1) Logic and inferences are important aspects of artificial intelligence as they allow systems to think and act rationally by making decisions based on available information and drawing conclusions.
2) Inference is the process of generating conclusions from facts and evidence. Formal logic represents knowledge through logical sentences using propositional or first-order logic.
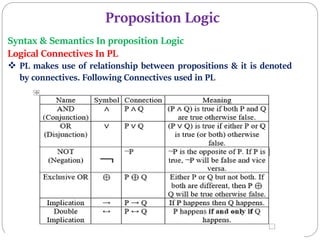
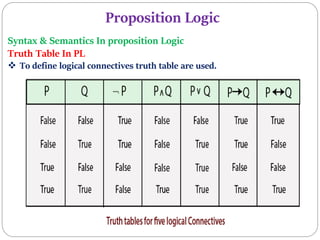
3) Propositional logic uses symbolic variables to represent propositions that can be either true or false. Compound propositions combine simpler propositions using logical connectives like "and" and "or". Truth tables define the values of logical connectives.






![Formal Logic
There are two Usable forms of Formal Logic
I] Proposition Logic
II]First Order Logic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ailecture-07unit03-210506093117/85/Ai-lecture-07-unit03-8-320.jpg)
![Proposition Logic
I] Propositional Logic (PL)
Propositional logic is an analytical statement which is either true or
false.
It is basically a technique that represents the knowledge in logical &
mathematical form.
There are two types of propositional logic; Atomic and Compound
Propositions.
Propositional logic (PL) is the simplest form of logic where all the
statements are made by propositions.
A proposition is a declarative statement which is either true or
false.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ailecture-07unit03-210506093117/85/Ai-lecture-07-unit03-9-320.jpg)
![Proposition Logic
I] Propositional Logic (PL)
Following are some basic facts about propositional logic:
Propositional logic is also called Boolean logic as it works on 0 and 1.
In propositional logic, we use symbolic variables to represent the
logic, and we can use any symbol for a representing a proposition,
such A, B, C, P, Q, R, etc.
Propositions can be either true or false, but it cannot be both.
Propositional logic consists of an object, relations or function, and
logical connectives.
These connectives are also called logical operators.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ailecture-07unit03-210506093117/85/Ai-lecture-07-unit03-10-320.jpg)
![Proposition Logic
I] Propositional Logic (PL)
Facts about Propositional Logic
The propositions and connectives are the basic elements of the
propositional logic.
Connectives can be said as a logical operator which connects two
sentences.
A proposition formula which is always true is called tautology, and
it is also called a valid sentence.
A proposition formula which is always false is called Contradiction.
Statements which are questions, commands, are not propositions
such as "Where is Sachin?", "How are you?", "What is your name?",
are not propositions.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ailecture-07unit03-210506093117/85/Ai-lecture-07-unit03-11-320.jpg)
![Proposition Logic
I] Propositional Logic (PL)
The examples of propositions are-
7 + 4 = 10
Apples are black.
Narendra Modi is president of India.
Two and two makes 5.
Delhi is in India.
Here,
All these statements are propositions.
This is because they are either true or false but not both.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ailecture-07unit03-210506093117/85/Ai-lecture-07-unit03-12-320.jpg)
![Proposition Logic
I] Propositional Logic (PL)
Types of proposition Logic
1. Atomic propositions
2. Compound propositions
1. Atomic Propositions-
Atomic propositions are the simple propositions. It consists of a
single proposition symbol. These are the sentences which must be
either true or false.
Example:
a) 2+2 is 4, it is an atomic proposition as it is a true fact.
b) "The Sun is cold" is also a proposition as it is a false fact.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ailecture-07unit03-210506093117/85/Ai-lecture-07-unit03-13-320.jpg)
![Proposition Logic
I] Propositional Logic (PL)
Syntax & Semantics In proposition Logic
2. Compound proposition:
Compound propositions are constructed by combining simpler or
atomic propositions, using parenthesis and logical connectives.
Example:
a) "It is raining today and street is wet."
b) "Ankit is a doctor and his clinic is in Mumbai."](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ailecture-07unit03-210506093117/85/Ai-lecture-07-unit03-14-320.jpg)
![Proposition Logic
I] Propositional Logic (PL)
Syntax & Semantics In proposition Logic
The syntax of propositional logic defines the allowable sentences for
the knowledge representation.
Propositional symbols are denoted with capital letters like :A, B,
C….Z
PL constants have a truth values generally like 0(false) and 1(true)
PL make use of wrapping parenthesis while writing atomic
sentences. As (…)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ailecture-07unit03-210506093117/85/Ai-lecture-07-unit03-15-320.jpg)