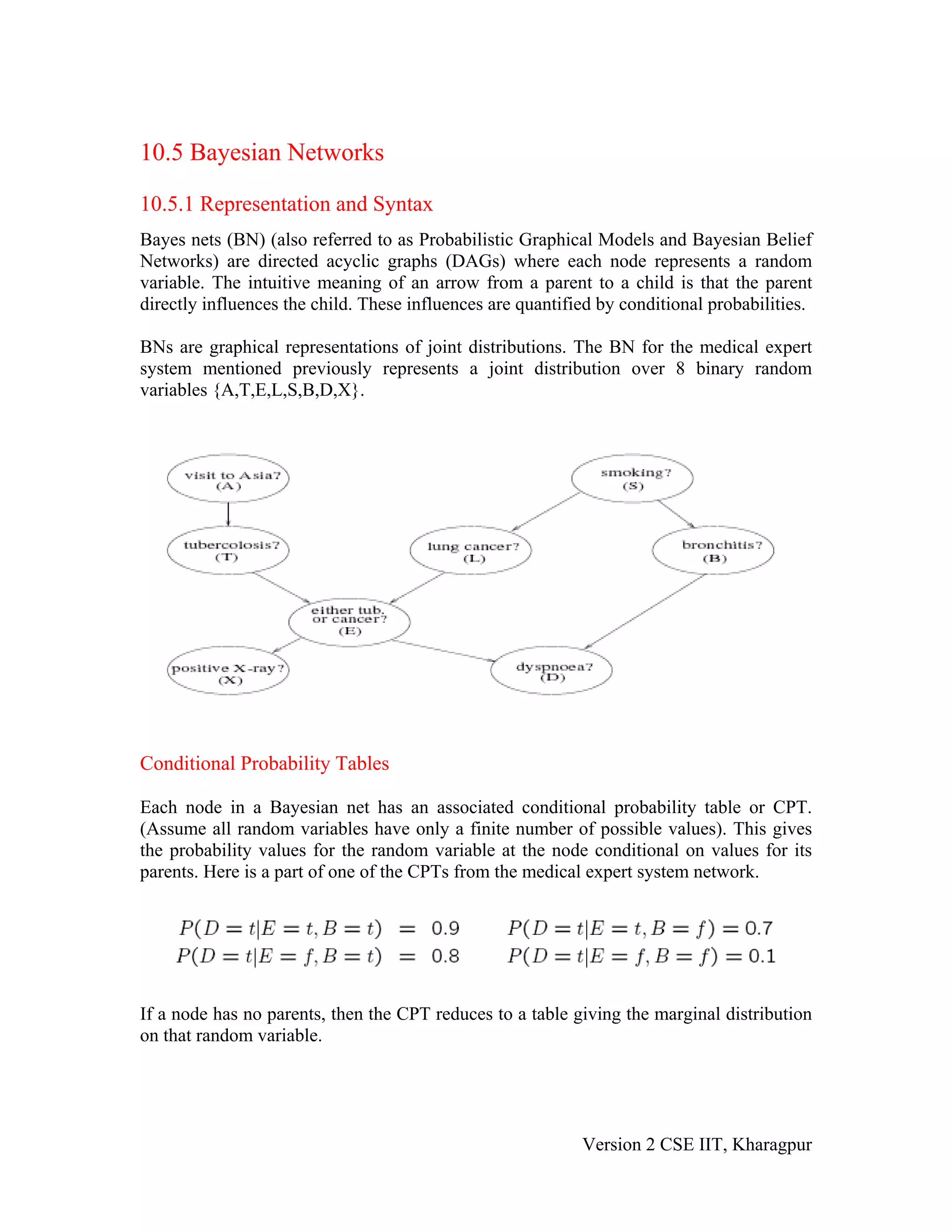
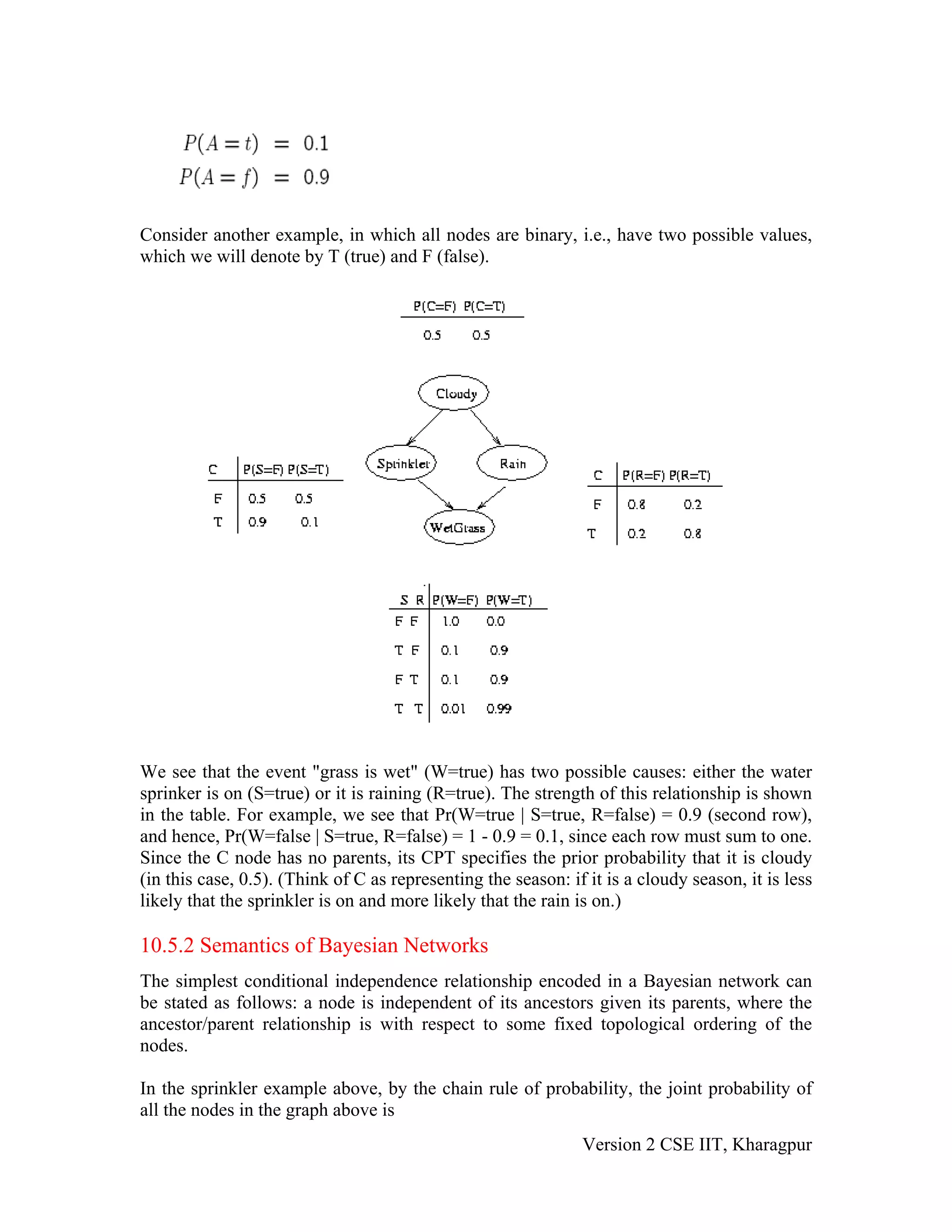
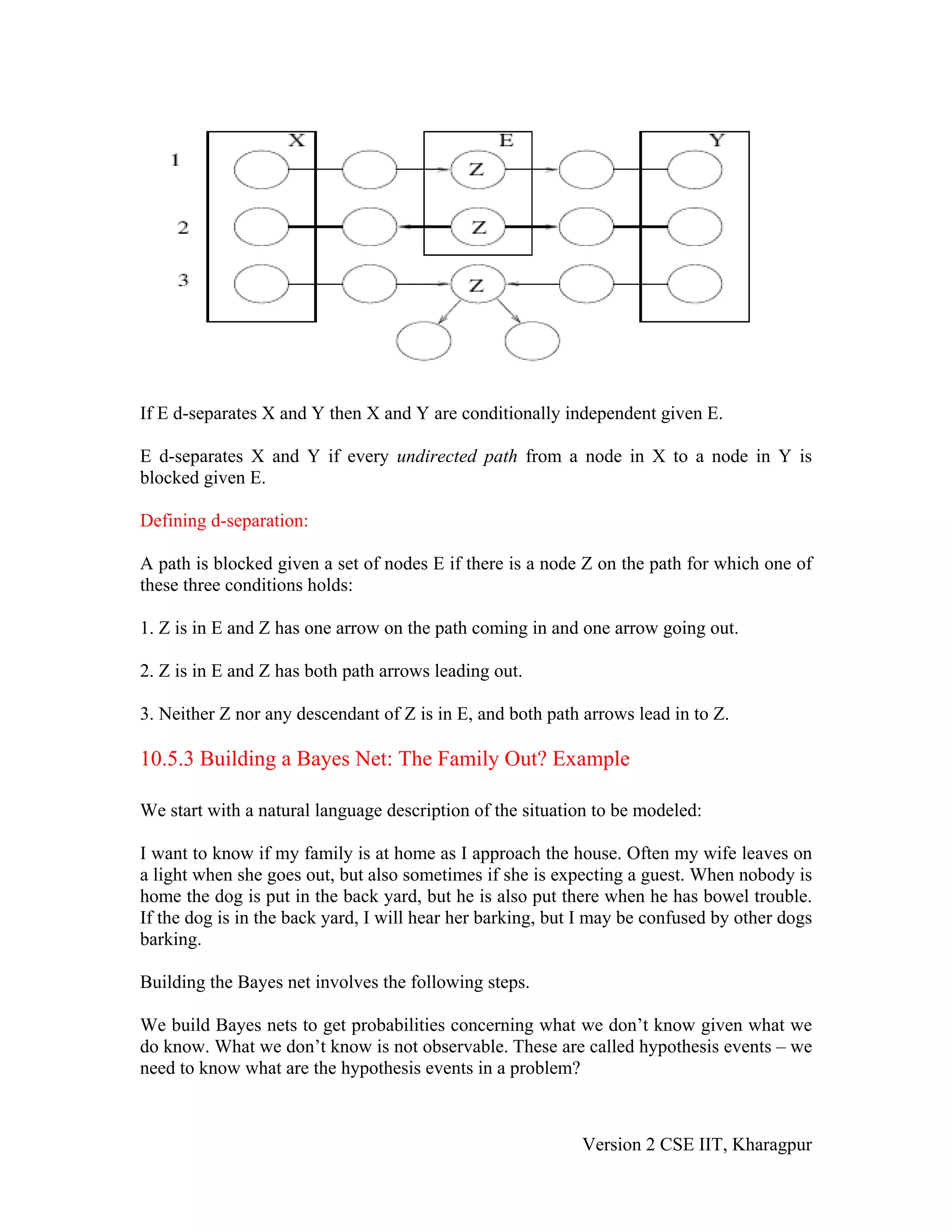
The document discusses Bayesian networks (BNs), which are directed acyclic graphs used to represent probabilistic relationships between variables. Each node in a BN represents a variable, and connections between nodes represent probabilistic dependencies. These dependencies are quantified with conditional probability tables (CPTs). BNs allow compact representation of joint probability distributions by exploiting conditional independence relationships. Learning BNs from data involves estimating both the network structure and the parameters of each CPT. When the structure is known and all variables are observable, parameters can be estimated with maximum likelihood.