1. This document contains an unsolved mathematics exam paper from 2003 containing 65 multiple choice questions across various topics including algebra, trigonometry, calculus, and vectors.
2. The questions cover concepts such as complex numbers, functions, limits, derivatives, integrals, differential equations, coordinate geometry, and vectors.
3. Multiple choice options ranging from a-d are provided for each question, with one being the correct answer.














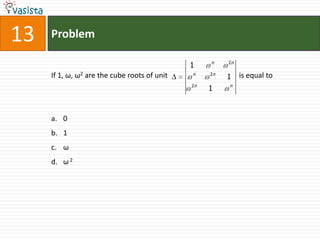
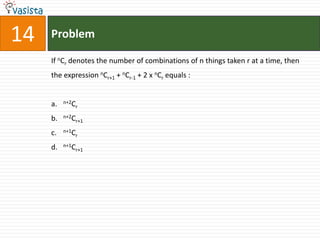



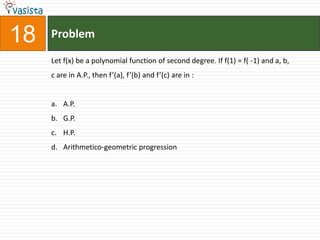

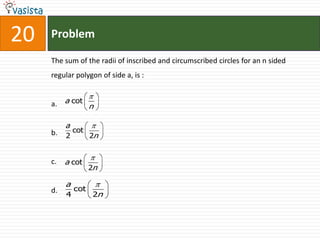







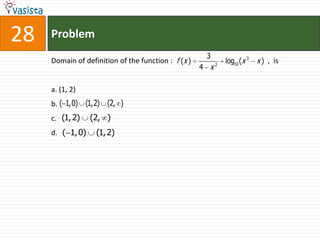









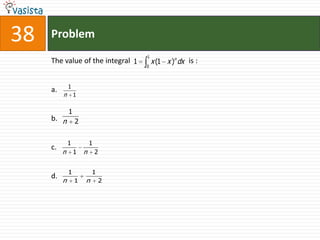

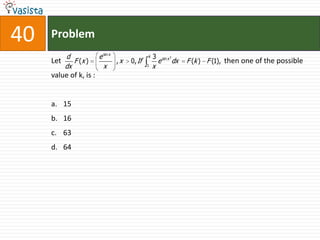




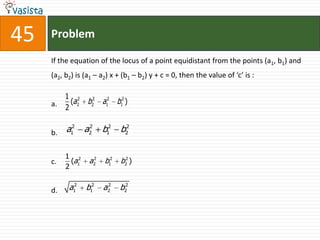
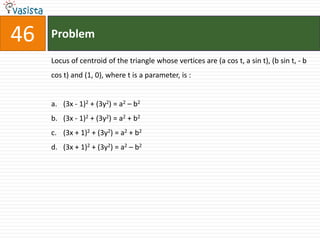





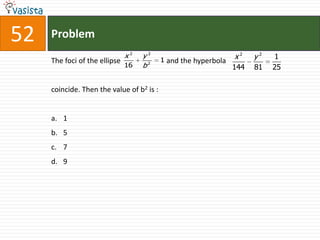















![Problem68Events A, B, C are mutually exclusive events such that . The set of possible values of x are in the interval : a.b.c.d. [0, 1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aieee-maths-2003-110924052144-phpapp02/85/Aieee-maths-2003-70-320.jpg)







