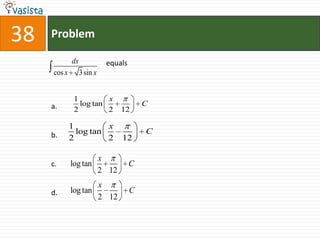
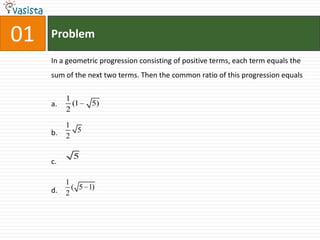
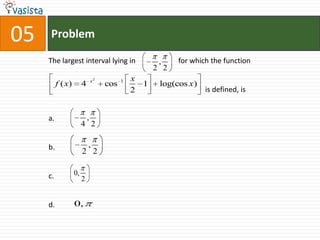
1. The document contains 40 multiple choice questions from an AIEEE mathematics past paper from 2007.
2. The questions cover a range of mathematics topics including geometry, trigonometry, algebra, calculus, and probability.
3. Answers to the questions are not provided, but the document states that a solution can be found by visiting a specific website.




















![Problem21A value of C for which the conclusion of Mean Value Theorem holds for the function f(x) = logex on the interval [1, 3] is2 log3e 1/2 loge3Log3eloge3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aieee-mathematics-2007-110928052115-phpapp02/85/Aieee-mathematics-2007-23-320.jpg)