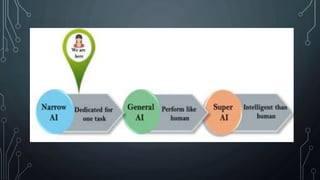
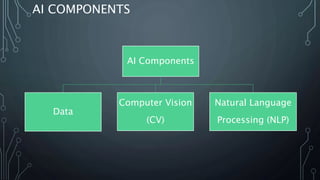
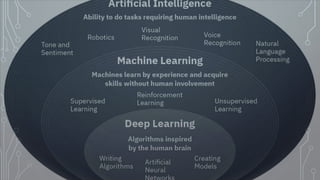
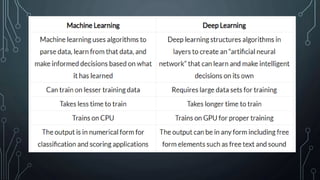
This document provides information about artificial intelligence and machine learning. It defines artificial intelligence as the field of computer science focused on developing intelligent machines. It discusses different types of AI like narrow AI, general AI, and artificial neural networks. Examples of applications of AI like IBM Watson and driverless cars are provided. Key components of AI like data, computer vision, and natural language processing are explained. The differences between machine learning and deep learning are summarized.